What foods flush out histamine
How the low histamine diet works and what to eat
The low histamine diet may help people who develop symptoms, such as sneezing, itching, or hives, in response to foods that contain histamine.
Histamine is a chemical that occurs naturally in the body and some foods. The low histamine diet can help a person find out which foods cause their symptoms. By avoiding those foods, they may see an improvement. A nutrition professional can guide someone through this process.
This article looks at how histamine affects the body, what histamine intolerance is, and the foods people may wish to avoid. It also provides an example meal plan and tips for grocery shopping and food preparation.

Histamine is a chemical that
When the body reacts to a substance it perceives as harmful, it releases histamine. This causes inflammation and dilates a persons blood vessels, leading to symptoms such as:
Despite the discomfort these symptoms can cause, histamine plays an important and complex role in the bodys defenses.
A
Laboratory experiments the authors quote also show that histamine may help with wound healing and inhibit tumor growth. However, researchers have not yet replicated these results in humans.
Some people develop symptoms in response to foods that contain or release histamine. Doctors call this condition histamine intolerance.
The symptoms of histamine intolerance are similar to that of an allergic reaction and can affect multiple systems in the body.
Symptoms include:
Diamine oxidase (DAO) is the enzyme responsible for breaking down histamine in the body.
People with lower levels of DAO have higher levels of histamine, and therefore may be more likely to develop allergies.
A small
Another
The impact of histamine
A 2018 study compared people with histamine intolerance to those with food intolerances, and others with no intolerances at all. The group with histamine intolerance had lower bacterial diversity in their gut and an impaired gut lining.
Several bacterial species occurring naturally in some foods and probiotic supplements produce histamine, which may make symptoms of histamine intolerance worse.
The low histamine diet aims to reduce the symptoms of histamine intolerance and allergies. There is limited evidence to suggest the diet may be helpful for some people.
A small
Scientists now need more high-quality studies on histamine intolerance to better understand the condition and the best treatments.
An article in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics suggests an individualized approach to nutrition is best for people with histamine intolerance.
Factors such as medication, stress levels, and a persons overall health all affect what works for them.
Before trying any type of restrictive diet, people should seek expert nutritional counseling to ensure they are getting adequate nutrients, and to avoid an unnecessary reduction in their quality of life.
The following foods contain higher levels of histamine:
- some types of fish
- aged cheeses
- processed meats
- wine and beer
- sauerkraut
- fermented products
- spinach
- eggplant
- tomato
- avocado
Studies indicate that some foods can release histamine in the body, even if they do not contain it. Scientists do not fully understand how this works, but some people may react to specific foods, including:
- milk
- shellfish
- eggs
- kiwi
- strawberry
- pineapple
- plum
Foods that contain chemicals called amines that are similar to histamine can also compete for DAO. This means that if someone eats lots of these foods, histamine will not break down as quickly and may cause symptoms.
Foods that contain other amines include:
- citrus fruits
- mushrooms
- soybeans
- bananas
- nuts
Other sources also report that the following foods are either high in histamine or histamine releasing or they block the DAO enzyme:
- pickled and canned foods
- chocolate and cocoa products
- vinegars
- wheatgerm
- yeast extract
- black tea
- Mate tea
- energy drinks
The following is an example of a low histamine diet plan that someone could follow while monitoring their symptoms.
Breakfast options
- oatmeal made with water or coconut milk
- puffed rice with coconut milk
- apple, melon, and pear fruit salad with chopped pistachios
- smoothie made with mango, coconut milk, chia seeds, and kale
Lunch options
- chicken and kale salad with chopped grapes
- chicken, lettuce, and grated carrot sandwich
- cottage cheese and cucumber on toast
- quinoa and herb salad
Dinner options
- Low histamine fish, such as trout or cod, freshly caught and served with zucchini and roasted carrots.
- Chicken with new potatoes, broccoli, and green beans.
- Pasta with olive oil, garlic, herbs, and chicken or borlotti beans.
- Homemade turkey burger with sweet potato wedges.
Snacks
- blueberries
- pistachios
- carrot sticks
- cottage cheese
- grapes
- celery sticks
- apple slices and natural peanut butter
Freshness has an impact on how much histamine a food contains. It is a good idea to learn how different methods of production and storage impact histamine levels in food.
How a person shops for and prepares food is also important.
A person with histamine intolerance can monitor and potentially reduce their symptoms by:
- planning meals in advance
- buying fresh food, shopping more often if necessary
- eating foods as soon as possible after purchase
- asking restaurants about their ingredients when eating out
- keeping a food journal to record symptoms and triggers
Some medications and supplements also influence histamine levels. If a person suspects something they are taking is exacerbating their symptoms, they should speak to their doctor.
A low histamine diet may benefit someone with histamine intolerance. Planning varied meals, avoiding high histamine foods, and allocating time to prepare fresh foods may help a person manage their symptoms.
If someone suspects they may have histamine intolerance, it is essential that they consult their doctor for advice.
People need to ensure that they do not miss out on essential nutrients when following a limited diet. People should not follow long-term exclusion diets without seeking advice from a registered dietitian or nutritionist.
7 Natural Ways to Clear Histamine From the Body
If you suffer from symptoms of histamine intolerance like hives, headaches, or GI symptoms, one of the best things you can do is work to prevent, control, or stop a histamine reaction. And the best way to do that is by clearing histamine from your body so that it has room for the unavoidable histamine that is part of our daily lives. From diet to lifestyle choices and supplements, here are my top 7 ways to naturally clear histamine from the body.
What is histamine?
Histamine is a molecule produced by the bodys immune and nervous systems involved in various physiological processes, including allergic reactions, inflammation, gastric acid secretion, and neurotransmission.
Histamine, stored in specialized cells called mast cells, is released in response to injury or invasion by foreign substances such as allergens, bacteria, and viruses, causing a range of symptoms, including itching, swelling, redness, and increased mucus production.
What is histamine intolerance?
Histamine intolerance is when a person experiences various symptoms after consuming foods or drinks high in histamine or exposure to environmental factors that cause histamine release. This is due to the bodys inability to break down and eliminate excess histamine effectively.

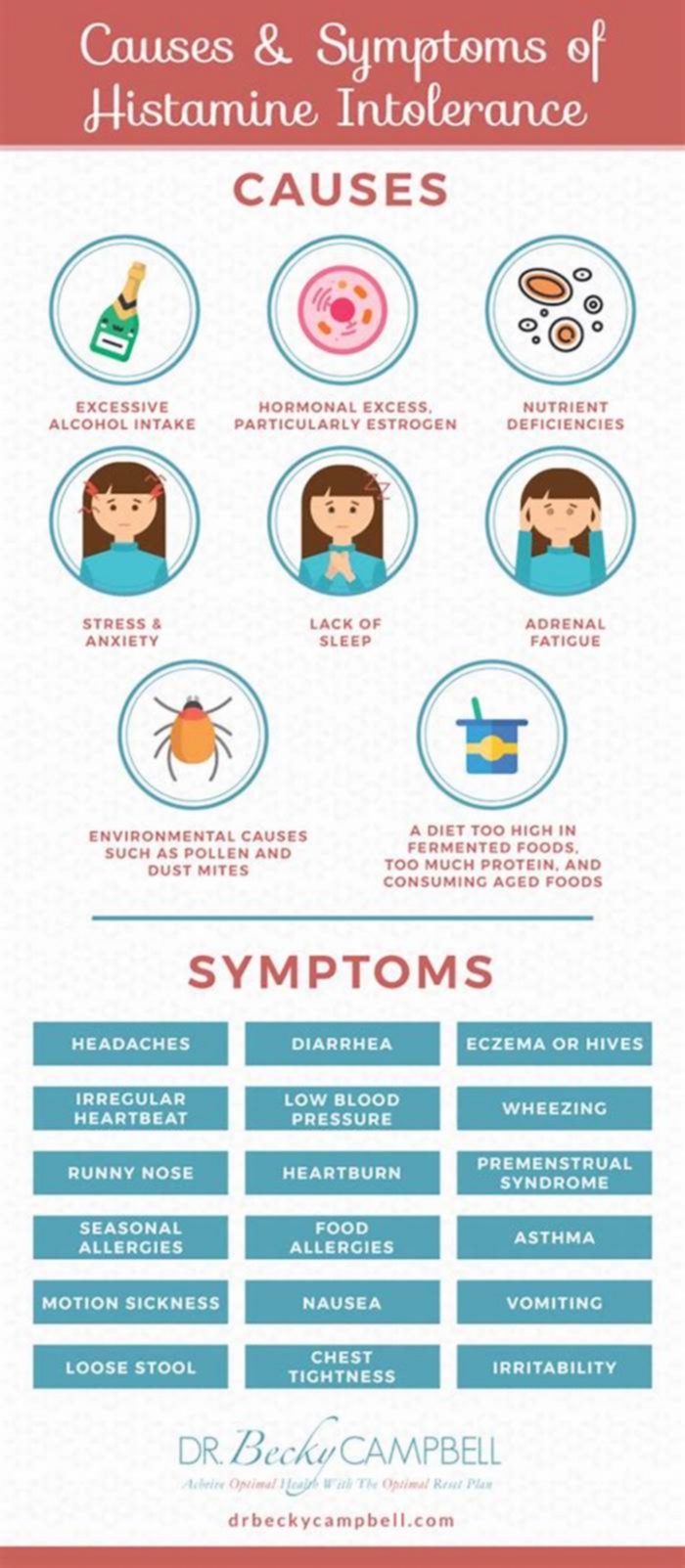
Symptoms of histamine intolerance can vary widely but may include the following:
- Headache
- Itching
- Flushing
- Hives
- Nasal congestion
- Gastrointestinal issues, including diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting
- Low blood pressure
- Difficulty breathing
Causes of Histamine Intolerance
The exact cause of histamine intolerance is not fully understood, but it is a multifactorial condition related to genetics, diet, and lifestyle. And the underlying cause can vary from person to person.
Some factors that may contribute to histamine intolerance include:
Histamine-rich Foods
Certain foods, such as aged or fermented foods, cured meats, canned fish, and certain fruits and vegetables, can contain high levels of histamine, which can trigger symptoms in people with histamine intolerance.
Enzyme Deficiencies
Enzymes in the body typically break down histamine, including diamine oxidase (DAO) and histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT) enzymes. If these enzymes are not functioning properly, histamine can accumulate in the body and cause symptoms of histamine intolerance.
Medications
Some medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can inhibit the activity of DAO, leading to an accumulation of histamine in the body.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
People with gastrointestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease, leaky gut syndrome, or SIBO, may have reduced DAO activity and increased histamine levels, leading to histamine intolerance.
Stress
Chronic stress can lead to an increase in histamine release, exacerbating histamine intolerance symptoms.
Genetics
Some people may be genetically predisposed to histamine intolerance, as certain genetic variations can affect the activity of DAO and HNMT enzymes.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) and autoimmune disorders, can increase histamine levels in the body and lead to the development of histamine intolerance.
Hormones
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during menstruation or pregnancy, can affect histamine levels in the body and trigger symptoms of histamine intolerance.

7 Natural Ways to Clear Histamine From the Body
Clearing histamine from the body can help alleviate a range of unpleasant symptoms and prevent severe allergic reactions. By reducing histamine levels through natural methods such as diet, exercise, and stress management, individuals with allergies or histamine intolerance can improve their quality of life while avoiding potentially dangerous allergic reactions.
Here are 7 natural ways to clear histamine from the body:
1. Eat a low histamine diet.
Some foods, such as aged cheeses, fermented foods, processed meats, shellfish, nuts, citrus fruits, chocolate, and tomatoes, are high in histamine. By avoiding these foods and opting for fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, you can reduce your intake of histamine or foods that can trigger the release of histamine.
2. Take a high-quality probiotic.
Research suggests that certain strains of high-quality probiotics, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium lactis, and Lactobacillus plantarum, may help to reduce histamine levels in the body. These probiotics improve gut health, reduce inflammation, and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria that can help break down histamine.
3. Incorporate a DAO supplement.
DAO supplements are dietary supplements that can break down histamine when the bodys natural DAO production is insufficient. Even though the research to support DAO supplements for people with histamine intolerance is limited, its believed that using DAO supplements can help break down excess histamine in the digestive system, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream and causing unwanted symptoms.
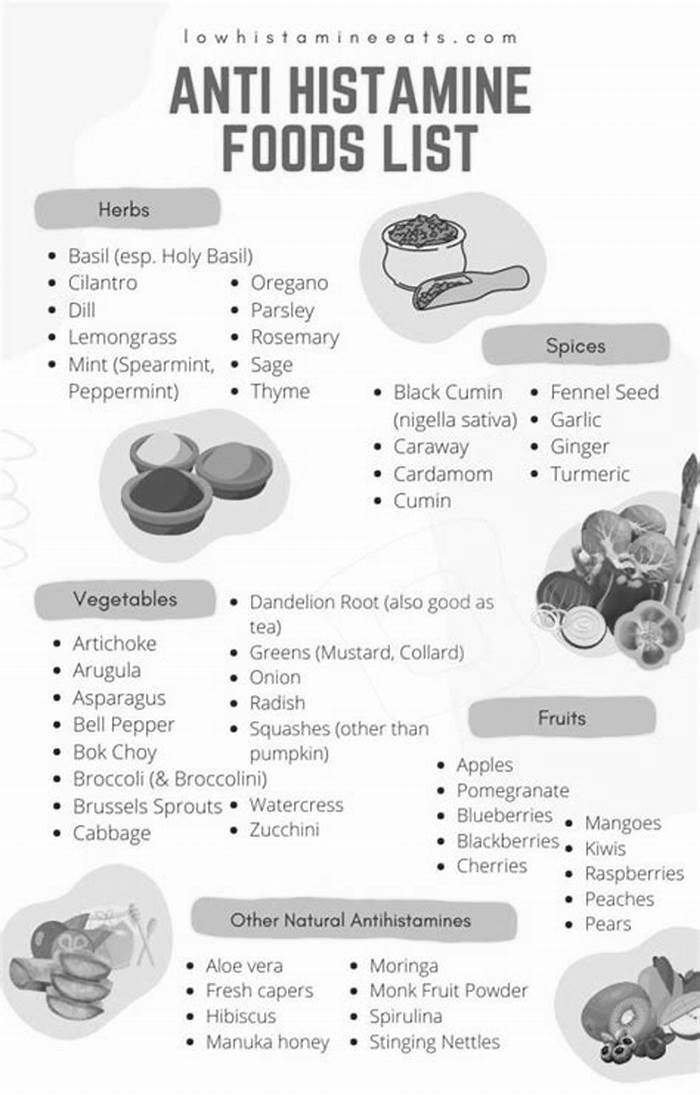
4. Utilize natural antihistamines.
Natural antihistamines found in certain herbs and supplements can help alleviate histamine intolerance symptoms by blocking the effects of histamine on the body. Natural antihistamines that may be helpful with histamine intolerance include the following:
- Quercetin: A flavonoid found in foods such as onions, apples, and berries.
- Vitamin C: A natural antihistamine that can help to reduce inflammation and support immune function.
- Nettle leaf: A natural antihistamine that can help to reduce allergy symptoms.
- Butterbur: A plant with natural antihistamine properties available in supplement form.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish or fish oil supplements can help to reduce inflammation in the body, which may help to alleviate allergy-like symptoms.
These natural antihistamines can be found in many supplements, but we recommend Optimal Reset Histo Relief. Optimal Reset HistoRelief combines many of these natural antihistamines along with proprietary blends that help support the immune system while helping support healthy histamine levels in the body.
5. Drink plenty of water.
Drinking enough water is essential for overall health and can help manage histamine intolerance symptoms. Heres how drinking water can help with histamine intolerance:
- Histamine is a byproduct of many cellular processes in the body and needs to be eliminated through urine. Drinking enough water can help to flush out histamine (along with other toxins) from the body and prevent it from building up and triggering symptoms.
- Dehydration can trigger the release of histamine in the body, leading to symptoms such as headaches and skin irritation.
- Proper digestion is important for managing histamine intolerance because poorly digested foods can trigger histamine release. Staying hydrated can help support proper digestion.
6. Focus on decreasing your stress.
Stress is a common trigger for histamine intolerance symptoms, as it can increase inflammation and trigger histamine release. So, managing stress through meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce histamine levels.
7. Sweat them out.
Regular sweat sessions (i.e., exercise) increase blood flow and lymphatic drainage, which can help to remove histamine from the body. Still, choosing the right type of exercise for your body is important. Here are some tips for exercising with histamine intolerance:
- Choose low-impact activities: High-impact activities such as running and jumping can increase histamine release and trigger symptoms. Instead, try incorporating lower-impact activities such as yoga, swimming, or walking. I also always recommend incorporating resistance training with rests between each set.
- Gradually increase activity levels: If youre not accustomed to regular exercise, its important to increase your activity levels gradually. This prevents overexertion and the release of histamine.
- Consider the timing for exercise: Many people with histamine intolerance find that exercising in the morning can be beneficial when histamine levels are naturally lower. But its important to listen to what feels good for your body.
How long does it take to lower histamine levels?
The time it takes to lower histamine levels in the body can vary depending on the individual and the cause of the histamine intolerance. In some cases, such as exposure to a histamine-rich food, symptoms may resolve within a few hours to a few days.
However, it may take longer for those with chronic histamine intolerance to lower histamine levels and alleviate symptoms. Making dietary and lifestyle changes, such as those mentioned above, can gradually help lower histamine levels over time, but only when you get to the root cause of your histamine intolerance will you find full recovery.
Its important to remember that lowering histamine levels is not a quick fix and may require ongoing management to prevent symptoms from recurring. And if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications that affect histamine levels, its important to work with your healthcare provider to identify the root cause and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Clear Histamine and Reset Your Body
Deep and lasting healing is only possible when the root causes of illness are addressed. Understanding the core systems of the body, how they are related, and how your function can be restored can prevent and even reverse histamine intolerance.
These 7 natural ways to clear histamine from your body are a great way to start. But resetting your body for true healing can require further investigation and support to uncover the root cause of your symptoms.
When you work with us, we partner to identify the underlying patterns contributing to your symptoms and devise a plan to provide lasting outcomes. Our revolutionary care model allows you to provide your body with the care and love it needs to feel like yourself again.
Schedule a new patient consultation today to get started.
Still preparing for a consultation? Try our Histamine Reset Online Program to begin healing your body on your time.
Resources
- Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art PMC NCBI. 14 Aug. 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7463562/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Biochemistry, Histamine StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf. 8 May. 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557790/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Histamine and histamine intolerance Oxford Academic. 1 May. 2007, https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/85/5/1185/4633007. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Histamine Intolerance Originates in the Gut PMC NCBI. 12 Apr. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8069563/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- What we know about nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NCBI. 31 Mar. 2016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4855107/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Histamine drives severity of innate inflammation via NCBI. 24 Jan. 2018, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5976516/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Acute stress modulates the histamine content of mast cells in NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2343625/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Genes of the Histamine Pathway and Common Diseases. 2 Feb. 2018, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134/S1022795418010088. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Role of Histamine in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Disease. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF03259251. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Estrogen effects in allergy and asthma PMC NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3537328/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Is There a Diet for Histamine Intolerance?. https://www.jandonline.org/article/S2212-2672(14)01454-3/pdf. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Probiotic Therapy as a Novel Approach for Allergic Disease NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3448073/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Diamine oxidase supplementation improves symptoms in patients . 24 May. 2019, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6859183/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Quercetin and Its Anti-Allergic Immune Response PMC NCBI. 12 May. 2016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6273625/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Impact of oral vitamin C on histamine levels and seasickness. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25095772/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- Nettle extract (Urtica dioica) affects key receptors and enzymes . https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19140159/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
- The effects of butterbur on the histamine and allergen cutaneous . https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14989395/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.
18. Exploring the Effects of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids NCBI. 6 Feb. 2016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4783952/. Accessed 30 Mar. 2023.