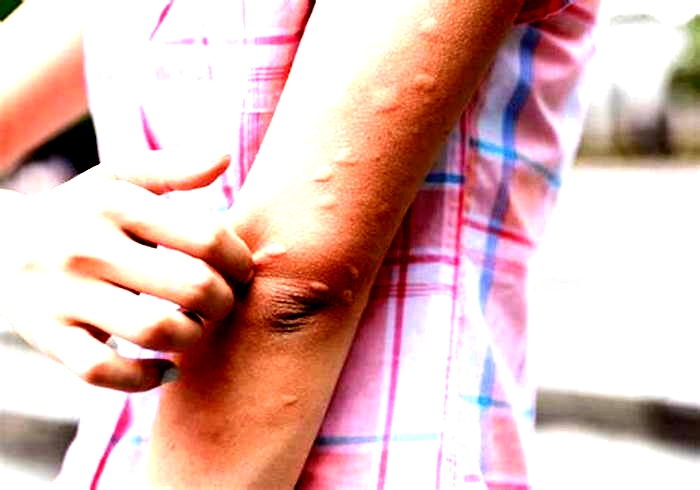
What can you catch from a dog scratch

Health Risks of a Dog Scratch
Dogs are among the most popular animal companions. In fact, its estimated that dogs live in about
Still, as with having any other pet, its important to be aware of the variety of diseases and health risks that may be transmitted from your canine companion. Some of these health risks may be derived from dog scratches that arise from playing, feeding, and coming into contact with an unknown animal.
Not all dog scratches are serious, but its important to be on the lookout for possible signs of infection, and call a doctor to rule out more serious health consequences.
Read on to learn about possible health risks from dog scratches and how to treat and prevent them.
Daily interactions with your dog including playtime can sometimes result in scratches. These might occur from your dogs nails when they step on you or jump up on you, as well as accidentally scratching you with their teeth while playing fetch or during feedings.
When you get scratched by a dog, you may notice red marks on your skin. These may temporarily become painful and swollen and, in more severe cases, lead to more serious health risks. Possibilities may include:
- excessive bleeding
- infections, such as Capnocytophaga bacteria
- tetanus, which is caused by Clostridium tetani bacteria
- rabies, a serious viral infection
- sepsis, a life-threatening emergency caused by the spread of an infection to vital organs
Any dog scratch including those that seem mild and harmless ought to be treated immediately to prevent infection and other health complications. Consider the following steps:
- First, wash (but dont scrub) the dog scratch wound with warm water and soap. Rinse for at least 5 minutes. Pat dry with a clean towel.
- If the dog scratch is bleeding, apply pressure to the area with a clean gauze pad.
- Apply an over-the-counter (OTC) antibiotic cream or ointment.
- Cover the wound with a sterile bandage.
Some dogs carry a bacteria in their mouths called Capnocytophaga. While these bacteria
Capnocytophaga infections can progress quickly, even becoming life-threatening. Possible symptoms
- swelling
- redness and blisters
- pus from the bite
- fever
- headache
- muscle or joint aches
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Call or visit a doctor if youre experiencing any signs of infection post-dog scratch. Its also a good idea to seek medical attention any time youve been scratched by a dog especially if the dog isnt your own.
Rabies is a type of viral infection that can occur when bitten by an animal thats infected. This is a serious infection that can be fatal in both animals and humans, due to the viruss attack on the nervous system.
While animal-to-animal transmission is possible, its not as common for humans to be infected by household pets in the United States. Part of this reduced risk is attributed to rabies vaccines in domesticated animals.
Still, rabies ought to be considered in the case of a serious wound from a dog, particularly if its a stray dog or one who hasnt been vaccinated against rabies. The virus may be transmitted through an infected dogs saliva from biting or accidental scratching.
How a dog with rabies may behave
A dog who is infected with rabies may have
- behavioral changes
- reduced appetite
- voice changes/changes to their barks
- panting
- anxiety and restlessness
- attempted attacks on people and other animals
- paralysis
What to do if you suspect youve been bitted by a dog with rabies
If youve been bitten or scratched by a dog with an unknown rabies vaccination status, call a doctor. They may recommend treatment with rabies vaccines as well as antibodies.
Humans (with the exception of veterinarians and other professionals who handle animals) dont typically get the rabies vaccine unless theyve been exposed to the virus from an infected animal.
Symptoms of a rabies infection
Symptoms of rabies are slow to develop,
Possible signs of rabies in humans may include:
- fatigue
- fever
- headache
- weakness
- anxiety
- hallucinations, and other neurological changes
While its not always possible to avoid all cases of dog scratches, you may help minimize your risk of getting sick by:
- washing your hands after playing with and feeding your dog
- carefully washing scratches that do occur
- bandaging dog scratches and any subsequent open wounds
- keeping your dog up-to-date on their vaccines
- avoiding contact with other dogs that may be feral or unvaccinated
- walking your dog on a leash to prevent exposure to wild animals
- asking your doctor if youre up to date on your vaccines
Also, if you have your own dog, you may help reduce the risk of scratches from toenails and bites by training your dog not to jump up on you, and to use their mouths softly during playtime and feedings.
Getting scratched by your dog can happen, especially during feeding and playtime. While you can train your dog to be more gentle, occasional scratches are still inevitable. Your risk may also be greater when coming into contact with a wild dog, or a domesticated one whos not your own.
Washing a dog scratch wound is critical in preventing infections. Depending on the severity of the wound, you may consider calling your doctor regarding next steps.
Seek medical care if youre injured by a dog who isnt yours, if youve been bitten, are bleeding excessively, or are experiencing flu-like symptoms.
How is rabies transmitted?
Rabies virus is transmitted through direct contact (such as through broken skin or mucous membranes in the eyes, nose, or mouth) with saliva or brain/nervous system tissue from an infected animal.
People usually get rabies from the bite of a rabid animal. It is also possible, but rare, for people to get rabies from non-bite exposures, which can include scratches, abrasions, or open wounds that are exposed to saliva or other potentially infectious material from a rabid animal. Other types of contact, such as petting a rabid animal or contact with the blood, urine or feces of a rabid animal, are not associated with risk for infection and are not considered to be exposures of concern for rabies.
Other modes of transmissionaside from bites and scratchesare uncommon. Inhalation of aerosolized rabies virus is one potential non-bite route of exposure, but except for laboratory workers, most people wont encounter an aerosol of rabies virus. Rabies transmission through corneal and solid organ transplants have been recorded, but they are also very rare. There have only been two known solid organ donor with rabies in the United States since 2008. Many organ procurement organizations have added a screening question about rabies exposure to their procedures for evaluating the suitability of each donor.
Bite and non-bite exposures from an infected person could theoretically transmit rabies, but no such cases have been documented. Casual contact, such as touching a person with rabies or contact with non-infectious fluid or tissue (urine, blood, feces), is not associated with risk for infection. Contact with someone who is receiving rabies vaccination does not constitute rabies exposure, does not pose a risk for infection, and does not require postexposure prophylaxis.
Rabies virus becomes noninfectious when it dries out and when it is exposed to sunlight. Different environmental conditions affect the rate at which the virus becomes inactive, but in general, if the material containing the virus is dry, the virus can be considered noninfectious.
What to Do If a Dog Scratches You
Many people know about cat scratch fever, but can a dog scratch be just as dangerous? Although you are less likely to contract severe illness from a dog scratch, there is still a possibility of it happening. If you are scratched by a dog, heres what you need to know.
Potential Infections Can Occur from a Dog Scratch
Dogs walk on all four feet and dig in whatever they can find, which means dog nail beds are very dirty. They can harbor all sorts of bacteria and fungi that can readily infect humans through broken skin, including tetanus. Dogs also lick their paws, transferring bacteria from the mouth onto the nails. This can, in rare cases, infect humans with MRSA or bacteria called Capnocytophaga if the scratch breaks the skin.
What About Rabies?
Can I get rabies from a dog scratch? is a popular online search. Even though it is highly unlikely that a human will contract rabies from an animal scratch, it can still happen. The virus that causes rabies is spread through contact with saliva or brain tissue from an animal infected with rabies, but it cannot penetrate unbroken skin. If a rabid dog with saliva-covered nails scratches a human, theoretically infection can occur; however, most dogs are vaccinated against rabies and are not at risk for infection. If your dog has had contact with a rabid animal, take additional precautions and seek veterinary care immediately.
How to Treat a Dog Scratch
Animal scratches may seem harmless, but they can turn into serious infections if the skin is broken. Puncture wounds may look the least serious, but they carry the highest risk of severe infection. If the scratch is bleeding heavily, apply pressure with a clean towel until the bleeding has stopped. Once the bleeding has subsided, wash the wound thoroughly with soap and water for three minutes. Clean and dry the skin, and then apply a small amount of antibiotic ointment and cover the wound with a bandage. Make sure to check the scratch for signs of infection, which include increased heat, redness, swelling, pain or red streaking on the skin. Monitor the wound for at least 72 hours, and if you experience any of those symptoms, seek the attention of a medical professional immediately.
WRITTEN BY
Sarah Wooten, DVMVeterinarian
Dr. Sarah Wooten graduated from UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine in 2002. A member of the American Society of Veterinary Journalists,...
Do you need a tetanus shot for a dog scratch? A Step-by-Step Guide
What to Do:
- the wound is on the face, neck, hand, foot, or near a joint
- the wound wont stop bleeding after 10 minutes of direct pressure
- the wound appears to be deep, large, or severe
- the attacking animal was stray or wild or behaving strangely
- the bite or scratch has pus coming from it, or becomes red, hot, swollen, or increasingly painful
- your child has a weakened immune system or other medical condition that might make an infection more likely
- your childs tetanus immunizations are not up to date
Teach your children to stay away from strange animals, and not to tease or provoke any animals, even family pets. Animals should not be disturbed while they are eating or sleeping.
If you own a pet, make sure its properly immunized and licensed.
Signs of an infection from a scratch wound
While your dog scratch wound heals, look for the following possible signs of an infection:
See a doctor if you notice any signs of infection from a dog scratch.
Some dogs carry a bacteria in their mouths called Capnocytophaga. While these bacteria rarely spread to people, theres still a chance of getting sick from exposure to an animals saliva, especially if you have a weakened immune system.
Capnocytophaga infections can progress quickly, even becoming life-threatening. Possible symptoms related to this type of infection include:
Call or visit a doctor if youre experiencing any signs of infection post-dog scratch. Its also a good idea to seek medical attention any time youve been scratched by a dog especially if the dog isnt your own.
In the case of a dog bite, you should seek medical care to rule out the risk of rabies and other potentially life-threatening diseases.
Rabies is a type of viral infection that can occur when bitten by an animal thats infected. This is a serious infection that can be fatal in both animals and humans, due to the viruss attack on the nervous system.
While animal-to-animal transmission is possible, its not as common for humans to be infected by household pets in the United States. Part of this reduced risk is attributed to rabies vaccines in domesticated animals.
Still, rabies ought to be considered in the case of a serious wound from a dog, particularly if its a stray dog or one who hasnt been vaccinated against rabies. The virus may be transmitted through an infected dogs saliva from biting or accidental scratching.
Can you get tetanus from dog scratch?
Potential Infections Can Occur from a Dog Scratch
Dogs walk on all four feet and dig in whatever they can find, which means dog nail beds are very dirty. They can harbor all sorts of bacteria and fungi that can readily infect humans through broken skin, including tetanus.
When to get a Tetanus Shot | Can you get Tetanus from a Scratch
Animal bites and scratches are extremely common, although often overlooked in terms of potential severity. Even a minor bite or scratch from an animal of any kind can become infected with bacteria that may be harmful, occasionally leading to serious complications. While scratches and bites may not look angry or infected, this is not to say that they dont come along with plenty of risksincluding the risk of tetanus.
As one might expect, animal bites and scratches can occur at any time and are highly dependent upon circumstance. Dog bites, for example, are common and account for 98% of rabies cases reported worldwide. Cat scratches and bites are equally common, and despite what many may think, theyre actually more likely to result in infection than dog bites.
Finally, scratches and bites from wild animals such as raccoons, coyotes, skunks, foxes and batsall of which are cause for concernoccur regularly and should always be addressed by a medical professional no matter how mild or severe they may be.
Symptoms of animal bites and scratches can vary quite dramatically depending upon the severity of the incident. These may include the following:
The first step in diagnosing an animal bite or scratch is for you and your treating provider to have a discussion about exactly how the injury happened. From there, an approach to treatment will be discussed. The wound will most commonly be cleaned and dressed to avoid any potential for infection (wounds missing skin or those that are particularly deep may require special dressings). Stitches may also be employed if necessary. Antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce the risk of infection.
In the case that the affected person is not up to date on their tetanus shot, a vaccine may be administered as a prophylactic.
Children who experience symptoms after suffering an animal bite or scratch should be seen by a treating provider as soon as possible after the injury. For children that have not been vaccinated, a tetanus shot may be provided.
At ConvenientMD, we encounter animal bites and scratches numerous times each and every day. While many can be treated quickly and efficiently, complications do arise and can only be avoided when injuries are addressed as soon as possible. If you or a family member has been bitten or scratched, were here to help.
Ready to get treated? Just stop into any of our convenient urgent care locations in New Hampshire, Maine, and Massachusettsyoull never need to make an appointment ahead of time.