Does lemon water lower histamine

Is Lemon Juice High In Histamine
Is Lemon Juice High In Histamine
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in histamine and its effects on health. One particular question that has surfaced is whether lemon juice, a popular ingredient in many recipes, is high in histamine. In this article, we will delve into the world of histamines, explore their role in the body, and determine the histamine content in lemon juice. Additionally, we will examine the effects of high histamine foods on health and discuss ways to manage histamine intake.
Understanding Histamines
Histamines are compounds naturally produced by the body's immune system. They play a crucial role in the body's defense mechanism, triggering an inflammatory response when the body perceives a threat. This response is often seen in the form of itching, sneezing, or swelling. Histamines are involved in various physiological processes, including regulating stomach acid production, neurotransmission, and immune response.
What are Histamines?
Histamines are biogenic amines derived from the amino acid histidine. They are found in virtually all body tissues, including the brain, skin, and gut. One of their primary functions is to mediate allergic reactions, ensuring a rapid response to potential allergens.
When an allergen enters the body, such as pollen or pet dander, the immune system recognizes it as a threat. In response, mast cells, which are found in various tissues throughout the body, release histamines. These histamines then bind to specific receptors on nearby cells, triggering a cascade of events that result in the characteristic symptoms of an allergic reaction.
For example, if someone with a pollen allergy inhales pollen particles, histamines are released in the nasal passages. This causes the blood vessels in the nose to dilate, leading to nasal congestion and sneezing. Histamines also increase mucus production, which can further contribute to a runny or stuffy nose.
The Role of Histamines in the Body
While histamines are best known for their involvement in allergic reactions, they also have essential roles in various physiological processes. For instance, histamines serve as neurotransmitters, transmitting signals between nerve cells in the brain. They are essential in regulating sleep-wake cycles, appetite, and mood.
In the brain, histamines are produced by a specific group of neurons in an area called the tuberomammillary nucleus. These neurons project their axons to different regions of the brain, including those involved in wakefulness and arousal. When histamine is released in these areas, it promotes wakefulness and alertness. Conversely, when histamine production is inhibited, it can lead to drowsiness and fatigue.
In addition to their role in the brain, histamines also play a crucial role in the digestive system. They stimulate the secretion of gastric acid in the stomach, which aids in the digestion and breakdown of food. This acid helps to kill bacteria and other pathogens that may be present in the food, protecting the body from potential infections.
Furthermore, histamines are involved in regulating the permeability of blood vessels. When histamines bind to specific receptors on the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels, it causes them to contract, reducing blood flow to the area. This response is important in limiting the spread of toxins or pathogens during an infection or injury.
Overall, histamines are multifunctional molecules that play a vital role in the body's immune response, neurotransmission, and digestive processes. While they can cause uncomfortable symptoms during an allergic reaction, it is important to remember that histamines also serve important physiological functions in maintaining overall health and well-being.
The Histamine Content in Foods
Now that we have a basic understanding of histamines, let's turn our attention to the histamine content in foods. Some foods naturally contain histamines, while others may trigger histamine release or inhibit its breakdown in the body. This variation can have implications for individuals with histamine intolerance or sensitivity.
Histamine is a compound that is naturally present in many foods. It plays a crucial role in the immune system, helping to regulate various physiological processes. However, for some people, consuming foods high in histamine can lead to adverse reactions. These reactions can range from mild symptoms like headaches and rashes to more severe ones such as difficulty breathing and gastrointestinal distress.
Common High-Histamine Foods
There are several foods that are commonly recognized as high in histamine. These include aged cheeses, fermented foods like sauerkraut and soy sauce, processed meats, and certain seafood like tuna and mackerel. These foods can provoke histamine-related symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Aged cheeses, such as blue cheese and Parmesan, are known to have high levels of histamine. The longer the cheese is aged, the higher the histamine content. Fermented foods like sauerkraut and soy sauce also contain significant amounts of histamine. These foods undergo a fermentation process that increases histamine levels. Processed meats, such as salami and hot dogs, are often cured with histamine-rich ingredients like vinegar and spices. Additionally, certain types of seafood, like tuna and mackerel, naturally contain high levels of histamine.
It's important to note that the histamine content in foods can vary depending on factors such as storage conditions and preparation methods. For example, if a food is not stored properly, histamine levels can increase. Similarly, certain cooking techniques, like grilling or smoking, can also lead to higher histamine levels in foods.
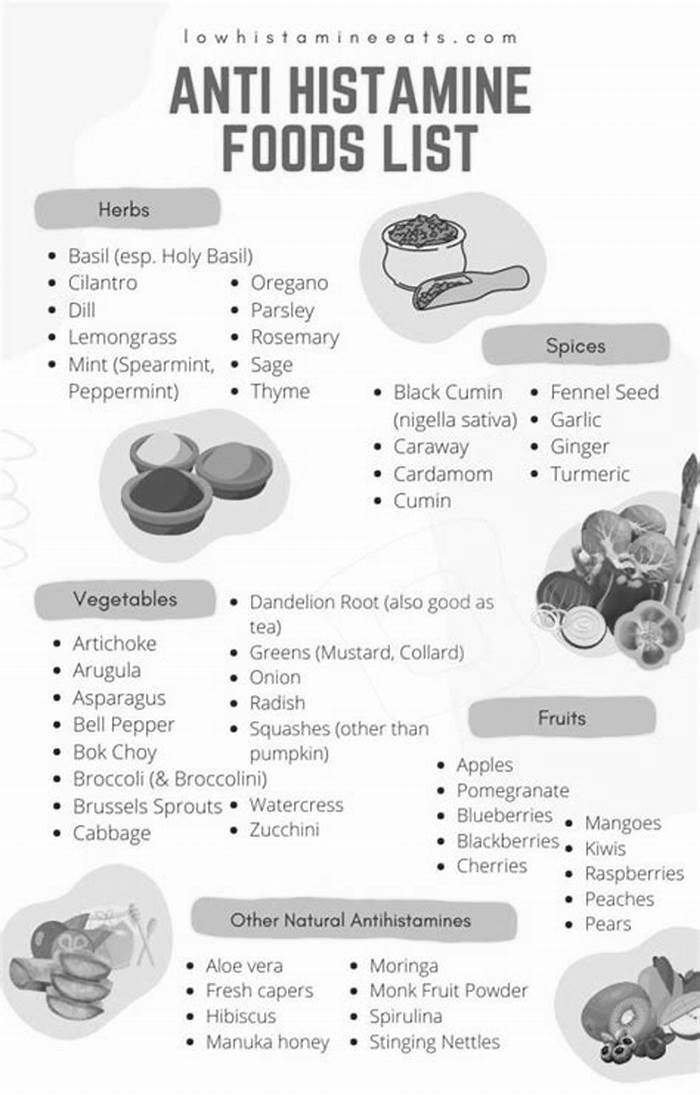
Low-Histamine Foods: What to Look For
While it may seem daunting to avoid histamine-rich foods altogether, there are plenty of low-histamine options available. Fresh fruits and vegetables, unprocessed meats, non-fermented dairy products, and gluten-free grains are generally considered low in histamine. However, it's important to note that individual tolerances can vary, and it may be necessary to customize one's diet based on personal preferences and reactions.
Fresh fruits and vegetables, such as apples, berries, broccoli, and spinach, are excellent choices for individuals looking to minimize their histamine intake. These foods are not only low in histamine but also rich in essential nutrients and antioxidants. Unprocessed meats, like chicken and turkey, are also low in histamine and provide a good source of protein. Non-fermented dairy products, such as fresh milk and butter, can be included in a low-histamine diet. Additionally, gluten-free grains like rice and quinoa are safe options for individuals with histamine intolerance.
It's worth mentioning that while these foods are generally considered low in histamine, individual reactions can still vary. Some people may find that they have specific intolerances or sensitivities to certain low-histamine foods. Keeping a food diary and working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help identify any potential triggers and create a personalized diet plan.
In conclusion, understanding the histamine content in foods is essential for individuals with histamine intolerance or sensitivity. By being aware of high-histamine foods and opting for low-histamine alternatives, individuals can make informed choices to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Lemon Juice and Histamines
Now, let's address the burning question: does lemon juice contain histamine? Let's delve into the nutritional profile of lemon juice and explore its histamine content.
Nutritional Profile of Lemon Juice
Lemon juice is known for its vibrant citrus flavor and high vitamin C content. It also contains other essential vitamins and minerals, such as potassium, vitamin B6, and folate. Additionally, lemon juice is rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body against oxidative stress.
But that's not all! Lemon juice is also a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes a healthy gut. The fiber content in lemon juice can help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. So, not only does lemon juice add a tangy taste to your dishes, but it also provides you with essential nutrients and promotes digestive health.
Moreover, lemon juice has been used for centuries as a natural remedy for various ailments. It is believed to have antibacterial and antiviral properties, making it a popular choice for boosting the immune system and fighting off common colds and flu. The high vitamin C content in lemon juice is known to support a healthy immune system and may help reduce the duration and severity of cold symptoms.
Is There Histamine in Lemon Juice?
Fortunately for lemon juice enthusiasts, it is considered very low in histamine. While individual sensitivities can vary, lemon juice is generally well-tolerated even by those with histamine intolerance. This makes it an excellent choice for those seeking to minimize histamine intake while still enjoying a burst of citrus flavor in their meals.
It's important to note that histamine intolerance is a condition where the body has difficulty breaking down histamine, leading to allergic-like symptoms. While lemon juice is low in histamine, other foods and beverages may contain higher levels. It's always a good idea to be aware of your own sensitivities and consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect histamine intolerance.
In conclusion, lemon juice not only adds a refreshing and tangy flavor to your favorite dishes, but it also provides a range of essential nutrients and potential health benefits. Whether you're squeezing it over a salad, using it as a marinade, or simply enjoying a glass of lemonade, you can savor the taste of lemon juice without worrying about excessive histamine content.
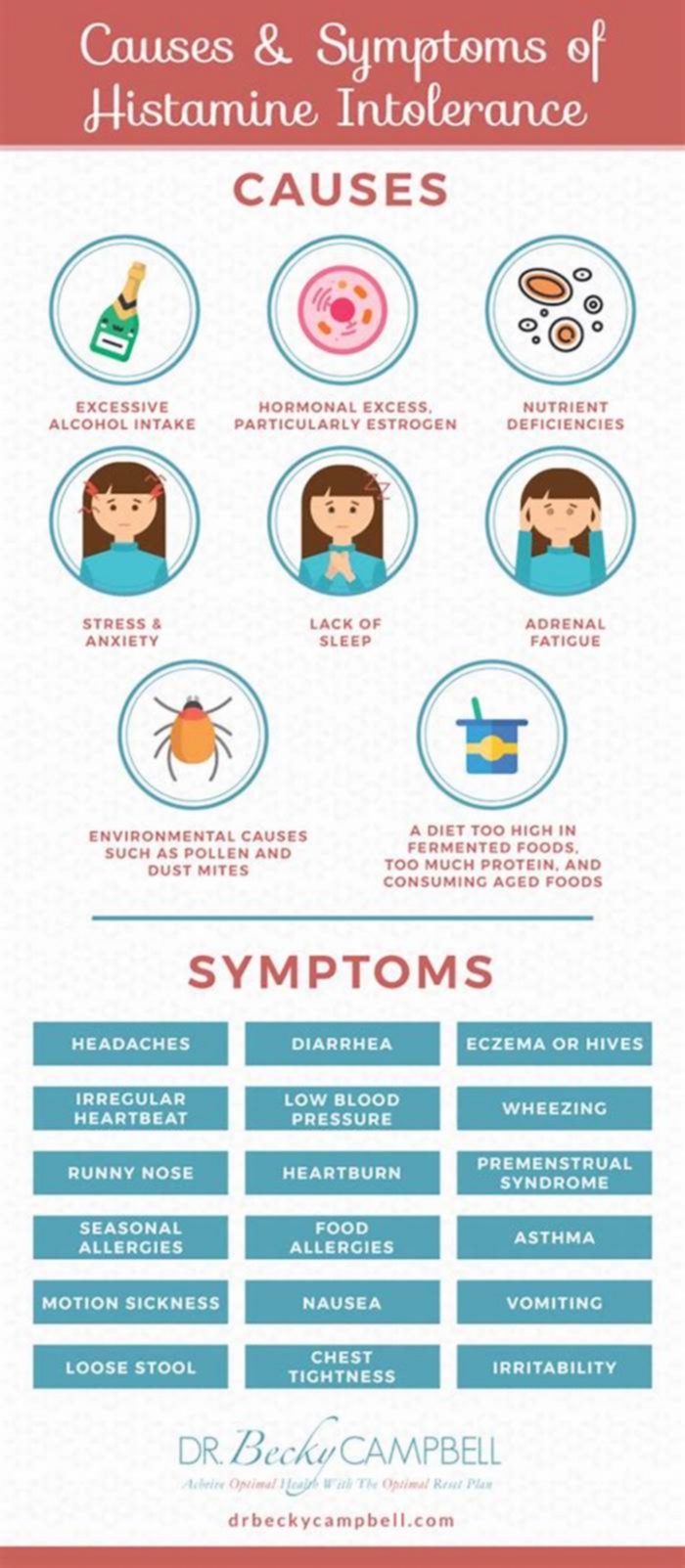
Effects of High Histamine Foods on Health
Consuming high histamine foods can have various implications for health, especially for individuals with histamine intolerance. Let's explore some of the symptoms associated with histamine intolerance and the potential long-term effects of high histamine intake.
Symptoms of Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance can manifest in a range of symptoms, including skin redness, hives, itching, digestive issues, headaches, and even respiratory difficulties. These symptoms can be bothersome and significantly impact daily life.
Long-Term Health Implications of High Histamine Intake
While occasional consumption of high histamine foods may not have severe consequences for most individuals, long-term high histamine intake can be detrimental to health. Chronic inflammation, gastrointestinal disturbances, and impaired immune function are among the potential health issues associated with prolonged histamine overload.
Managing Histamine Intake
For individuals with histamine intolerance or those seeking to reduce histamine intake, managing dietary choices is key. Here are some strategies to consider:
Diet Adjustments for Lower Histamine Intake
Adopting a low-histamine diet involves avoiding or minimizing high-histamine foods and opting for fresh, unprocessed alternatives. This may include a focus on fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and homemade meals.
Medical Treatments for Histamine Intolerance
In addition to dietary adjustments, medical treatments such as antihistamines or supplements that support histamine breakdown may be prescribed for individuals with histamine intolerance. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there are foods that are high in histamine, lemon juice is generally low in histamine content. Understanding histamine intolerance and its symptoms can help individuals make informed dietary choices. By managing histamine intake through diet adjustments and, if necessary, medical treatments, individuals can better navigate and mitigate the potential detrimental effects of high histamine intake. So go ahead and enjoy that zesty lemon flavor without worrying about its histamine content!
Is Lemon High In Histamine
Is Lemon High In Histamine
Lemons are a popular citrus fruit known for their refreshing taste and tangy flavor. They are widely used in culinary dishes, beverages, and even household cleaning products. However, if you suffer from histamine intolerance or are following a low-histamine diet, you may be wondering if lemons are safe to consume. In this article, we will delve into the question, "Is lemon high in histamine?"
Understanding Histamines: An Overview
Before discussing the histamine content of lemons, it's crucial to have a basic understanding of what histamines are and their role in the body.
Histamines are natural compounds that are involved in various physiological processes in the body, such as regulating immune responses, gastric acid secretion, and neurotransmission. They are small molecules derived from the amino acid histidine and are found in almost all tissues of the body.
While histamines are essential for maintaining normal bodily functions, excessive levels can lead to adverse effects in individuals who are sensitive to them. This sensitivity, known as histamine intolerance, can cause a wide range of symptoms, including headaches, nasal congestion, hives, digestive issues, and even anxiety or depression.
What are Histamines?
Histamines are produced and released by mast cells and basophils, which are types of white blood cells. These cells are an integral part of the immune system and play a crucial role in defending the body against harmful substances.
When the body encounters an allergen or a foreign invader, such as pollen or a virus, mast cells and basophils release histamines as part of the immune response. The histamines then bind to specific receptors on nearby cells, triggering a cascade of reactions that help the body eliminate the threat.
One of the primary functions of histamines is to increase blood flow and permeability in the affected area, allowing immune cells to reach the site of infection or injury more easily. This increased blood flow can cause redness, swelling, and heat, which are typical signs of inflammation.
The Role of Histamines in the Body
Histamines play a vital role in the body's immune response, aiding in the defense against allergens, toxins, and pathogens. They act as chemical messengers, communicating with various cells and tissues to coordinate the immune system's actions.
In addition to their role in immunity, histamines also have other functions in the body. They are involved in regulating gastric acid secretion in the stomach, helping to break down food and facilitate digestion. Histamines also play a role in neurotransmission, acting as neurotransmitters in the central nervous system.
However, histamines can also have unwanted effects when their levels become imbalanced. In individuals with allergies or histamine intolerance, even small amounts of histamines can trigger an exaggerated immune response. This can lead to symptoms such as itching, sneezing, runny nose, watery eyes, and skin rashes.
It's important to note that histamine intolerance is different from a true allergy. While allergies involve an immune response to a specific allergen, histamine intolerance is a non-allergic condition characterized by an inability to properly metabolize or break down histamines.
In conclusion, histamines are essential compounds in the body that play a crucial role in various physiological processes. Understanding their functions and the potential adverse effects of histamine intolerance can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and lifestyle to manage their symptoms effectively.
The Histamine Content in Foods
Now that we have a basic understanding of histamines, let's explore the histamine content in different foods, including lemons.
Histamines are organic compounds that are naturally present in various foods. They play a crucial role in the immune system and are involved in allergic reactions. However, some individuals may be histamine intolerant, meaning that their bodies have difficulty breaking down and metabolizing histamines. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including headaches, hives, nasal congestion, and digestive issues.
Common High-Histamine Foods
Various foods are known to have high levels of histamines. These histamine-rich foods can trigger histamine reactions in individuals who are histamine intolerant. It is important for those with histamine sensitivity to be aware of these foods and avoid or limit their consumption.
Aged cheeses, such as blue cheese, cheddar, and Parmesan, are notorious for their high histamine content. The aging process of these cheeses allows histamines to accumulate, making them a potential trigger for histamine intolerance. Similarly, fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and pickles contain high levels of histamines due to the fermentation process.
Processed meats, such as salami, bacon, and hot dogs, are also known to be high in histamines. The curing and preservation methods used in these meats can increase histamine levels, making them a potential source of histamine intolerance symptoms.
Alcoholic beverages, particularly red wine and beer, can also be problematic for individuals with histamine sensitivity. The fermentation and aging processes involved in the production of these beverages can lead to elevated histamine levels.
Certain types of fish, such as tuna and mackerel, are known to contain high levels of histamines. These histamine-rich fish can pose a challenge for individuals with histamine intolerance, especially if consumed in large quantities or when combined with other high-histamine foods.
Low-Histamine Foods: What to Include in Your Diet
On the other hand, there are several low-histamine foods that can be included in a histamine-friendly diet. These foods have minimal histamine content and are generally safe choices for those with histamine sensitivity.
Fresh fruits and vegetables, such as apples, pears, broccoli, and spinach, are excellent options for individuals with histamine intolerance. These foods are not only low in histamines but also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health.
Lean proteins like chicken and turkey are considered low in histamines and can be included in a histamine-friendly diet. These meats are excellent sources of high-quality protein and can be prepared in various ways to add flavor and variety to meals.
Gluten-free grains, such as rice, quinoa, and oats, are generally well-tolerated by individuals with histamine sensitivity. These grains provide a good source of carbohydrates and can be used as a base for meals or as a side dish.
For those who are lactose intolerant or prefer dairy alternatives, there are some low-histamine options available. Coconut milk, almond milk, and rice milk are examples of dairy alternatives that can be incorporated into a histamine-friendly diet.
It is important to note that individual tolerance to histamine-rich foods can vary. While some individuals may be able to tolerate certain high-histamine foods in moderation, others may need to strictly avoid them. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support in managing histamine intolerance through diet.
Lemon and Histamine: The Connection
Now, let's focus specifically on lemons and their histamine content.
When it comes to lemons, there is more to them than just their bright yellow color and acidic taste. Lemons are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients that can benefit your overall health.
Nutritional Profile of Lemons
Lemons are known for their high vitamin C content, which is a powerful antioxidant that helps boost the immune system and fight off free radicals. In fact, a single lemon can provide you with about 51% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C.
But that's not all. Lemons are also a good source of other essential nutrients such as potassium and magnesium. These minerals play a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and supporting proper muscle function.
Furthermore, lemons are low in calories, making them a great addition to a balanced diet. They are also rich in dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps keep you feeling full for longer.
Are Lemons High in Histamines?
Fortunately for lemon enthusiasts, lemons are not known to be high in histamine content. This is great news for individuals who are histamine intolerant and often have to be cautious about the foods they consume.
Histamine intolerance is a condition where the body has difficulty breaking down histamine, leading to allergic-like symptoms such as headaches, hives, and digestive issues. However, lemons are generally well-tolerated by individuals with histamine intolerance and do not typically provoke any histamine reactions.
So, if you love lemons, you can usually enjoy them without worrying about triggering any allergic symptoms. Whether you squeeze them into your water, use them in cooking, or add them to your favorite recipes, lemons can be a refreshing and nutritious addition to your diet.
Impact of High Histamine Foods on Health
While lemons are generally safe for individuals with histamine intolerance, it's essential to understand the potential symptoms associated with high histamine foods and how to manage them.
High histamine foods can have a significant impact on our health, especially for those with histamine intolerance. Histamine is a compound that is naturally produced by our bodies and is also present in certain foods. When consumed, histamine can trigger a range of symptoms that can vary from person to person.
Symptoms of Histamine Intolerance
People with histamine intolerance may experience a range of symptoms after consuming foods high in histamines. These symptoms can vary from person to person but may include headaches, nasal congestion, skin rashes, digestive issues, and even anxiety or irritability. The severity of these symptoms can also vary, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort while others may face more severe reactions.
Headaches are a common symptom of histamine intolerance and can range from a dull ache to a throbbing pain. Nasal congestion, on the other hand, can make breathing difficult and lead to a stuffy or runny nose. Skin rashes may manifest as red, itchy patches or hives, causing discomfort and irritation.
Digestive issues such as bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea can also occur after consuming high histamine foods. These symptoms can be particularly distressing and affect daily activities. Additionally, some individuals may experience anxiety or irritability, which can further impact their overall well-being.
If you suspect histamine intolerance, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They can help identify the specific triggers and provide guidance on managing the symptoms effectively.
Managing Histamine Levels through Diet
Managing histamine levels can be achieved through dietary changes. Following a low-histamine diet involves avoiding or minimizing the consumption of high-histamine foods while increasing the intake of low-histamine alternatives. It is crucial to listen to your body and pay attention to how different foods affect your symptoms.
Some high-histamine foods to avoid include aged cheeses, fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi, cured meats, and certain types of fish. On the other hand, low-histamine alternatives such as fresh fruits and vegetables, lean meats, and gluten-free grains can be incorporated into the diet.
It is important to note that individual tolerance to histamine can vary, and what works for one person may not work for another. Keeping a food diary can be helpful in identifying specific triggers and understanding how your body reacts to different foods. This information can then be used to create a personalized diet plan that suits your needs.
In addition to dietary changes, other lifestyle factors can also impact histamine levels. Stress, for example, can worsen symptoms, so incorporating stress-reducing activities such as meditation or yoga into your routine may be beneficial.
By managing histamine levels through diet and lifestyle modifications, individuals with histamine intolerance can experience improved overall health and well-being. It may take some trial and error to find the right balance, but with patience and guidance from healthcare professionals, it is possible to effectively manage histamine intolerance and minimize its impact on daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Histamines and Food
Now, let's address some common questions regarding histamines and their connection to food.
Can Cooking Affect Histamine Levels in Foods?
Cooking methods can influence histamine levels in certain foods. While some cooking processes, such as fermentation, might increase histamine levels, other techniques, like boiling or grilling, can help reduce histamines. If you are concerned about histamine levels in a specific food item, consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for guidance.
Are There Any Histamine-Free Diets?
While there is no specific "histamine-free" diet, individuals with histamine intolerance can benefit from following a low-histamine diet that reduces their exposure to high histamine foods. By working with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian, personalized dietary recommendations can be provided based on individual needs and tolerances.
In Conclusion
In summary, lemons are generally not high in histamine content and can usually be enjoyed by individuals with histamine intolerance. However, it's crucial to be mindful of your body's reactions and symptoms when consuming any food. If you suspect histamine intolerance or have any concerns, it is best to seek advice from a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance for managing your diet and overall health.