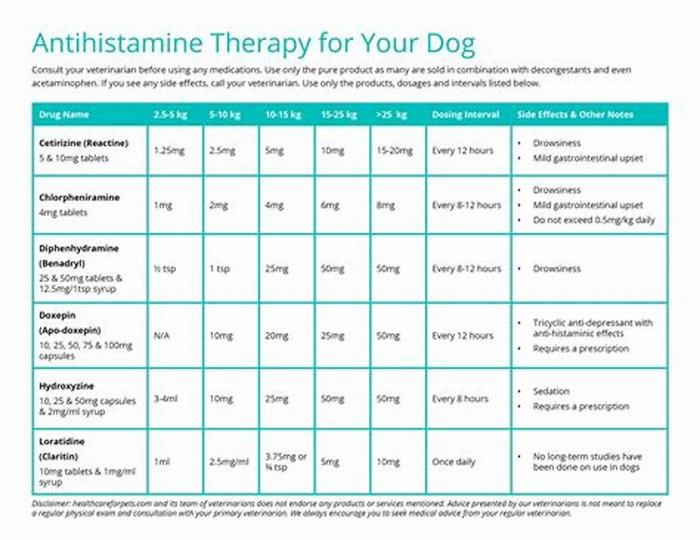
What antihistamine is good for dogs with hives

What to Do When Antihistamines Arent Working for Hives
Antihistamines may not work for some people, depending on the severity of their hives. You may need an increased dosage or a different medication altogether.
After a chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) diagnosis, your doctor will likely prescribe an oral antihistamine to treat your symptoms. However, antihistamines arent always effective.
If youve already tried an antihistamine and you arent seeing results, schedule an appointment with your doctor to learn about possible next steps.
Here are some questions you can ask your doctor at your follow-up appointment and some information about what you might hear in response.
Its hard to say why antihistamines work for some people and not for others. But its not uncommon for antihistamines to be or become ineffective.
Research on the effectiveness of antihistamines for chronic hives has shown a response rate as low as
Antihistamines may stop working because hives can become worse over time or because the intensity of hives can wax and wane over time.
Its also possible that antihistamines become less effective because people arent taking them as prescribed.
Even if you cant identify the cause of your CIU, you may be able to pinpoint triggers that bring on outbreaks or increase the severity of your hives.
See whether any of the following common triggers seem to affect you:
- pets or pet dander
- exposure to extreme heat or cold
- exposure to direct sunlight
- vigorous exercise
- pressure on the skin
- stress or anxiety
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen)
By understanding your personal triggers, you can put yourself in a better position to avoid them.
After seeing little to no results from an antihistamine, your doctor may suggest that you try the following treatments, usually in the following order:
- Higher dose: Sometimes increasing the dose of your current antihistamine can yield better results.
- A different antihistamine or a combination of several different antihistamines. Your doctor may consider switching you to a different antihistamine or putting you on a regimen of two types of antihistamines. For example, they may recommend an H1-antihistamine combined with an H2-antihistamine, which targets different receptors in the body.
- Oral corticosteroids. While doctors usually dont recommend prolonged use of steroids due to potential side effects, they may recommend a short course. This is especially likely if your hives are severe or if theyre accompanied by swelling.
- Cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune): This is an immunosuppressant drug that has led to remission from hives in
50% of cases , according to research. - Omalizumab (Xolair). Your doctor may recommend omalizumab, a medication thats injected once a month if your hives are difficult to treat, but is effective in 80% of cases.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs): Two drugs, zafirlukast (Accolate) and montelukast, might be prescribed in cases of hives caused by Aspirin, and there isnt enough data on their effectiveness on hives overall.
If your medication isnt giving you the relief you need, you can try the following methods to ease itching:
- Moisturize regularly with lotion.
- Use cool water when you shower.
- Apply a cold compress or an ice pack to affected areas.
- Try using over-the-counter creams such as calamine lotion.
- Wear loose clothing made from 100% cotton or 100% silk.
While none of the above methods will treat your CIU, they can at least provide comfort during a flare-up.
Dietary changes to help prevent hives
Researchers are still studying whether changing your diet can impact the severity and duration of CIU flare-ups.
A 2018 preliminary Korean study suggests that an antihistamine diet, where you avoid foods that contain high levels of histamine, may help reduce the severity on an individual level.
Since this and other similar studies only involved a small group of participants, researchers arent ready to draw wide conclusions about the diets success rate.
Even so, it may be worth talking with your doctor to see whether changing your diet is a good option.
No. Hives are never contagious, so you dont need to worry about spreading them to friends, family members, or others who are in close contact.
You also dont have to worry about the hives spreading if you touch other parts of your body after touching your hives.
If youre concerned about what other people will think when they see the welts on your skin, you can ask your doctor to provide a note explaining the nature of CIU and its symptoms. This can be especially useful for school-aged children.
No. While it may be frustrating to learn that antihistamines arent effective at treating your hives, you dont need to worry that they will leave any permanent marks or scars.
Most hives last for no longer than 24 hours and should fade and disappear after that.
While most cases of CIU arent dangerous, there are several warning signs that you should be aware of. Sudden and severe hives can mean youre experiencing an allergic reaction and need urgent medical attention.
If you experience any of the symptoms of anaphylaxis alongside a hives outbreak, call 911 or go to the emergency room:
By definition, chronic means that your hives will last for 6 weeks or more. But theres no way to say for sure exactly how long a specific outbreak episode will last. It could be months or even years.
Each individual welt will probably last for several hours, but theyre often quickly replaced by new ones.
The good news is that CIU can go away, its just hard to predict when.
Should I see an allergist?
If youve already been diagnosed with CIU, your doctor believes the cause is unknown and an allergy isnt to blame. But if you suspect that your doctor overlooked an underlying allergy, you may want to consider seeing an allergist.
What happens if hives dont go away with Benadryl?
Benadryl (diphenhydramine) is an over-the-counter antihistamine that can be used to treat mild allergic reactions, including hives. It is an H1 antihistamine, which means it is one of the ones your doctor may want you to try first. It is also available in higher doses as a prescription if the OTC version doesnt work for you. If its still ineffective, your doctor will likely switch you to H2 antihistamines, other medications, or a combination of drugs.
Why is Benadryl not stopping my allergic reaction?
If there is an ongoing trigger for your hives in your environment, you might continue to develop them or they may worsen even if youre taking an antihistamine like Benadryl. In addition to taking medication, its important to try to identify the trigger and eliminate it. To do this, make an appointment with a dermatologist or allergist for testing, and track your flare-ups. That said, sometimes there is no identifiable cause. Make sure you are taking your medication exactly as prescribed or following the directions on the box of any OTC drug.
If antihistamines dont work for you, dont become discouraged. This happens for certain people and under certain circumstances.
Ask your doctor about possible next steps. Whether that involves a different form of medication or introducing some natural steps to reduce itching, you have options to decrease CIU-related discomfort.
Antihistamines
Typesof antihistamine
There aremany types of antihistamine.
They're usually divided into2 main groups:
They also come in several different forms includingtablets, capsules, liquids, syrups, creams, lotions, gels, eyedrops and nasal sprays.
Which type is best?
There'snot muchevidence to suggest any particularantihistamine is better than any other at relieving allergy symptoms.
Some people findcertain types work well for them and others do not. You may need to try several types to find one that works for you.
Non-drowsy antihistamines are generally the best option, as they're less likely to make you feel sleepy. But types that make you feel sleepy may be better if your symptoms stop you sleeping.
Ask a pharmacist for advice if you're unsure which medicine to try as not all antihistamines are suitable for everyone.
Howto take antihistamines
Take your medicine as advised by the pharmacist or doctor, or as described in the leaflet that comes with it.
Before taking an antihistamine, you should know:
- how to take it including whether it needs to be taken with water or food, or how to use it correctly(ifeyedrops or a nasal spray)
- how much to take (the dose) this can vary depending on things such as your age and weight
- when to take it including how many times a day you can take it andwhen to take it (some types shouldbe taken before bedtime)
- how long to take it for some types can be used for a long time, but some are only recommended for a few days
- what to do if you miss a dose or take too much (overdose)
The advice varies depending on the exact medicine you're taking. If you're not sure how to take your medicine, ask a pharmacist.
Sideeffects of antihistamines
Like all medicines, antihistamines can cause side effects.
Side effects of antihistamines that make you drowsy can include:
- sleepiness (drowsiness) and reduced co-ordination, reaction speed and judgement do not drive or use machinery after taking these antihistamines
- dry mouth
- blurred vision
- difficulty peeing
Side effects ofnon-drowsy antihistamines caninclude:
- headache
- dry mouth
- feeling sick
- drowsiness although this is less common than witholder types of antihistamines
Check the leaflet that comes with your medicine for a full list of possible side effects and advice about when to get medicalhelp.
If you think your medicine has caused an unwanted side effect, you can report it through the Yellow Card Scheme.
Takingantihistamines with other medicines, food or alcohol
Speak toa pharmacist or GP before taking antihistamines if you're already taking other medicines.
There may be a risk the medicines do not mix, which could stop either from working properlyor increase the risk of side effects.
Examples of medicines thatcouldcause problems if takenwith antihistamines include some types of:
Try not to drink alcohol while taking an antihistamine, particularly if it's a type that makes you drowsy,as it can increase the chances of it making you feel sleepy.
Food and other drinks do not affect most antihistamines, but check the leaflet that comes with your medicine to make sure.
Whocan take antihistamines
Most people can safely take antihistamines.
But speak to a pharmacist or GPfor adviceif you:
Some antihistamines may not be suitable in these cases. A pharmacist or doctor can recommend one that's bestfor you.
Loratadine is usually recommended if you need to take an antihistamine in pregnancy. Loratadine or cetirizine are usually OK to take while breastfeeding.
Always check the leaflet that comes with yourmedicine to see if it's safe for you before taking it or giving it to your child.
Howantihistamines work
Antihistamines block the effects of a substance called histamine in your body.
Histamine is normally released when your body detects something harmful, such as an infection. It causes blood vessels to expand and the skin to swell, which helpsprotect the body.
But in people with allergies, the body mistakes something harmless such as pollen,animal hair or house dust for a threat and produces histamine. The histamine causes an allergic reaction with unpleasant symptoms including itchy, watering eyes, a running or blocked nose, sneezing and skin rashes.
Antihistamines help stop this happening if you take them beforeyou come into contact with the substance you're allergic to. Or they can reduce the severity ofsymptoms if you take them afterwards.
Find out more about your medicine
The leaflet that comes in the packet with your medicine will have detailed information about it, including how to take it and what side effects you might get.
If you no longerhave the leaflet that came with your medicine, you can search for an online versionof it using our medicines A to Z.
You may also find information on individual antihistamines onthese websites:
Page last reviewed: 16 May 2023 Next review due: 16 May 2026
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives (the common term for urticaria), are pink or red itchy rashes, that may appear as blotches or raised red lumps (wheals), on the skin. They range from the size of a pinhead to that of a dinner plate. When hives first start to appear, they can be mistaken for mosquito bites. Swellings usually disappear within minutes to hours in one spot, but may come and go for days or weeks at a time, sometimes longer. In most cases hives are not due to allergy and they can be effectively treated with a non-drowsy antihistamine. When hives occur most days for more than six weeks this is defined as chronic (ongoing) urticaria, which may require additional medication.
![]() ASCIA PCC Hives Urticaria 2021131.12 KB
ASCIA PCC Hives Urticaria 2021131.12 KB
Hives occur in the skin and are common
Up to 20% of people will develop hives at some time during their life. In most cases, hives are not due to allergy. Underneath the lining of the skin and other body organs (including the stomach, lungs, nose and eyes) are mast cells. Mast cells contain chemicals including histamine. When these are released into the skin they irritate nerve endings to cause local itch and irritation and make local blood vessels expand and leak fluid, triggering redness and swelling.
Can hives occur anywhere else?
Hives can also cause deeper swellings in the skin and mucosa, this is called angioedema. These swellings are often bigger, last longer, may itch less, sometimes hurt or burn and respond less well to antihistamines. Large swellings over joints, for example, can cause pain that feels like arthritis, even if the joint is not involved. Angioedema most frequently affects the face and lips. Although hives and facial swelling can be uncomfortable and cosmetically embarrassing, theyare not usually dangerous. Information on angioedema is available on the ASCIA website.
Hives are rarely due to a serious underlying disease
Whilst a clear cause of hives in not obvious in many cases, causes may include:
- Infection from a virus is the most common cause of hives in children, especially if they last for more than 24 hours.
- Contact allergy to plants or animals may cause localized hives.
- Allergic reactions to food, medicines or insect stings can appear as hives. They usually occur within one to two hours of exposure and disappear in most cases within six to eight hours.
An allergic cause for hives should be suspected if episodes are rare, short-lived and occur under specific circumstances, for example:
- Only when exercising.
- Always within two hours of a meal.
- When symptoms involving other organs occur around the same time, such as stomach pain, vomiting, difficulty breathing or dizziness.
- If hives occur with swelling of the tongue or throat, difficulty breathing or low blood pressure, anaphylaxis should be suspected. Urgent administration of adrenaline and medical assessment is required. Information about anaphylaxis is available on the ASCIA website.
Ongoing hives lasting days at a time are almost never allergic in origin, with the exception of some cases of allergy to medicines. Stress is a very rarely the cause of hives but may make the symptoms worse.
In some people hives are caused by physical triggers, including cold (such as cold air, water or ice), heat, sunlight (solar), vibration, rubbing or scratching of the skin (dermatographism), and delayed pressure (such as after carrying heavy bags. In other people, exercise (sweating), stress, alcohol, spicy food or coffee may cause symptoms.
Chronic urticaria is defined when hives occur most days for more than six weeks
Symptoms of chronic urticaria usually resolve, although this can take months or several years. Most people with chronic urticaria manage with appropriate doses of non-drowsy antihistamines. People with severe symptoms interfering with quality of life may be referred to a clinical immunology/allergy specialist or dermatologist for assessment and consideration of additional medications.
Most people with hives do not need tests
Tests are sometimes done when hives go on for long periods, or when unusual symptoms are occurring around the same time. This is to exclude other diseases, which may appear as hives first, and other conditions later. If hives are associated with high fever, bruising, bleeding into the skin, purple lumps that last for several days, or sore joints, a doctors appointment should be arranged promptly.
Allergy testing is performed when the history suggests an allergic cause.
Treatment of hives
Whilst most hives resolve within a couple of weeks without any specific treatment, the following treatments may be useful:
- Avoid aggravating factors such as avoiding excessive heat, spicy foods or alcohol.
- Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)should be avoided as they often make symptoms worse.
- Medications like non-drowsy antihistamines are often used to reduce the severity of the itch. Severe throat swelling requires early use of adrenaline and attention by your doctor or treatment in hospital.
- Severe chronic urticaria sometimes requires a trial of medicines which reduce inflammation, often called immune modulators or immunosuppressive medications. Recurrent courses of cortisone/steroid tablets need to be avoided due to a significant risk of side effects.
- Special diets appear to have a limited role to play in the management of hives. Unfortunately, it is difficult to predict who will, or will not respond to diet on the basis of history or allergy testing. A temporary elimination diet under close medical supervision, followed by challenges may be useful in a small number of cases.
For patient support organisations goto www.allergy.org.au/patients/patient-support-organisations
ASCIA 2021
ASCIA is the peak professional body of clinical immunology/allergy specialists in Australia and New Zealand.
ASCIA resources are based on published literature and expert review, however, they are not intended to replace medical advice. The content of ASCIA resources is not influenced by any commercial organisations.
For more information go towww.allergy.org.au/patients/skin-allergy
To support allergy and immunology research go to www.allergyimmunology.org.au/donate
Updated March 2021