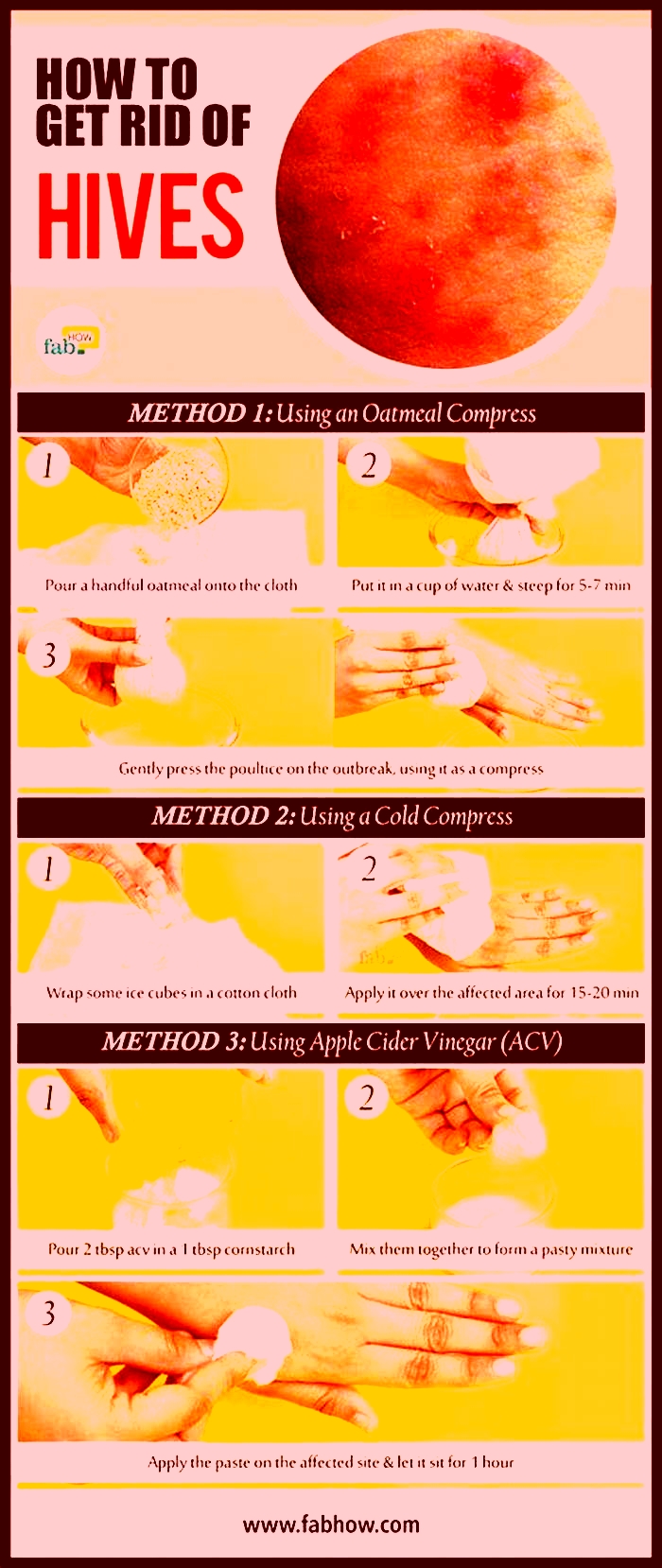
Can pets trigger hives

What can trigger chronic idiopathic urticaria?
Chronic idiopathic urticaria is the medical term for hives, and doctors usually refer to it as chronic spontaneous urticaria. Although there are no known causes, various triggers may include allergies, pets, medications, and foods.
Urticaria means hives, or an itchy rash of welts on the skin. Idiopathic means that doctors do not know the underlying cause of the condition, which occurs spontaneously.
Idiopathic urticaria is a chronic, or long-term, condition when the symptoms come and go for at least 6 weeks. Doctors think that the condition is an immune system response, despite not knowing the exact mechanism behind why it happens. However, they do know a number of triggers that can bring on the hives.
This article explains what can trigger chronic idiopathic urticaria.
In rare cases, a type 1 allergy can trigger chronic idiopathic urticaria. Type 2 allergies are
These allergies include atopic conditions, such as allergic:
They also include immune responses to allergens, such as:
- anaphylaxis, which is a severe allergic reaction that can develop quickly and may be life threatening
- urticaria
- angioedema, which is swelling resulting from fluid buildup under the skin
- food
- medications
Several types of medication, such as antibiotics, aspirin, and ibuprofen, can trigger hives.
These medications can trigger the skin condition straight away, within days or weeks, or even years after a person starts taking them.
Pet allergies, including reactions to cats and dogs, can trigger hives. People can come into contact with pet hair at work, at school, in day care, and in other indoor environments, even when no animal is present.
Learn more about animal allergies.
Physical urticaria means hives that have a physical cause. For instance, rubbing or scratching the skin is the most common cause of physical urticaria.
The hives can appear within a few minutes but usually last less than an hour.
Several foods can trigger hives, such as nuts, peanuts, eggs, and shellfish. The hives usually develop within one hour of eating the trigger food.
Foods such as bananas, chestnuts, kiwis, and mangos can also trigger hives in people with a latex allergy.
Sometimes it is the additives in a food rather than the food itself that trigger a persons hives for instance, food colorings and preservatives, such as sorbic acid.
In these two scenarios, the hives normally develop within 1224 hours of eating the food.
Additives in vitamin supplements and other supplements, spices, cosmetics, and personal care products can also trigger hives within 1224 hours of use.
Additionally, plants such as stinging nettle, cinnamon, and latex commonly trigger hives, which appear within minutes and can sometimes accompany difficulty breathing. This can also happen in case of contact with a jellyfish.
Other triggers can include:
- exercise
- heat and hot showers
- cold
- UV light
- vibration (rarely)
- pressure on the skin, such as from tight clothing or a purse strap
- water (rarely)
Hives usually develop from an itchy patch of skin that changes into swollen welts.
Idiopathic means that doctors do not know what causes the hives, which appear spontaneously.
Symptoms
Chronic hives usually present with the same symptoms as hives that do not last as long.
Chronic tends to mean that the hives occur twice a week or more often and do not go away for 6 weeks or more.
Symptoms include raised itchy bumps, which are the same color as the skin, and blanching, which means that the center of a hive turns white when pressed.
When doctors define chronic urticaria as idiopathic, it means that there is no known trigger. However, immune-system-related causes can include an autoimmune reaction or a reaction to a food or drug that does not fit the definition of an allergy.
Additionally, an acute or chronic infection may cause chronic idiopathic urticaria for instance, due to:
The
Doctors may also prescribe medications, such as antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists, which people take for chronic asthma, along with short bursts of corticosteroids to dampen the inflammatory response.
If the condition does not improve, doctors may refer a person to a specialist, who may then prescribe omalizumab or cyclosporine. These medications regulate the overreactivity of a persons immune system.
More than half of people with chronic urticaria get rid of their symptoms or experience improvement within 1 year.
Chronic idiopathic urticaria is hives with no known cause. They usually develop at least twice a week for a period of at least 6 weeks.
Several environmental triggers may bring on the raised, itchy bumps for instance, allergies, medications, stress, pet hair, food, stinging nettles, and UV light.
While doctors have not identified a single cause of chronic idiopathic urticaria, it may relate to an overactive immune system or an infection.
Besides avoiding triggers, a person can try taking antihistamines to reduce their symptoms. If these persist, a person can talk with their doctor about stronger prescription medications.
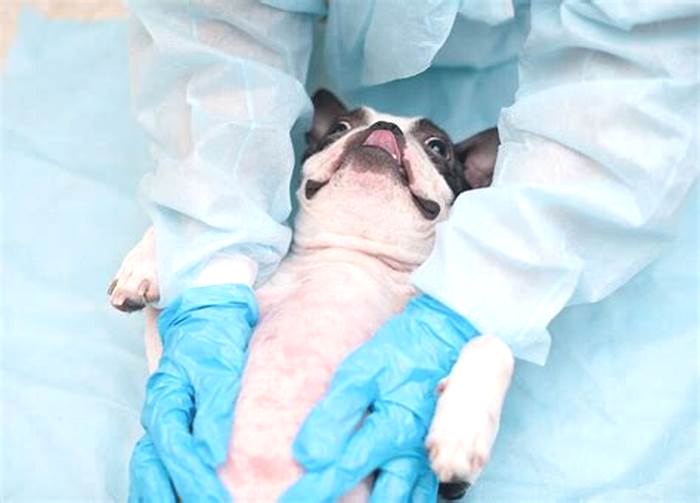
Understanding the Triggers: Causes of Hives in Dogs

Hives in dogs can be a distressing condition for both pets and their owners. These raised, itchy bumps on a dogs skin can appear suddenly and cause discomfort. Understanding the causes of hives in dogs is essential in order to alleviate the symptoms and prevent future outbreaks.
One of the most common triggers for hives in dogs is an allergic reaction. Just like humans, dogs can be allergic to a variety of things, such as certain foods, medications, or environmental factors like pollen or dust mites. These allergens can cause the dogs immune system to overreact, resulting in the release of histamines that lead to the development of hives.
Insect bites and stings are another frequent cause of hives in dogs. When a dog is bitten or stung by an insect, such as a bee or a wasp, it can elicit an allergic reaction that manifests as hives. The bodys immune system reacts to the venom injected by the insect, triggering the release of histamine and other chemicals that cause the characteristic swelling and itching.
Stress and anxiety can also be underlying factors that trigger hives in dogs. Just like humans, dogs can experience stress and anxiety that can manifest in physical symptoms, including hives. Situations like being left alone for long periods, traveling, or exposure to loud noises can cause stress in dogs, leading to hives as a result of an overactive immune response.
Finally, some dogs may develop hives due to contact with certain irritants. This could include coming into contact with specific plants, chemicals, or even certain types of fabric. These irritants can cause an allergic reaction in dogs, resulting in the formation of hives on their skin.
Understanding the causes of hives in dogs is crucial to effectively managing this condition. By identifying the triggers that lead to the development of hives, pet owners can take appropriate measures to prevent and reduce their dogs discomfort.
Common Allergens
Allergies in dogs can be caused by a variety of common allergens, including:
| Allergen | Description |
|---|---|
| Pollen | Seasonal allergies caused by pollen from grasses, trees, and weeds. |
| Dust mites | Microscopic insects that live in house dust and can trigger allergy symptoms. |
| Mold | Fungi that can grow indoors or outdoors and release spores that cause allergic reactions. |
| Fleas | Flea saliva can cause an allergic reaction in dogs, leading to itching and hives. |
| Food | Ingredients such as beef, chicken, wheat, soy, or dairy products may trigger food allergies in dogs. |
| Medications | Certain medications can cause allergic reactions in dogs, including antibiotics, vaccines, or flea control products. |
If your dog has hives, it is important to identify and avoid the allergen to prevent future reactions. Your veterinarian can perform allergy testing and recommend treatments, such as antihistamines or immunotherapy, to help manage your dogs allergies.
Food Allergies
Food allergies can be a common cause of hives in dogs. Just like in humans, dogs can have allergies to certain foods. Common food allergens for dogs include beef, chicken, dairy products, eggs, and wheat. When a dog with a food allergy consumes a trigger food, their immune system reacts and releases histamines, which can lead to hives.
Symptoms of food allergies in dogs may include hives, itching, gastrointestinal upset, and in severe cases, difficulty breathing. It can be challenging to identify the specific food allergen, as there are many potential options. One way to determine if a dog has a food allergy is through an elimination diet, which involves removing potential trigger foods and reintroducing them one at a time to observe any reaction.
If a food allergy is suspected, it is important to consult with a veterinarian to create a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. The veterinarian may recommend a hypoallergenic or limited ingredient diet for the dog. This type of diet eliminates common allergens and provides the dog with a well-balanced and nutritious meal.
It is essential for dog owners to carefully read and understand the ingredient labels on dog food, as many commercial pet foods contain potential allergens. By identifying and avoiding trigger foods, dog owners can help manage hives caused by food allergies and improve their pets overall health and well-being.
Environmental Allergies
Environmental allergies are one of the most common causes of hives in dogs. These allergies are triggered by various substances found in the environment, such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, and chemicals. Dogs with environmental allergies may develop hives when they come into contact with these allergens.
Pollen is a common environmental allergen that can cause hives in dogs. It is released by plants during certain times of the year and can be found in the air. Dogs can inhale or come into contact with pollen when they are outside, leading to an allergic reaction and the development of hives.
Dust mites are tiny organisms that live in mattresses, carpets, and upholstery. They can trigger an allergic reaction in dogs, leading to the development of hives. Dogs can be exposed to dust mites by spending time in areas where they are present, such as homes with carpets or bedding.
Mold spores are another environmental allergen that can cause hives in dogs. Mold can grow in damp areas, such as basements, bathrooms, and kitchens. Dogs may develop hives if they inhale or come into contact with mold spores.
Chemicals found in cleaning products, pesticides, and certain plants can also trigger an allergic reaction in dogs, leading to the development of hives. It is important to keep dogs away from areas where these chemicals are present to reduce the risk of an allergic reaction and hives.
If your dog is prone to hives and has been diagnosed with environmental allergies, it is important to identify and avoid the triggers. This may involve keeping your dog indoors during peak pollen times, regularly cleaning and vacuuming your home to reduce dust mites, reducing moisture in areas prone to mold growth, and avoiding exposure to chemicals that can cause an allergic reaction.
Insect Allergies
Insect allergies are one of the common triggers for hives in dogs. Just like humans, dogs can develop a hypersensitivity to insect bites or stings. When a dog with an insect allergy is bitten or stung, the bodys immune system overreacts to the insects saliva or venom, leading to a release of histamine and other chemicals that cause an allergic reaction. This reaction can manifest as hives, swelling, redness, itching, and even more severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
The insects most commonly associated with causing allergies in dogs include fleas, mosquitoes, ticks, and bees. These insects bite or sting dogs while searching for a blood meal or when they feel threatened. The saliva or venom they inject into the dogs skin can trigger an allergic reaction. Flea allergy dermatitis is a common allergic skin condition in dogs, caused by an allergic reaction to flea saliva. Mosquito bites can also lead to hives in dogs that are allergic to mosquito saliva.
If your dog has a known insect allergy, it is important to take preventive measures to minimize their exposure to these insects. Regular use of flea and tick preventives can help control flea and tick infestations, reducing the risk of allergic reactions in dogs. Keeping your dog indoors during peak mosquito activity times and using mosquito repellents can also help prevent mosquito bites.
If your dog develops hives after being bitten or stung by an insect, it is important to seek veterinary care. The veterinarian can assess the severity of the allergic reaction and provide appropriate treatment, which may include antihistamines, corticosteroids, or, in severe cases, emergency medications like epinephrine.
It is crucial to remember that insect allergies can be life-threatening for dogs. In severe cases, anaphylactic shock can occur, leading to difficulty breathing and even death. Therefore, it is essential to monitor your dog closely for any signs of an allergic reaction and seek immediate veterinary care if needed. With proper management and preventive measures, dogs with insect allergies can lead happy and comfortable lives.
Other Triggers
In addition to the common triggers mentioned above, there are several other factors that can lead to hives in dogs. While these triggers may not be as common, they can still cause an allergic reaction in sensitive dogs. Its important to be aware of these triggers and take steps to avoid them if your dog is prone to hives.
Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and vaccines, can sometimes trigger an allergic reaction in dogs, leading to the development of hives. If your dog has had a previous allergic reaction to a medication, its important to inform your veterinarian to avoid future exposure.
Insect bites and stings: Dogs can also develop hives as a result of insect bites or stings, such as those from fleas, ticks, bees, wasps, or mosquitoes. Insect saliva or venom can trigger an immune response, leading to the development of hives. Its important to keep your dog protected from insects and check for any signs of bites or stings.
Chemicals and cleaning products: Chemicals and cleaning products can sometimes irritate a dogs skin and trigger an allergic reaction. This can include household cleaners, shampoos, detergents, and other products that come into contact with your dogs skin. Avoid using harsh chemicals and opt for pet-friendly products whenever possible.
Environmental allergens: Just like humans, dogs can develop hives as a result of exposure to environmental allergens, such as pollen, mold, dust mites, or grass. These allergens can cause an immune response in sensitive dogs, leading to the development of hives. Its important to keep your dogs environment clean and free from allergens as much as possible.
Stress and anxiety: In some cases, stress and anxiety can also trigger hives in dogs. Stressful situations, such as travel, changes in routine, or loud noises, can cause an immune response and lead to the development of hives. Keeping your dog calm and providing a safe and comfortable environment can help reduce the risk of stress-related hives.
Its important to note that hives can vary in severity and may require veterinary attention, especially if your dog experiences difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or other signs of a severe allergic reaction. If your dog develops hives, its best to contact your veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Medications
In some cases, hives in dogs can be triggered by medications. Just like humans, dogs can have allergic reactions to certain drugs. Common medications that may cause hives in dogs include antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and vaccines.
If your dog develops hives shortly after starting a new medication, it is important to notify your veterinarian immediately. They can evaluate the situation and determine if the medication is the cause of the hives. Your veterinarian may need to discontinue the medication and prescribe an alternative. It is crucial not to stop giving your dog any medication without consulting with your veterinarian first.
When it comes to medications, it is also important to take note of any other symptoms your dog may be experiencing. Some dogs may develop hives in combination with other signs of an allergic reaction, such as facial swelling, difficulty breathing, or vomiting. These symptoms can indicate a more severe allergic reaction and require immediate medical attention.
When administering medications to your dog, be sure to follow the veterinarians instructions carefully. This includes the dosage, frequency, and duration of treatment. If your dog has a history of allergic reactions or hives to certain medications, make sure to inform your veterinarian about it. They can select alternative medications that are less likely to cause an allergic reaction.
Overall, it is essential to be cautious when giving your dog any type of medication to prevent hives and other adverse reactions. Communicating with your veterinarian and being aware of the potential side effects can help keep your furry friend safe and healthy.
Stress
Stress can be a major trigger for hives in dogs. Just like humans, dogs can experience stress due to a variety of factors, such as changes in their environment, separation from their owner, or exposure to loud noises or unfamiliar situations. When a dog is stressed, their body releases stress hormones, which can affect their immune system and make them more prone to developing hives.
Stress-induced hives often present as small, itchy bumps on the dogs skin. In some cases, the hives may be accompanied by other signs of stress, such as excessive panting, restlessness, or changes in appetite or behavior.
If you suspect that your dogs hives are caused by stress, its important to try to identify and address the underlying stressors. This may involve providing a calm and stable environment for your dog, ensuring they have plenty of mental and physical stimulation, and using techniques such as desensitization or counter-conditioning to help them become more comfortable in stressful situations.
In some cases, it may be necessary to seek professional help from a veterinarian or a certified animal behaviorist to develop a specialized stress management plan for your dog. They can provide guidance on techniques and strategies to help reduce your dogs stress levels and prevent future hives outbreaks.
Question-answer:
What are hives in dogs?
Hives in dogs are raised, itchy bumps that can appear on their skin. They are also known as urticaria and are typically caused by an allergic reaction.
What are the common triggers of hives in dogs?
Common triggers of hives in dogs include certain foods, environmental allergens such as pollen or dust mites, insect bites or stings, and certain medications.
How can I tell if my dog has hives?
You can tell if your dog has hives by examining their skin for raised bumps or welts. These bumps may be red or pale in color and can vary in size. Your dog may also show signs of itching, licking, or scratching the affected areas.
Can stress or anxiety cause hives in dogs?
Yes, stress or anxiety can potentially trigger hives in dogs. Just like humans, dogs can have physical reactions to emotional stress, which can manifest as hives.
Are hives in dogs contagious?
No, hives in dogs are not contagious. They are a result of an individual dogs allergic reaction to a specific trigger and cannot be passed on to other dogs or humans.
What are hives in dogs?
Hives, also known as urticaria, are an allergic reaction that causes an outbreak of swollen, red, and itchy bumps on a dogs skin. They can appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly, or they can last for days or even weeks.
What are some common triggers of hives in dogs?
There are many potential triggers for hives in dogs, including food allergies, insect bites or stings, certain medications, exposure to certain plants or chemicals, or even stress. Its important to identify and eliminate the trigger to prevent future outbreaks.