What do autoimmune hives look like
Hives: Pictures, Causes, and How to Treat Them
Hives typically occur as an allergic response to something in your environment or something you ate. But they may sometimes happen because of an underlying health issue.
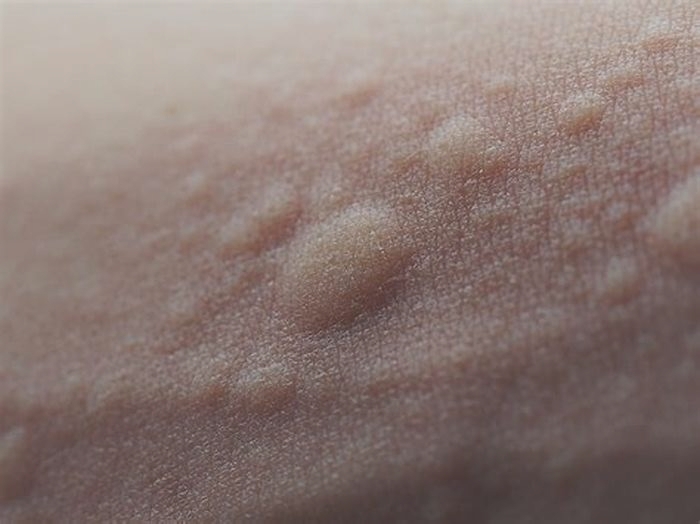
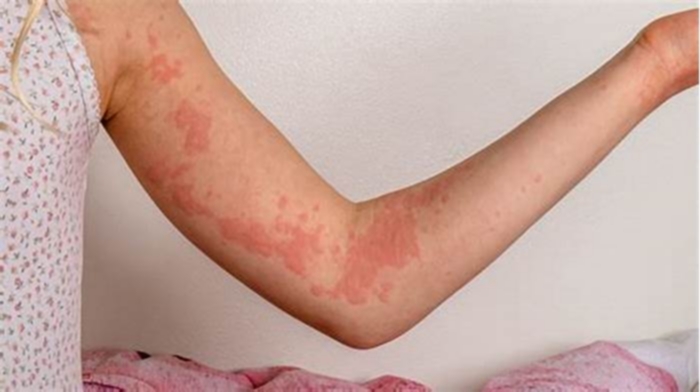
Hives, also known as urticaria, are itchy, raised welts that are found on the skin. Theyre usually red, pink, or flesh colored on lighter skin and may be flesh colored or slightly lighter or darker than your skin tone on brown or black skin.
Sometimes they sting or hurt. In most cases, hives are caused by an allergic reaction to a medication or food or are a reaction to an irritant in the environment.
In many cases, hives are an acute (temporary) problem that may be alleviated with allergy medications. Most rashes go away on their own. However, chronic (ongoing) cases, as well as hives accompanied by a severe allergic reaction, are larger medical concerns.



Hives are usually caused by an
In some people, histamines can cause swelling, itching, and many of the symptoms that are experienced with hives. In terms of allergens, hives can be
Hives might also be caused by circumstances besides allergies. Its not uncommon for people to experience hives as the result of stress, tight clothes, exercise, illnesses, or infections.
Its also possible to develop hives as the result of excessive exposure to hot or cold temperatures or from irritation due to excessive sweating. Because there are several potential triggers, many times the actual cause of hives cant be determined.
People who are known to have allergies are more likely to get hives. You may also be at risk of developing hives if youre taking medication or if youre unknowingly exposed to things you may be allergic to, such as food or pollen. If youre already ill with an infection or a health condition, you may be more vulnerable to developing hives.
The most noticeable symptom of hives is the welts that appear on the skin. Welts may be red but can also be the same color as your skin. They can be small and round, ring-shaped, or large and of random shape. Hives are itchy, and they tend to appear in batches on the affected part of the body. They can grow larger, change shape, and spread.
Hives may disappear or reappear over the course of the outbreak. Individual hives welts can last anywhere from
Hives can occur in a variety of places on the body. Call 911 or get medical attention immediately if you develop a hives outbreak around your throat or on your tongue or have trouble breathing along with hives.
Hives can occur in response to an allergic reaction or may not have an identifiable cause.
Allergic reactions
The most common causes of hives are allergic reactions. These can be caused by any allergen you might be sensitive to, including:
- foods (such as nuts, milk, and eggs)
- pet dander
- pollen
- dust mites
- insect bites or stings
- medications (primarily antibiotics, cancer drugs, or ibuprofen)
Mild cases of hives caused by allergies are typically treated with long- or short-term allergy medications and avoidance of the trigger.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life threatening allergic reaction. In this condition, hives are often
Chronic hives
Chronic hives are ongoing cases that dont necessarily have an identifiable cause. Also called chronic urticaria, this condition is marked by recurring hives that can interfere with your daily life. Chronic cases
You may suspect chronic hives if you have welts that dont go away within 6 weeks. While not life threatening, this form of hives can be uncomfortable and difficult to treat. Chronic hives may also be a symptom of an
- an autoimmune disorder
- celiac disease
- lupus
- type 1 diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis
- thyroid disease
Dermatographism
This form of acute hives is considered mild. Excessive scratching or continuous pressure on the skin causes it. Dermatographism usually clears up on its own in a short period of time without treatment.
Temperature-induced hives
Sometimes changes in temperature can induce hives in people who are sensitive to such changes. Cold-induced hives may occur from cold water or air exposure, while body heat from physical activity may cause exercise-induced hives. Exposure to sunlight or tanning beds may also bring about solar hives in some people.
Infection-induced hives
Both viral and bacterial infections can cause hives. Common bacterial infections causing hives include urinary tract infections and strep throat. Viruses that cause infectious mononucleosis (mono), hepatitis, and colds often cause hives.
The first step in getting treatment is to figure out if you actually have hives. In most cases, a doctor will be able to determine if you have hives from a physical exam. Your skin will show signs of the welts that are linked with hives.
A doctor may also perform blood tests or skin tests to find out what may have caused your hives especially if your hives were the result of an allergic reaction.
You may not need prescription treatment if youre experiencing a mild case of hives not related to allergies or other health conditions. In these circumstances, a doctor might suggest that you find temporary relief by:
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency that needs to be treated immediately by a physician. If you think you may be experiencing anaphylaxis, contact 911 or your local emergency services.
Simple changes to your lifestyle may be able to help you prevent hives from reoccurring in the future. If you have allergies and you know which substances are likely to cause an allergic reaction, a doctor will suggest that you avoid any possible exposure to these factors. Allergy shots are another option that may help you reduce the risk of experiencing hives again.
Avoid being in high humidity areas or wearing tight clothing if you have recently had a hives outbreak.
Below are some of the most commonly asked questions about hives.
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious and cant spread from one person to another.
Do hives mean Im allergic to something?
In many cases, hives are the result of an allergic reaction to something you have been exposed to, such as certain medications or pollen. It could also be caused by an infection, stress, or wearing clothes that are too tight. If you have hives that persist for more than a few days, contact a doctor to see if an allergy test is needed to determine the cause of your symptoms.
How long do hives last?
A hives outbreak can last anywhere from
Are there any home remedies for hives?
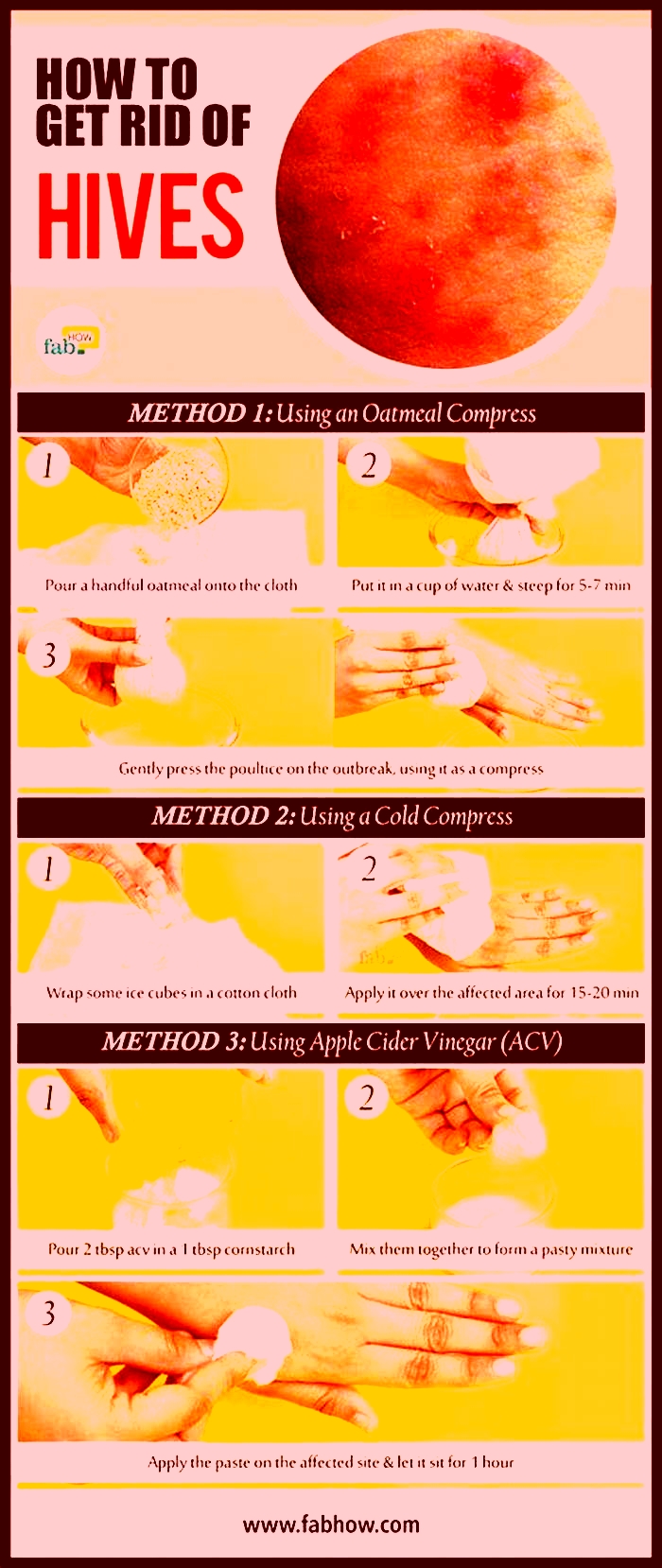
Yes, there are several home remedies that may help alleviate the symptoms of hives. Taking an antihistamine is one option, as well as taking a cool or lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal or baking soda. Avoid hot water, as this may aggravate the hives. Also, try to avoid any potential irritants or allergens that may have caused the hives in the first place.
Although hives can be itchy and uncomfortable, usually theyre not severe and will disappear after a period of time. However, be aware that as some hives go away, new ones may pop up.
Mild cases of hives are considered harmless. Hives can be dangerous if you are having a serious allergic reaction and your throat is swelling. Prompt treatment for a severe case of hives is important for a good outlook.
What Do Autoimmune Rashes Look Like?
An autoimmune disease occurs when your bodys immune system attacks healthy cells within the body. This dysfunctional immune response may lead to various symptoms, like hair loss, skin rash, or even joint pain. When the body mistakenly targets skin cells, you may develop an uncomfortable or concerning rash.
I work with patients suffering from autoimmune disease on a daily basis. Because 5-8% of Americans are likely to experience an autoimmune skin disorder at some point and women are especially at risk (thanks, genetics), I find that its easiest to inspect a rash a patient presents with to determine whats behind it.
The most common autoimmune diseases that may cause rashes include:
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Lupus
- Sjogrens syndrome
- Dermatomyositis
- Hypothyroidism & myxedema
- Celiac disease
- Scleroderma
- Lichen planus
- Behets disease
What Does an Autoimmune Rash Feel Like?
Some of the symptoms most common to autoimmune rashes are:
- Inflamed, red skin: Like with any rash, your skin may turn red or otherwise discolored (some autoimmune rashes are more purple or brown in color) and feel warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Itch: Some, though not all, rashes associated with autoimmune disease cause an urge to itch.
- Pain or discomfort: Some rashes may hurt or feel tender when touched, while others may cause persistent discomfort.
- Varied shapes, sizes, and rash patterns: If you have an autoimmune rash, you may observe its size or shape change. Rash patterns vary and may also morph over time.
What Causes an Autoimmune Rash?
Various types of autoimmune activity may cause any number of rashes. There are several factors that may lead to autoimmune disease and dysregulated immune responses, such as:
- Genetics: Like many conditions, a genetic predisposition to autoimmune disease increases the likelihood you will develop autoimmunity. The more blood relatives you have who suffer from these diseases, the higher your chances will be.
- Hormones: Your hormonal makeup impacts the way your immune system functions. Major changes to hormone levels, like those that occur during menopause and pregnancy, can trigger autoimmunity and related skin rashes. Thats one reason females are more likely than males to have autoimmune issues.
- Mental health: Particularly if you already have an autoimmune condition, anxiety, stress, or other mental health concerns may trigger flare-ups. Your gut and brain are closely connected, so significant changes to your mental health or nervous system function play a part in autoimmune responses.
- Environmental triggers: If youre sensitive to certain chemicals in everyday items such as detergent, body wash, or makeup, these chemicals may increase your likelihood of developing an autoimmune rash.
Lets take a look at the specific autoimmune conditions that are most likely to cause a rash and how these rashes may present.
Psoriasis


Psoriasis is the most common autoimmune skin rash, presenting as scaly, dry, and often red skin. Psoriasis can show up anywhere on the body but most commonly affects the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp. Its likely to cause itching and pain or sensitivity to the touch. As much as possible, avoid scratching these patches of scaly skin, which may cause bleeding and lead to infection.
Eczema

Eczema is an itchy skin condition that affects children more than adults. Though eczema often goes away after puberty, it can persist into adulthood. Some eczema attacks are contact dermatitis, caused by exposure to a chemical irritant or an allergic reaction. However, the most common form of eczema is atopic dermatitis, caused by genetics and/or autoimmune disease. Many people experience atopic dermatitis, asthma, and hay fever together.
If you have eczema, you may experience rashes all over your body, especially on the hands, feet, arms, legs, elbow, knees, scalp, and the back of the neck.
Lupus

Among other symptoms, two-thirds of lupus patients will develop a skin condition. Skin disease in lupus may present as rashes, sores, lesions, or cherry angiomas a bright red, raised patch of skin. Up to 70% of lupus cases are worsened by sun exposure or extended time under fluorescent lights. Many lupus-related rashes will appear in sun-exposed areas of the skin, often a butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks.
Cutaneous lupus refers to a form of lupus that only affects the skin. (When people say lupus, theyre usually talking about systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), which is different from cutaneous lupus.) You can have multiple forms of lupus or only one form.
Neonatal lupus is a very rare condition that affects infants of mothers who have some form of lupus. At birth, the infant may exhibit a skin rash, low blood cell count, liver problems, or a slow heartbeat.
Sjgrens Syndrome

Sjgrens syndrome is an autoimmune disease that most frequently causes dry eyes and dry mouth. Its most common in women over the age of 40, and it can cause multiple skin problems, such as:
- Dry, rough skin (AKA xerosis)
- Blood spots on your legs (AKA purpura) due to blood vessel inflammation (AKA vasculitis)
- Purple-to-red skin rash that does not lighten under pressure
- Red, ring-shaped skin lesions around a pale center (AKA annular erythema)
If you experience purpura or annular erythema, schedule a visit with your doctor or dermatologist right away.
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a very rare autoimmune disorder that can cause:
- Red or purple skin rash on a sun-exposed area
- Calcium deposits underneath your skin (AKA calcinosis)
- Inflammation around your fingernails
- Muscle weakness
- Trouble swallowing (AKA dysphagia)
- Difficulty talking
- Fatigue
Dermatomyositis-related skin rashes most often occur in these 8 parts of the body:
- Eyelids
- Nose
- Cheeks
- Back
- Upper chest
- Elbows
- Knees
- Knuckles
Individuals who experience skin rash but not muscle weakness likely suffer from amyopathic dermatomyositis, also called dermatomyositis sine myositis.
Read Next: What Is Methylene Blue?
Hypothyroidism & Myxedema

Severe, untreated hypothyroidism may lead to myxedema, which either means severely advanced hypothyroidism or skin problems related to severely advanced hypothyroidism. Myxedema leads to skin changes, though these may not technically be considered rashes. Myxedema may result in swelling and thickening of your skin.
Myxedema and severe hypothyroidism require immediate treatment and management. Myxedema crisis is when the body no longer tolerates the severe hypothyroidism symptoms. Your body starts to shut down. Myxedema crisis may result in coma, seizures, and death.
Call your doctor or emergency services immediately if you believe youre having a myxedema crisis.
Celiac Disease

Although celiac disease most frequently triggers gastrointestinal distress, it can also trigger an autoimmune rash called dermatitis herpetiformis, an itchy, blistering rash on your skin. This usually appears on the elbows, knees, or buttocks.
Fewer than 10% of individuals with celiac experience both skin problems and the more common digestive symptoms. More often than not, patients have only one or the other.
Scleroderma

Also known as systemic sclerosis, scleroderma is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your own healthy tissues, namely, the skin. When you have scleroderma, your skin changes in appearance and feel, due to increased collagen production. It may become shiny and thicker.
Morphea is sometimes synonymous with scleroderma, but morphea is actually a severe type of scleroderma. Morphea specifically refers to oval-shaped areas of thick, red skin.
Lichen Planus
Oral lichen planus is an autoimmune disease that may trigger swelling and irritation on your skin, scalp, nails, genitals, and mucous membranes. Lichen planus typically causes purple, itchy, flat bumps on the skin. It may also result in lacy-white lesions in the mouth.
Behets disease

Behets disease is a very rare autoimmune disorder that leads to blood vessel inflammation (vasculitis).
Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
Weve been talking a lot about skin rashes. However, some autoimmune conditions can cause skin blistering, too.
Also known as autoimmune bullous diseases, the most common autoimmune diseases that can cause blistering are:
- Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
- IgA-mediated bullous dermatoses
- Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Pemphigus
When to Call Your Doctor
Its always advisable to keep an eye on a new rash. Here are some signs that you should see a healthcare professional:
- Sudden onset of a new rash
- Fever
- Pain
- Blisters
- Swelling
- Discharge
- Bruising
- A bad smell
- The rash area is spreading
FAQs
What autoimmune diseases cause an itchy rash?
Some autoimmune diseases that may cause an itchy rash are cutaneous lupus, oral lichen planus, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
Certain conditions are also known for causing scalp itch, including:
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Lichen planus
- Lupus
- Scleroderma
- Sjgrens syndrome
Why do autoimmune conditions cause a rash?
Autoimmune conditions may cause a rash because they trigger inflammation in skin cells. These diseases are often characterized by chronic inflammation in your internal organs, your skin, and everywhere in between.
How long does an autoimmune rash last?
Autoimmune rashes last varying lengths of time based on the type of rash and the autoimmune disease that caused it. Some rashes can go away after a few days, while others may last up to years.
What do autoimmune rashes look like?
Autoimmune rashes can look like scaly red patches, purplish bumps, or more. The appearance of autoimmune rashes will be different, depending on which autoimmune condition is triggering the skin rash.For example, cutaneous lupus may cause a scaly red patch that does not hurt or itch. Scalp psoriasis may cause plaque buildup that results in hair loss. Lichen planus may cause purplish, itchy, flat bumps on your skin.
What autoimmune conditions may cause hives?
Autoimmune hives are itchy red bumps or welts often caused by allergic reactions. An overactive immune system can also cause them. Autoimmune diseases that may cause hives are:
- Lupus
- Sjgrens
- Celiac disease
- Type 1 diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Vitiligo
How will my doctor test for autoimmune disease?
No single test is designed to test for all autoimmune diseases. If youre seeking a diagnosis, several blood tests can help your healthcare provider determine if you have an autoimmune disease.
Here are 4 common diagnostic tests for autoimmune disease:
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA)
- Autoantibodies
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Will I need a skin biopsy? Your doctor may recommend a biopsy to learn more about a new rash. This is to rule out bacterial or fungal infections, cancer, or other skin conditions.
What to Do About Autoimmune Rashes
The best way to treat autoimmune rash (and autoimmune disorders in general) is to identify and treat the underlying cause. There are many possible causes of autoimmunity. For immediate relief, over-the-counter corticosteroid creams may help with discomfort. For a long-term solution, talk to a healthcare provider near you about the best approach to treatment and management.
If youre in Colorado, come see us at PrimeHealth! We spend 1-2 hours at each appointment with our patients to thoroughly understand their unique needs and circumstances.