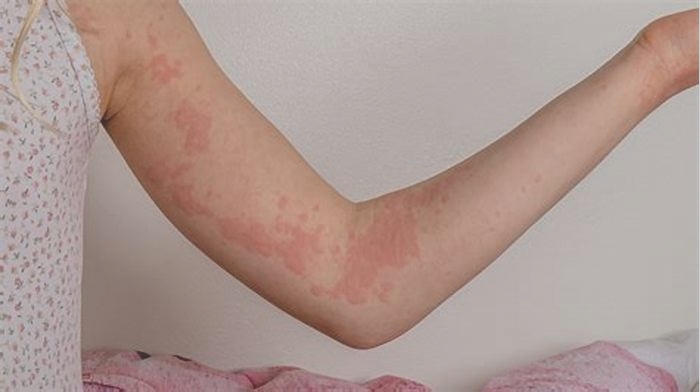
How do you get rid of hives from scratching
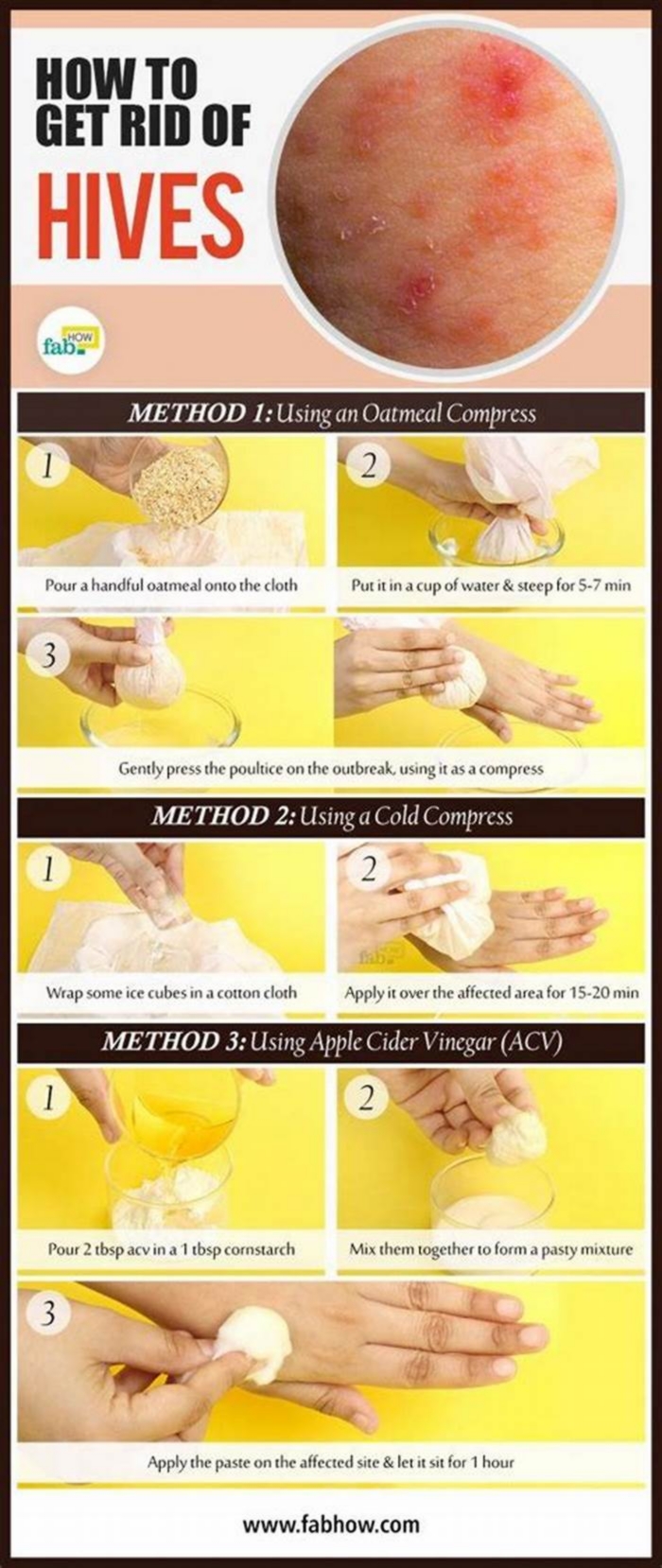
How to treat hives
Home remedies and medications can help treat hives quickly and effectively. Examples include cold compresses, aloe vera, antihistamines, and more.
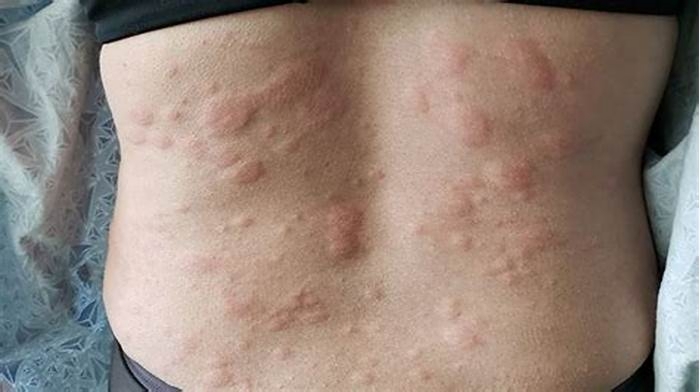
Hives are intensely itchy, discolored, raised areas of skin. They may occur anywhere on the body. Hives usually have a trigger, both allergic and non-allergic.
While the symptoms of hives can be very irritating, there are many ways to treat, soothe, and get rid of them.
In this article, we detail how to treat hives at home, medical options, and possible complications.
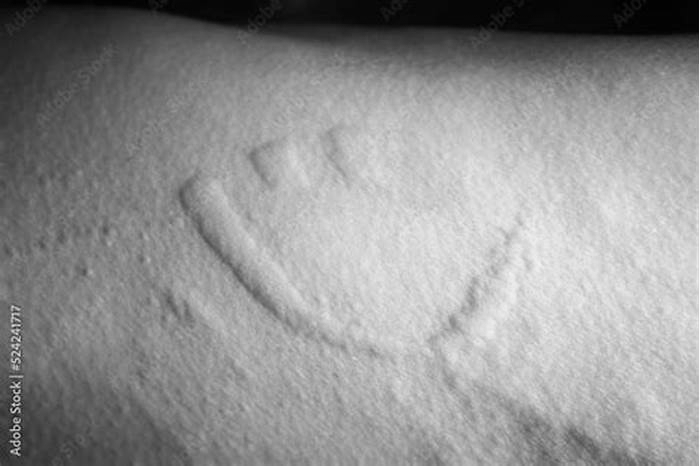
What does hives look like? Pictures and more
People often use home remedies to treat hives and do not seek further medical attention or intervention. In fact, many cases of hives disappear naturally within minutes or hours of appearing. Most often, symptoms of hives will disappear within 24 hours, but in some cases, it may take a few days.
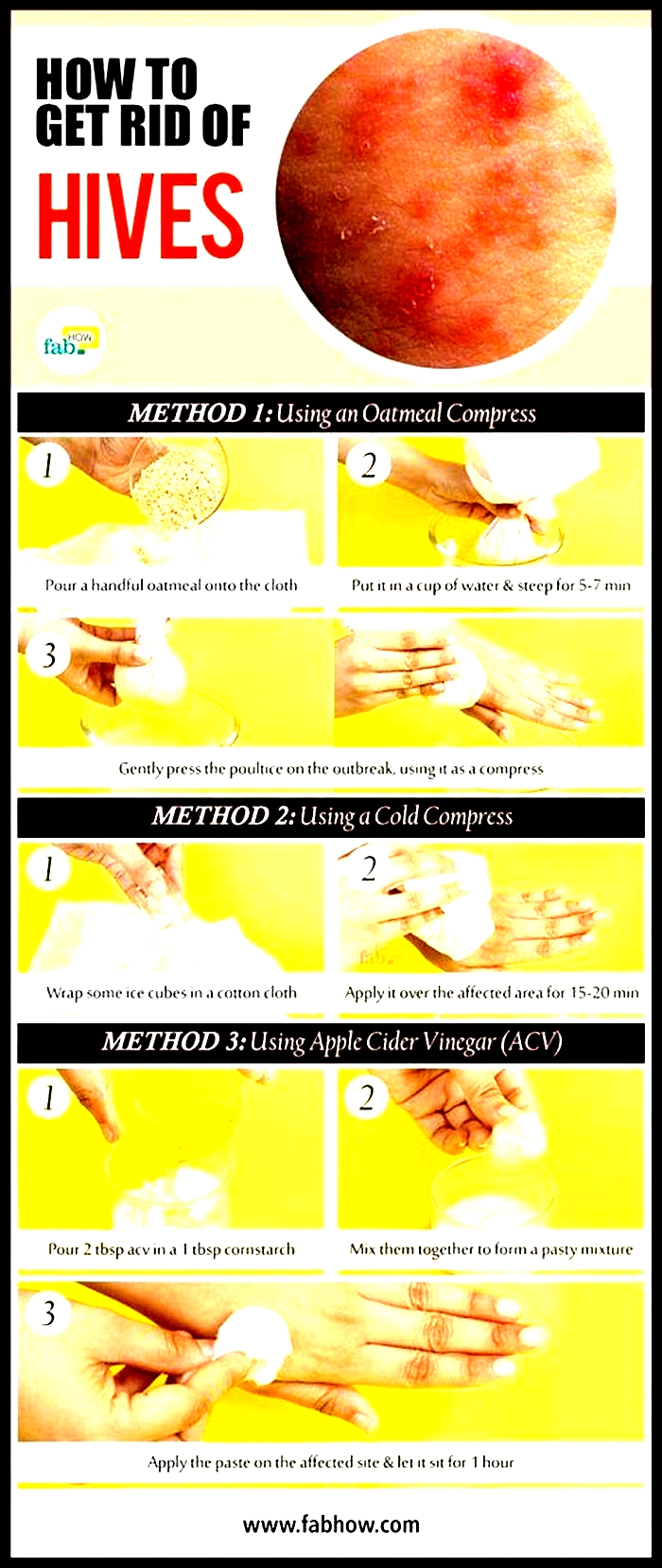
Effective home remedies to treat hives include:
- Applying a cold compress: A person can apply a cool, damp cloth to the affected area. This can provide relief from itchiness and help reduce inflammation. A person can use a cold compress as often as necessary.
- Bathing in an anti-itch solution: Oatmeal and baking soda baths can soothe skin and reduce irritation. Adding witch hazel to a bath is another effective home remedy.
- Applying aloe vera: The healing properties of aloe vera may soothe and reduce hives. However, it is best to do a patch test before applying aloe vera to a wider area.
- Avoiding irritants: This includes perfumes, fragranced soaps or moisturizers, and staying out of the sun. A person should also aim to maintain a comfortable temperature and wear loose, cotton clothing.
Some people with chronic hives
In more severe cases of hives, medical treatment may be preferable. Some over-the-counter options include:
People with more severe and persistent hives may need to see a dermatologist. These doctors specialize in conditions of the skin, hair, and nails.
Hives are a skin condition that usually results in a raised, itchy rash. There are several different types of hives, although the effects are mostly the same.
Hives may be the same color as the surrounding skin or may have a reddish hue. This discoloration may be less evident on darker skin tones.
Learn more about hives on black skin here.
Acute urticaria and acute angioedema
Acute urticaria is a short-lived type of hives. In this condition, rashes last less than 6 weeks and usually occur due to an adverse or allergic reaction to certain foods or medications. Urticaria only affects the upper layer of the skin, called the dermis.
Infections and insect bites can also cause this type of rash.
Angioedema is the rapid swelling of the area beneath the skin, known as the mucosa. A person with hives will not always experience this type of swelling. Angioedema can occur with many different disorders.
Acute angioedema can occur with acute urticaria and is essentially anaphylaxis of the subcutaneous tissues. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction. It can lead to anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal.
Learn more about anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock here.
Chronic urticaria and chronic angioedema
Chronic urticaria and chronic angioedema last for more than 6 weeks.
In these conditions, a person will typically experience daily, or almost daily, symptoms without an allergic, infectious, or drug-related cause.
Chronic urticaria and chronic angioedema more commonly result from underlying medical causes, such as thyroid disease, cancer, or hepatitis.
Hives affect around 20% of people at some point during their lifetime. They are more common in children and female adults than in male adults.
A hives outbreak happens when high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers release into the skin, causing a rash and other symptoms to surface.
The high levels of histamine cause blood vessels in the affected area to open up and start to leak. The resulting fluid in the tissues causes swelling and itchiness.
Different triggers may cause a person to have an outbreak of hives. Some common causes include:
- an allergic reaction to food, an insect bite, or an animal
- a reaction to a plant irritant, such as nettles
- an infection, such as the flu or a cold
- certain medications
- preservatives and food additives
If hives develop, it is useful to identify the trigger. Factors that can worsen hives include:
Physical urticaria
The effects of heat exposure and overheating can cause a type of hives called physical urticaria.
Common triggers for physical urticaria include:
- extreme heat or cold
- overexposure to the sun
- excessive sweating
- clothes rubbing the skin
This rash rarely spreads beyond its original location.
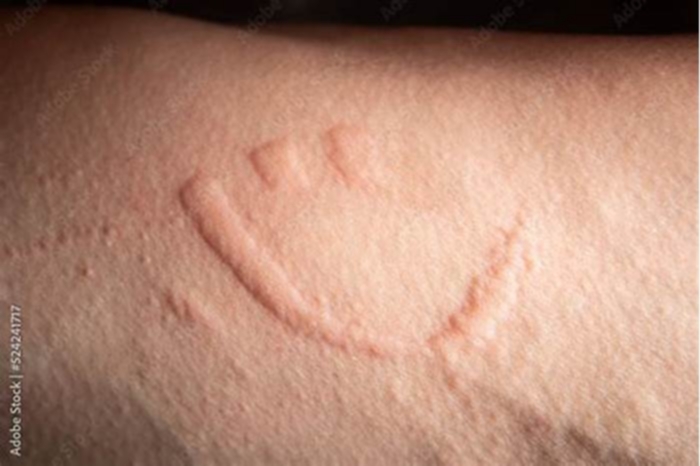
Some people experience dermatographism, a type of physical urticaria. This condition occurs
Some people refer to dermatographism as skin writing. The condition is
What is the difference between hives and a rash? Pictures and more
The severity of a hives can vary between individuals. Most symptoms are manageable at home, but medical attention may be necessary in some cases.
A person should see a doctor if:
- symptoms last more than a few days
- symptoms worsen over time
- the rash is painful or leaves a bruise
- symptoms interfere with daily life
- they experience dizziness
A person will need immediate medication attention if they experience:
- any swelling of the tongue, mouth, or throatSimilarly
- difficulty breathing
- tightness in their chest
A doctor will examine the rash and ask questions to determine the cause. Doctors may also use blood and allergy tests to rule out specific causes.
Hives are usually treatable and do not cause complications on their own. However, in more severe cases, angioedema may occur.
Angioedema is a buildup of fluid in layers of the skin that causes swelling and can affect the eyes, lips, hands, feet, and genitals. Doctors can prescribe medication to manage and reduce swelling.
Recurrent hives can negatively impact the quality of a persons life, causing them to feel stressed or anxious and can even lead to depression. A person should always speak to a doctor if hives are affecting their quality of life.
Here are some questions people often ask about hives.
How do you treat hives naturally?
Ways of treating hives naturally include:
- avoiding scratching
- applying a cool compress
- bathing in lukewarm water with colloidal oatmeal
- wearing loose, cotton clothing
- avoiding soaps with fragrances or strong chemicals
- applying aloe vera
What is the fastest remedy for hives?
A cool compress may offer immediate relief from discomfort, but topical medicines may be more effective. Ask a pharmacist about over-the-counter options.
Hives are a skin condition that results in itchy, raised, patches of skin. There may also be discoloration.
Hive can result from allergic or non-allergic causes. Home remedies and medications can often reduce symptoms.
People with severe hives may have a risk of further complications. A person should seek medical advice if symptoms are severe, ongoing, or affect their quality of life.
Hives (Urticaria)
What are hives?
Hives, or urticaria, are flat red welts that can appear anywhere on the skin and usually itch. Hives often occur as an allergic reaction to something eaten or something that has contacted the skin. Foods, medicines, and plants are common causes, but sun exposure, stress, infections, and autoimmune diseases have also been known to cause hives.
Symptoms include an itchy, stinging pink rash of slightly swollen skin. The rash may wax and wane in severity. Acute hives typically resolve within six weeks, but chronic hives (urticaria) can persist for months or years.
Hives often resolve on their own, especially in children. Otherwise, treatment for acute hives involves oral antihistamine medications to help relieve the itching and stinging. Chronic hives that do not improve with antihistamines may be treated additionally with corticosteroids, antibiotics, and other stronger medicines. A study found that 35% of people with chronic hives, are symptom free within one year, with another 29% having some reduction of symptoms.
You can safely treat this condition on your own as long as you does not develop trouble breathing. Any antihistamine (like Zyrtec, Clarinex, etc) works.
Healthdirect Free Australian health advice you can count on.
Key facts
- Hives, also known as 'urticaria' or 'nettle rash', is a skin rash that can occur for a range of reasons, including allergies, medicines or infections.
- A hive rash looks like red or skin-coloured raised bumps or welts on the skin, which are usually itchy.
- A hives rash is caused when the body produces a substance called histamine, which is released by the body in response to a perceived threat.
- Hives is diagnosed clinically, meaning that your doctor can diagnose the rash by talking to you and looking at your rash.
- The rash usually resolves on its own, but if a hives rash continues or get worse, antihistamines can help relieve the symptoms.
What is hives?
Hives is also known as 'urticaria' or 'nettle rash'. This skin rash can have a range of triggers, most commonly an allergic reaction. Other triggers include medicines or infections. Sometimes the trigger is unknown.
What are the symptoms of hives?
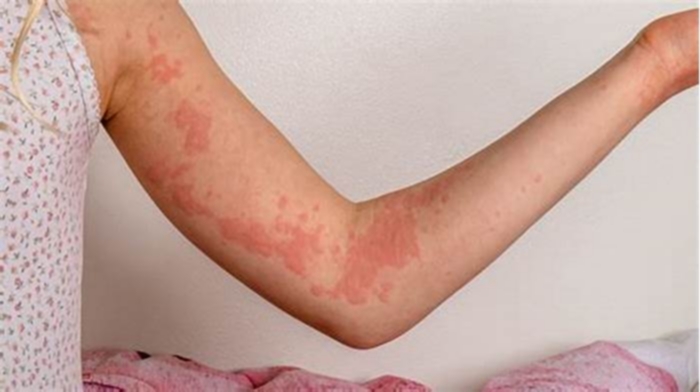
The hives rash looks like raised bumps or welts on the skin that are usually itchy, but may also sting. These can be red or skin-coloured. The raised areas of skin are known as wheals.
Patches of hives often join together to form larger swollen patches or urticaria. The affected area of skin can vary in size from quite small to about as large as a dinner plate. The patches of hives often join together to look like larger swollen patches of urticaria.
The hives rash can last for a few minutes to hours, and usually disappears within 24 hours. In rare cases, the rash can last for weeks.
CHECK YOUR SYMPTOMS Use the Symptom Checker and find out if you need to seek medical help.
What causes hives?
A hives rash is caused when your body produces a substance called histamine. This is a protein released by the body in response to a perceived threat (trigger).
In most cases, it is not known what triggers this reaction. Sometimes, urticaria can occur in response to:
Other triggers may include:
- cold air or water
- heat or sunlight
- vibration
- scratching
- sweating
- certain foods and drinks, such as spicy food, alcohol or coffee
In children, hives can be caused by a viral infection. This is why they sometimes go together with a cold or diarrhoea.
Hives that lasts for days at a time are almost never due to an allergy, apart from some cases of medicine allergy.
Stress rarely causes hives, but stress can make the symptoms worse.
When should I see my doctor?
You should see you doctor if you have a rash that looks like hives.
Some people have hives that don't go away or recur on a frequent basis. This is known as chronic urticaria. See your doctor if you have hives that keep coming back.
If you have taken antihistamines for your hives but they do not control the symptoms, discuss alternative treatment options with your doctor.
If your baby gets hives repeatedly, it's important to see your doctor. This could indicate an allergy to something they are frequently fed, such as cow's milk.
Sometimes hives can last for a long time. If you have hives for more than 6 weeks, your doctor may refer you for more tests to check if an underlying infection or chronic immune disorder is causing the symptoms.
FIND A HEALTH SERVICE The Service Finder can help you find doctors, pharmacies, hospitals and other health services.
How are hives diagnosed?
Hives is diagnosed clinically. Your doctor can diagnose the rash by talking to you and looking at your rash.
How are hives treated?
Hives usually resolve on its own without treatment. However, if the hives rash continues or gets worse, it can be treated with antihistamines. You can buy antihistamines over the counter at pharmacies.
Ask your pharmacist for advice on which antihistamine to take, as some will cause drowsiness, and can be taken at bed time if your rash is itchy and keeping you awake at night. Other antihistamines are not likely to cause drowsiness, so you can take them before driving or going to work or school.
To search medicines by active ingredient or brand name, use the healthdirect Medicines search feature.
Can hives be prevented?
If your hives are caused by a specific trigger, such as a food or medicine, you should avoid your known triggers.
Since most people don't know what caused their hives, it can be difficult to prevent.
Resources and support
For more information about the causes and management of hives see the Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy website.
The Royal Children's Hospital has a fact sheet on hives for parents to learn about care at home and more severe reactions.
You can also call healthdirect on 1800 022 222 at any time to speak to a registered nurse (known as NURSE-ON-CALL in Victoria) for more information and advice.