How long do hives last from dog allergy
How long can hives last?
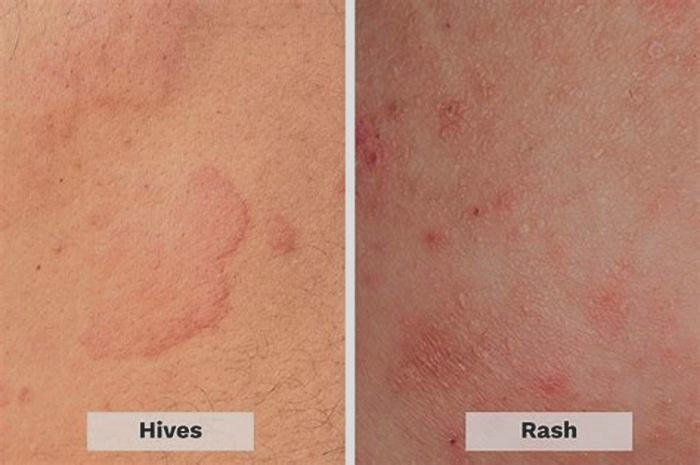
Hives can appear and disappear quickly, with each hive only lasting around 23 hours. However, depending on the cause, they may reappear and continue affecting someone for days, weeks, or longer.
People can have acute hives, which occurs due to a specific trigger and resolves within
This article looks at how long hives last, factors that influence their duration, and treatment.
Each hive lasts only
Acute hives appear quickly and do not last long. Doctors classify hives as acute if the overall duration is less than 6 weeks.
However, around 25% of people go on to develop chronic hives. This is when hives regularly reappear over 6 weeks or more.
For many individuals, chronic hives eventually clear on their own, but this can take months. According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD), around half of people with chronic hives spontaneously recover within 1 year.
Acute hives often occur in response to an allergen or irritant. When the immune system perceives a substance as a threat, it releases histamine and other chemicals. This causes tiny blood vessels under someones skin to leak fluid, which accumulates and causes the bump.
Some
- food allergens, such as milk, eggs, tree nuts, peanuts, or shellfish
- contact allergens, such as latex or animal dander
- insect bites or stings
- medications
Any drug can cause hives, but some of the medications most commonly associated with this symptom include:
Acute hives can also occur in response to viral infections, parasitic infections, or during times of stress.
According to a 2018 review, doctors are unsure of the cause of acute hives in
Chronic hives may have the same cause as acute hives, but with symptoms lasting longer than 6 weeks. However, chronic hives are often not due to an allergen and instead have a physical cause.
There are two subcategories of chronic hives: inducible urticaria and chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Chronic idiopathic hives
Chronic idiopathic urticaria has no clear cause and is the most common form of chronic hives. Researchers are working to understand why this type of hives occurs, but a leading theory links it with autoimmunity.
Autoimmunity occurs when a persons immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, and several autoimmune conditions are associated with chronic hives. The most common is thyroid disease, which is present in
This suggests that the hives may result from someones immune system not functioning as it should. Other conditions that can occur alongside chronic hives include type 1 diabetes, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Infections can also be associated with the onset of chronic hives. This includes bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections. Again, this may result from autoimmunity an infection may trigger a change in how the persons immune system works.
Inducible hives
Inducible or physical urticaria is less common than chronic idiopathic urticaria. With this subtype, it is possible to purposely induce the hives by a person exposing their skin to certain triggers, which could include:
- Scratching or pressure: The
most common type of inducible hives is known as dermatographia. This condition involves developing hives as a response to scratching or drawing on the skin. - Cold: Cold hives occur on someones skin or mouth after exposure to cold temperatures. Triggers include consuming iced drinks, touching cold water, or going outside in cold weather.
- Heat: Cholinergic hives occurs when an individuals body becomes hot or sweaty. Hot baths, exercise, and spicy food can be triggers.
- UV light: Solar hives occur in response to UV light from the sun and certain light bulbs, such as those in tanning beds.
- Water: Some people develop hives if their skin comes into contact with water. This is known as aquagenic urticaria and is very rare.
Doctors diagnose hives by performing a physical examination. There is no test to determine whether the persons hives are acute or chronic, so they will use the length of time they recur to do this.
The doctor may also ask an individual:
- when the rash began
- the shape, size, and distribution of the rash
- where on the body they first noticed the rash
- if they have had any insect bites
- if they live or work with common hive triggers, such as chemicals, animals, or latex gloves
- if they have bone or joint pain, fever, or abdominal pain
- if anyone in their family experiences hives
- if they take any medications or supplements
The doctor may use a skin prick test and serum-specific IgE test to check if the acute hives result from a specific substance, such as food, dust mites, or chemicals. Alternatively, they may refer someone to an allergy clinic for these tests.
However, in cases of chronic hives, allergy testing is rarely useful. A doctor may check for other underlying health conditions by performing additional tests, such as:
The most suitable treatment depends on whether the person has acute hives or chronic hives.
Acute hives
Doctors typically recommend second-generation antihistamines as the first-line treatment for acute hives, such as:
- loratadine (Claritin)
- desloratadine (Clarinex)
- fexofenadine (Allegra)
- cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- levocetirizine (Xyzal)
They may prescribe a standard dose or increase by up to 4 times if the individual does not respond.
If these medications do not improve symptoms, the doctor may recommend an additional antihistamine, such as cimetidine (Tagamet), famotidine (Pepcid), or ranitidine (Zantac). They may recommend a 310-day course of corticosteroids to help control the symptoms in severe cases.
The doctor may prescribe an epinephrine auto-injector if they think the individual is at risk of anaphylaxis, which is a severe allergic reaction that restricts breathing. This provides emergency medicine to treat anaphylaxis quickly.
The doctor will then reassess the individual in 26 weeks.
Chronic hives
Doctors may recommend a four-step treatment plan for chronic hives. This approach involves using an antihistamine daily, which may be up to 4 times the regular dosage depending on how the individual responds.If necessary, they may prescribe a second antihistamine or another medication, such as montelukast (Singulair). With persistent hives, they may suggest a high potency antihistamine, such as hydroxyzine or doxepin.
The final step is for a doctor to refer the individual to a specialist for immunomodulatory therapy. This may involve taking medications such as omalizumab (Xolair) or cyclosporine (Sandimmune).
Once symptoms are under control, a doctor may gradually reduce the dosage of these medications. If the hives have an identifiable cause, such as cold or heat exposure, adopting changes to avoid the triggers wherever possible is also important.
The AAD suggests the following methods for people to reduce irritation and itchiness in hives:
- applying topical anti-itch medications, such as calamine lotion
- wearing loose-fitting clothing
- moisturizing with fragrance-free lotion to prevent dry skin
- using cold compresses several times per day
However, it is important for individuals to try to determine whether the hives have a specific trigger, in addition to relieving symptoms. If someone has cold hives, for example, a cold compress may make them worse.
Therefore, it is a good idea for people to keep a symptom diary, recording when the hives occur and any factors that might have contributed. Symptom diaries are also useful to refer to at medical appointments. A person can take note of:
- the date and time the hives appear
- what they were doing just before they developed
- what they have had to eat or drink
If any common factors emerge when the hives occur, a person can try to temporarily avoid these to see if it helps. It is important for people to do this with the guidance of a doctor, allergist, or dietitian if someone has food-related hives.
Learn more about remedies and treatments for hives here.
Hives do not last long, taking only 23 hours to fade. However, more can appear, which makes the symptoms last longer. Acute hives can develop and resolve on their own within 6 weeks, while chronic hives can last much longer.
Doctors treat acute and chronic hives differently, so it is advisable for people to speak with a medical professional about this symptom, especially if the hives last longer than 6 weeks.
If hives or swelling occur in the mouth and airways, making it difficult to breathe, dial 911 or the number of the nearest emergency department immediately.
Hives and Rashes (Urticaria) in Dogs
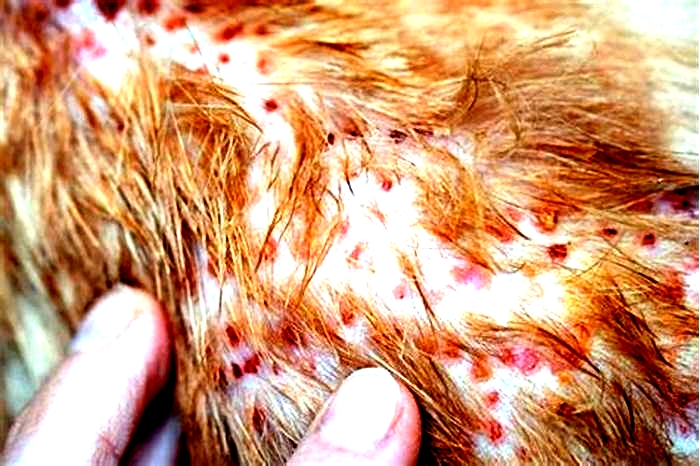
Hives or skin rashes (urticaria) are localized patches of red, swollen, usually itchy, skin. They often develop and disappear suddenly. Hives are relatively uncommon in dogs. The most frequent causes are insect bites or stings, shampoos, and medications. Other causes include contact with toxic plants or chemicals. Friction, sunlight, heat, exercise, stress, and genetic abnormalities may cause or intensify the rash. Hives may develop after inhaling or consuming allergens. Hives can be seen while a dog is in estrus ("in heat") or seen in puppies with intestinal parasites ("worms").
The wheals (eruptions) appear within a few minutes or hours of exposure to the causative agent. In severe cases, the skin eruptions are preceded by fever, poor appetite, or dullness. They can develop on any part of the body but occur mainly on the back, flanks, neck, eyelids, and legs. In advanced cases, they may be found on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, lining of the eyes, rectum, and vagina.
Often, hives disappear as rapidly as they arise, usually within a few hours. Treatment may not be required. They may return rapidly if exposure to the cause is not eliminated, however. Also, if your dog develops hives after receiving a vaccination or medication, contact your veterinarian immediately to see if treatment is needed. Treatment may include rapid-acting corticosteroids. If hives are chronic, environmental or food allergens should be considered as potential causes. Death does not commonly occur, unless anaphylaxis (a severe allergic event) or swelling of the respiratory tract is present.
Also see professional content regarding urticaria.
Am I allergic to my dog?
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
People who are allergic to dogs may experience a rash, hives, or watery eyes when exposed to dog saliva or dog dander.
In many cases, symptoms of a dog allergy are mild, and a person may still be able to live with a dog if they can manage their symptoms. Some home remedies can reduce symptoms. However, the only truly effective way to eliminate dog allergies is to avoid exposure to dogs.
In this article, we look at symptoms of allergic reactions to dogs and ways to manage them, including home remedies and medical treatments.
Specific symptoms and when they occur depend on the severity of the allergy. People who have severe allergic reactions to dogs may experience symptoms soon after exposure, while those with more minor allergies may take longer to develop symptoms.
Symptoms include:
- a skin rash that is red or consists of small, red, raised bumps called hives
- nasal congestion
- a runny nose and sneezing
- itchy, red, and watering eyes
- coughing
- wheezing
- tightness in the chest and shortness of breath
If a person lives with a dog, it is difficult to make the environment allergen-free. Dog dander (dead skin cells) can linger in the air for a long time and can stick to household items, such as curtains, furniture, bedding, and carpets.
Hypoallergenic breeds of dogs shed less than others so they may be less likely to cause allergic reactions. However, some
The only sure way to eliminate dog allergies is by avoiding contact with dogs. However, if a person does spend time with dogs, the following home remedies may help them to manage symptoms:
- Using a saline sinus rinse. Rinse the nostrils using a mixture made of 3 teaspoons of salt (iodine free), 1 teaspoon of baking soda, and 8 ounces of warm water. Use an ear dropper to put the solution into the nostril or purchase a sinus rinsing device from a pharmacy or online.
- Plant supplements. Taking certain plant supplements, such as those containing rosmarinic acid, may reduce allergy symptoms according to a 2014 study.
Lifestyle tips that can reduce the impact of dog allergies include:
- avoiding touching eyes or face after contact with dogs
- washing hands with soap after contact with dogs
- avoiding close contact with dogs, such as hugging or kissing them
- using a vacuum cleaner designed to trap and contain airborne allergens
- cleaning the house, washing the bedding weekly, and keeping the house tidy
- cleaning more often during winter months
- restricting dogs to specific rooms or spaces
- keeping dogs out of the bedroom and off furniture
- bathing dogs every 1 to 2 weeks
- wearing a dust mask and gloves while cleaning or in areas with dogs
- brushing and cleaning dogs outdoors when possible
If anyone is considering bringing a dog into their home, they should do an allergy test or undertake a trial period before committing to this.
There are over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medications available that can help reduce or resolve the symptoms for people who are allergic to dogs.
OTC remedies for dog allergies include:
Antihistamines
Antihistamine medications block histamine, a compound that helps initiate local immune responses and cause allergy symptoms. Popular OTC brands for long-term exposure may contain loratadine, cetirizine hydrochloride, or fexofenadine hydrochloride.
Antihistamines can be bought online or obtained on prescription from a doctor.
Nasal decongestants and nasal corticosteroids
These medications help reverse the inflammation caused by immune responses and relieve nasal congestion. Some nasal corticosteroids are now available without a prescription and can be purchased online.
Immunotherapy
An allergist (a specialist in diagnosing allergies) may treat severe or chronic allergy symptoms using immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots.
Immunotherapy involves injecting allergens into a person in gradually increasing amounts. These allergy shots help a person to build a tolerance to allergens. It usually takes several sessions over several months to complete immunotherapy.
Other treatments
Many people with pet allergies also have asthma, and exposure to the pet allergens can cause asthmatic episodes or worsen a persons symptoms. In these situations, a doctor may prescribe inhalable corticosteroids or bronchodilators that help keep the airways open.
Dogs produce a variety of proteins that cause allergies in some people. The highest concentrations of these proteins are in dog saliva, with lower amounts found in dander and urine.
Dander tends to build up on hair follicles, so dog hair usually carries a large number of allergens.
If a doctor thinks that a person may be allergic to dogs, they will refer them to an allergist.
In most cases, an allergist will use a skin-prick test to diagnose allergies.
During a skin-prick test, an allergist will put a droplet containing a tiny amount of dog proteins onto the skin. They will then make a small prick in the skin, allowing the mixture to enter the body.
Most people who are allergic to the mixture will have a response within 15 to 30 minutes.
Sometimes, an allergist will decide that an individual who thinks they are allergic to dogs is actually responding to other allergens commonly found on dogs or dog hair, such as dust or pollen.
People who are allergic to dogs can get relief from symptoms by avoiding dogs and places where there are dogs. Many people choose to manage their symptoms by making lifestyle adjustments, such as more frequent housecleaning, but this can be extremely challenging.
OTC medications, such as antihistamines and nasal decongestants, can also help a person reduce or manage their allergy symptoms.
People with more severe or chronic dog allergies should speak with a doctor about prescription medications and therapies that can help manage symptoms.