How do I know if my pitbull has hives

Dog Hives
What Are Dog Hives?
Hives (also referred to as urticaria) are areas of the skin that appear reddened and raised. Just as with humans, hives can be very itchy for your dog. Theyre a sign that an allergy is causing the immune system to overreact.
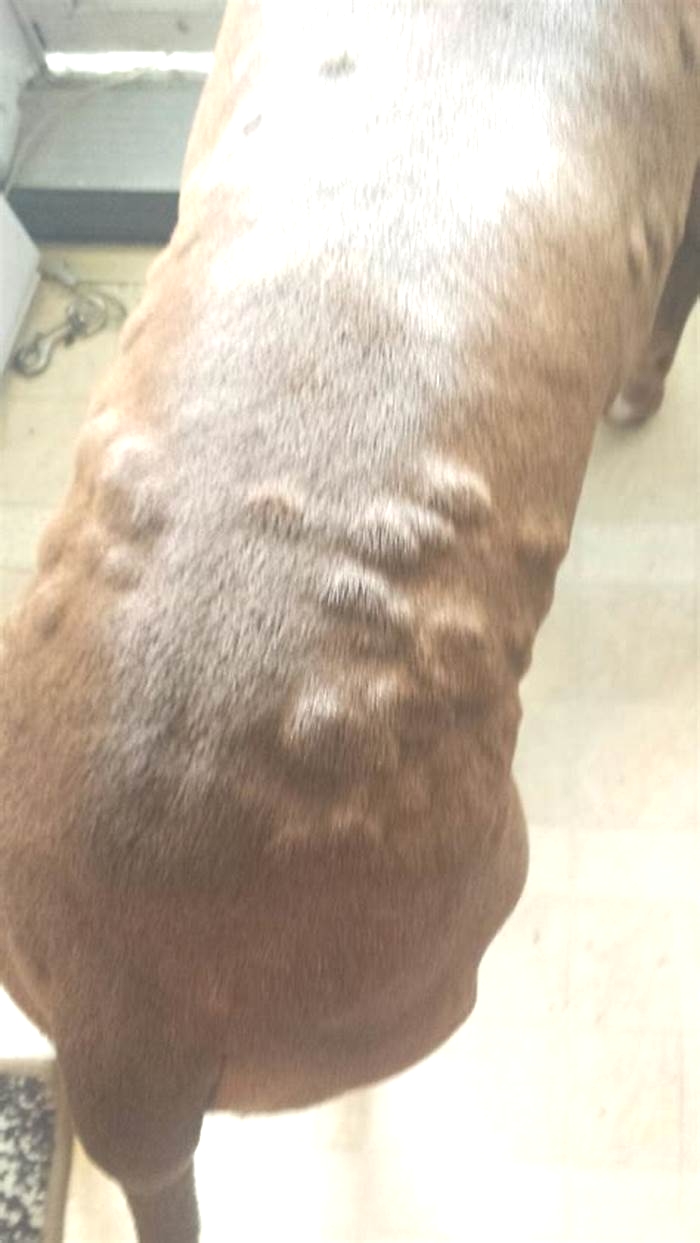
Hives can appear very quicklyand disappear just as quickly. The raised red area of the skin is referred to as a wheal, and it can appear anywhere from a few minutes to hours after exposure to an allergen. Wheals can appear anywhere on your dogs body, but theyre usually found on the head, neck, back, stomach, and legs.
In mild cases, the hives will generally disappear within 12-48 hours after contact with the allergen. However, because of the risk that the reaction can worsen to dangerous swelling of your dogs airways or a serious allergic reaction called anaphylaxis, you should seek out treatment any time you see hives on your dog. This is especially true for hives that occur on the face or around the throat, which can lead to dangerous swelling and possible blockage of the airways.
Symptoms of Dog Hives
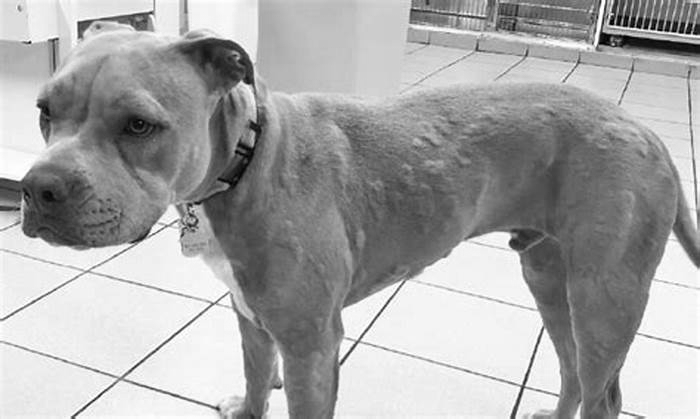
Red raised areas of skin called wheals, which can occur anywhere (including mucous membranes) but are most commonly seen on the head, neck, back, abdomen, and legs
Intense itching
Excessive drooling if the mouth is swollen
Swelling (angioedema), which is particularly concerning when it involves the face and respiratory system and can have severe and life-threatening consequences
Causes of Dog Hives
The allergen that causes the hives may be environmental, chemical, or dietary. Any allergen your dog is sensitive can also lead to hives. Common causes include:
Insects bites, chemical contact, and medications are the most common.
How Vets Diagnose Hives
Your vet will closely examine your dog to locate the distinctive wheals associated with hives. Wheals typically have hair on them, and may appear in clusters. Beyond the physical examination, other parts of the diagnosis include:
Any history you are able to provide; be as thorough as you can in describing allergens your dog might have come into contact with and when and where you first saw the hives
Your dogs response to treatment
Treatment for Dog Hives
Dogs with hives usually respond quickly to treatment, which may include:
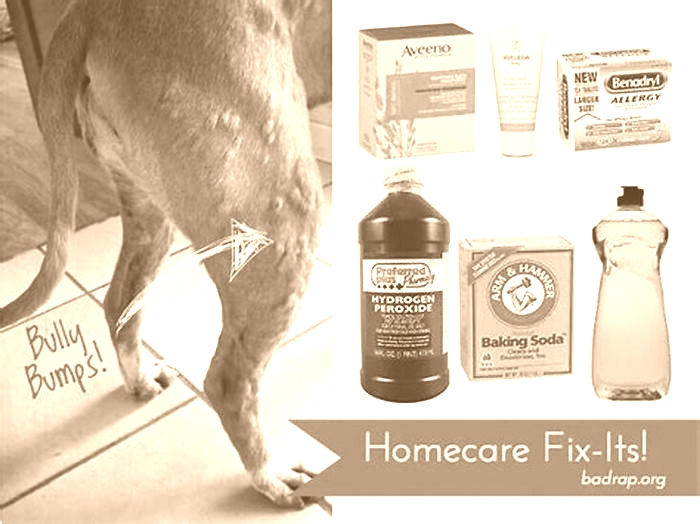
At-home treatments may include:
Cold compresses over the hives or swollen areas to give relief from itching
Antihistamines, but only under the supervision of your vet
Management of Dog Hives
Work with your vet to determine the cause of the hives, using both your dogs health history and history of exposure to allergens. Depending on the cause and the frequency, your vet may recommend:
Allergy testing to confirm environmental allergens
Immunotherapy treatment to desensitize your dog to specific allergens
A food trial to find ingredients that cause a reaction and develop specific dietary recommendations
Dog Hives FAQs
Are dog hives an emergency?
Yes. Hives indicate an allergic reaction within the body. Although the hives themselves are mostly just uncomfortable, they could lead to very dangerous complications, including anaphylaxis and death. Its best to treat even mild cases of hives.
What can I give my dog for hives?
It is important to speak to your veterinarian before giving your dog any medication. The vet may recommend certain medications to give your dog now or to have ready for future episodes.
How long do hives last?
Hives can disappear within a few hours or last up to 48 hours.
Can anxiety cause hives in dogs?
Theres a small chance that psychological stress can cause dog hives, but generally, anxiety merely worsens hives that are already present.
Should I take my dog to the vet for hives?
Yes, hives indicate a larger issuean allergic reactionand require treatment to make your dog comfortable and keep the reaction from progressing.
What do hives look like on a dog?
Hives are red, often swollen areas of skin that may be very itchy. They can be anywhere on the body, but youll often spot them on your dogs head, neck, back, stomach, or legs.
What foods cause hives in dogs?
There is no one food that generally causes hives in dogs. However, if your dog is allergic to a particular food or ingredient, that can cause hives for your individual dog.
Dog Hives (Urticaria | welts): Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
What Are Dog Hives (Urticaria)?
Hives, otherwise known as urticaria by medical professionals, are one abnormality you may see. They occur when your dog is allergic to something, such as an insect, medication, or food. Recognizing hives in dogs and understanding the cause is essential to relieving your dogs discomfort and preventing dog hives in the future.
What do dog hives look like?
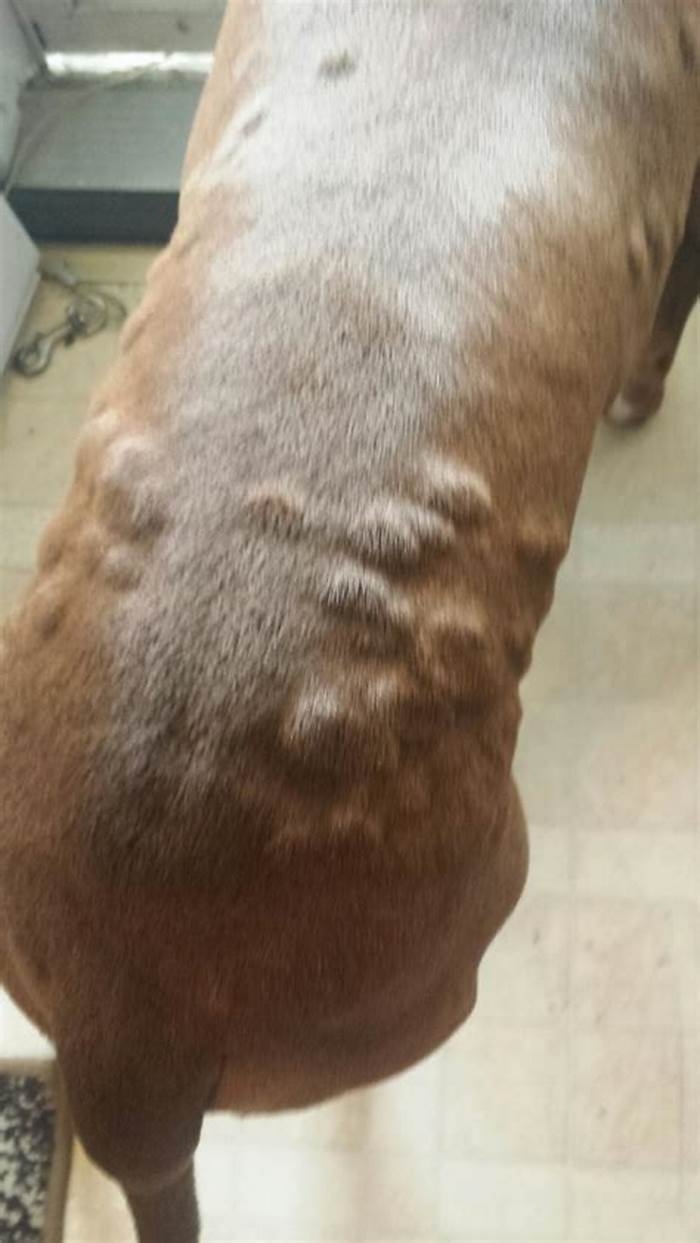
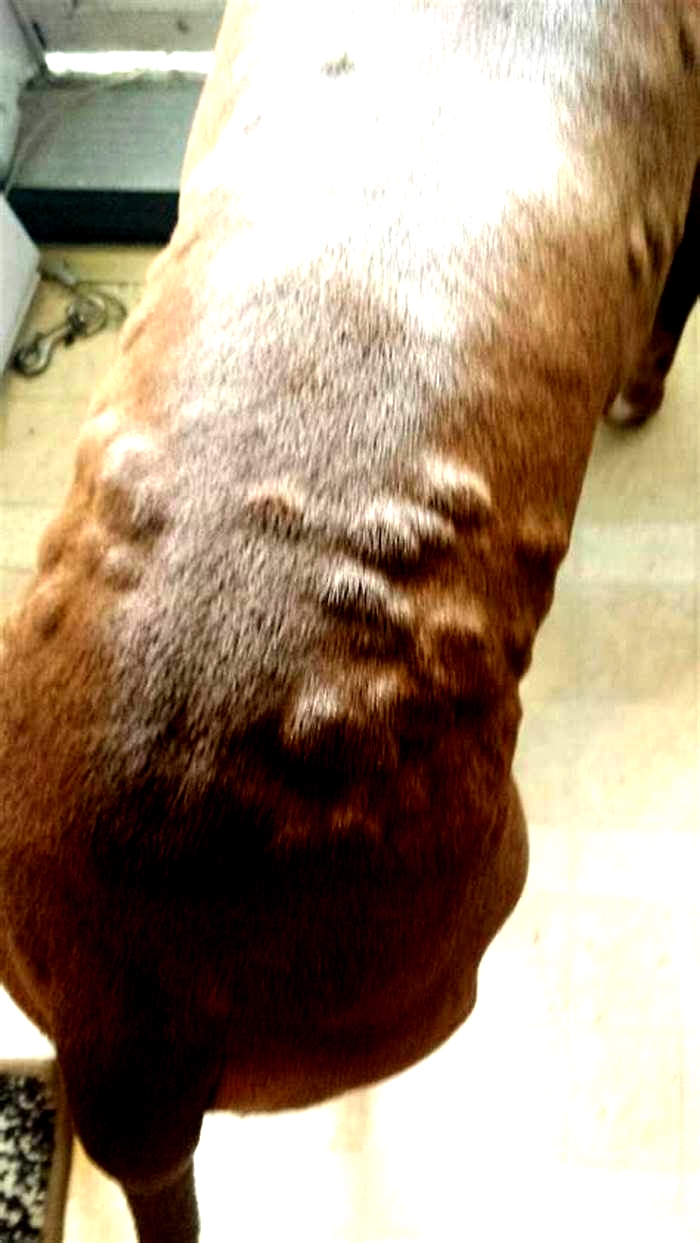
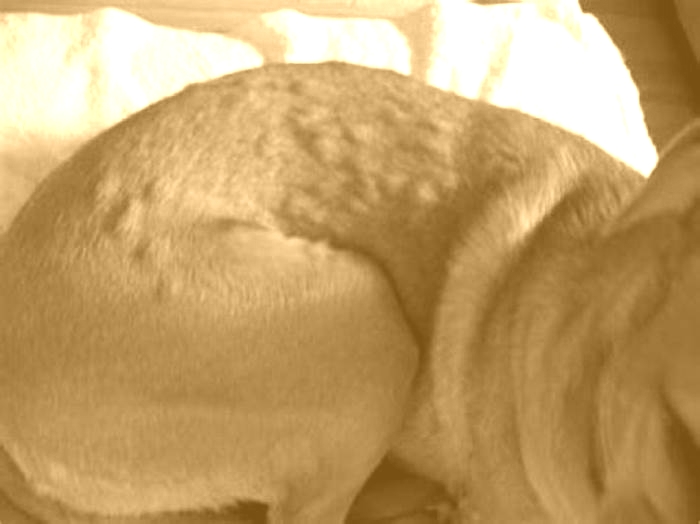
- Dog hives look like raised bumps on the skin, usually about the size of a nickel.
- Hives are usually red in color; however, you may not notice redness if they are on a very furry part of your dog. In this case, your pets hives may only look like fur-covered bumps. Sometimes, its difficult to see the raised bumps, and you may only feel them when petting your dog.
- Dog hives can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, tongue, neck, legs, chest, abdomen, or back. They can affect just one area of the body or the entire body.
- Dog hives are very itchy. This may be the first thing you notice before seeing or feeling hives on your dogs skin. Your dog will likely be trying to scratch, lick, or bite the areas affected as it will be itchy.
- Hives usually happen very fast within minutes after exposure to whatever caused them.
- You may notice excessive drooling and a swollen/puffy face if the hives affect your dogs throat or mouth.
What causes hives on a dog?
Dog hives are almost always related to exposure to an allergen. Once exposed to an allergen, mast cells in your dogs body release a substance called histamine. Histamine causes blood vessels to dilate, which leads to raised welts on your dogs skin.
The most common allergens causing dog hives include:
- Insect bite or sting, or ingesting an insect (photo recommendation: dog playing with bee)
- Vaccinations
- Acute allergic reactions to medications (chemotherapy, vitamin K, antibiotics)
- Food allergies
- Environmental allergies (grasses, trees, mold, dust mites, etc.)
- Contact allergens such as shampoos, insecticides, cleaning products
- Ingesting or skin exposure to toxic plants
Much less common causes of hives in dogs include prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures (hot or cold), strenuous exercise, parasites, or significant psychological stress.
Insect bites/stings, food, and medications are the most common causes of hives in dogs.
How are dog hives diagnosed?
As a pet parent, it can be worrisome to see these skin rashes, but luckily, for your vet to diagnose your dogs hives. Your vet will use a combination of your history and their physical examination findings.
Its essential to think about anything new your dog may have been exposed to. Did you see them playing with a bee? Were they recently vaccinated? Did they start a new medication or a new food? During the physical exam, your veterinarian will look at your dogs skin to evaluate hives and where the hives are located.
If your veterinarian is having trouble diagnosing your dogs hives or the reason for their hives, they may perform additional diagnostics, such as blood work, skin cytology, skin scrapings, or fecal analysis.
How to treat & get rid of dog hives?
Treatment for hives in dogs can be simple or more extensive, depending on the cause, severity, and duration of the allergic reaction.
To get your dog quick relief from the swelling and itchiness related to hives, your veterinarian will usually administer an injection of diphenhydramine (an antihistamine) and a corticosteroid. Once your dog is feeling better and discharged from the hospital, your veterinarian may also recommend that you continue giving your dog Benadryl two to three times a day at home for a couple of days.
To prevent hives from reoccurring, you need to understand what caused them in the first place so that you can avoid the allergen in the future. If there is no apparent cause for your dogs hives (such as insect bite, medication, or vaccinations), it may be more challenging to understand how to prevent hives in the future. Environmental and dietary allergies are two possible causes of hives that may require further diagnostics and treatment.
Environmental allergies
If your dog has recurrent hives or has other signs of allergies, your veterinarian may recommend testing for environmental allergies with serum allergy testing or intradermal allergy testing. With these results, your veterinarian can create a plan to desensitize your dog to these allergies with allergen-specific immunotherapy.
If you determine that you cannot eliminate the allergens in your dogs environment or pursue allergen-specific immunotherapy treatment, your veterinarian may recommend:
- Giving your dog daily antihistamines (such as Benadryl, zyrtec, or hydroxyzine)
- Giving your dog other prescription-strength allergy medications such as apoquel or cytopoint
- Starting daily skin health supplements, such as omega-three fatty acids.
- Frequently bathing your dog with medicated high-quality shampoo
Food allergies
Allergies that stem from food can also cause recurrent episodes of hives in dogs. The most common cause of allergies in dogs include chicken, beef, dairy, and egg 2. Recurrent episodes of hives can also be related to dietary allergies. To diagnose a food allergy, your veterinarian may recommend a diet trial for 6-8 weeks with a prescription food or an over-the-counter diet with a different protein source, like fish or venison. If your dog responds positively to a food trial, you can continue the special diet long term.
Are dog hives dangerous?
Dog hives are rarely life-threatening. However, there are a few less common situations where hives can affect your dogs breathing and become dangerous.
- Hives in the face, neck, or throat can cause severe swelling that impacts breathing, which can become life-threatening.
- The presence of hives anywhere may indicate your dog is having or about to have an anaphylactic reaction, which causes constriction of airways and difficulty breathing. 3 Besides hives, other signs of anaphylaxis include vomiting, diarrhea, facial swelling, drooling, blue gum color, and collapse.
If you notice that your dog has hives, pay particular attention to how they are breathing and for any other concerning changes in their behavior. If you are concerned your dog may be having severe allergic reactions, take them to the emergency room immediately to rule out a medical emergency.
At-home remedies for dog hives
If possible, take your dog to the veterinarian if you notice they have hives, especially if this is a first-time problem. If your dog chronically or intermittently has hives and the issue has previously been discussed with a veterinarian, some at-home remedies may help relieve the allergic reaction.
- If the hives are not affecting your dogs face, neck, throat, or ability to swallow, you can administer Benadryl by mouth. Always discuss if this is appropriate for your dog with your veterinarian first and receive instructions about dosage and frequency.
- If the hives were caused by a contact allergen (such as grasses/trees or chemicals) or insect bites you can help relieve itchiness by bathing with a gentle oatmeal-based dog shampoo can help your dog feel more comfortable.
- Apply a cold compress to the hives or the most severely affected areas of your dogs skin. Be careful never to apply a cold compress for more than 10 minutes at one time, and always wrap the ice or cold object in a towel before applying it to your dogs skin.
Hives and Rashes (Urticaria) in Dogs
Hives or skin rashes (urticaria) are localized patches of red, swollen, usually itchy, skin. They often develop and disappear suddenly. Hives are relatively uncommon in dogs. The most frequent causes are insect bites or stings, shampoos, and medications. Other causes include contact with toxic plants or chemicals. Friction, sunlight, heat, exercise, stress, and genetic abnormalities may cause or intensify the rash. Hives may develop after inhaling or consuming allergens. Hives can be seen while a dog is in estrus ("in heat") or seen in puppies with intestinal parasites ("worms").
The wheals (eruptions) appear within a few minutes or hours of exposure to the causative agent. In severe cases, the skin eruptions are preceded by fever, poor appetite, or dullness. They can develop on any part of the body but occur mainly on the back, flanks, neck, eyelids, and legs. In advanced cases, they may be found on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, lining of the eyes, rectum, and vagina.
Often, hives disappear as rapidly as they arise, usually within a few hours. Treatment may not be required. They may return rapidly if exposure to the cause is not eliminated, however. Also, if your dog develops hives after receiving a vaccination or medication, contact your veterinarian immediately to see if treatment is needed. Treatment may include rapid-acting corticosteroids. If hives are chronic, environmental or food allergens should be considered as potential causes. Death does not commonly occur, unless anaphylaxis (a severe allergic event) or swelling of the respiratory tract is present.
Also see professional content regarding urticaria.