What foods stop hives

10 ways to get relief from chronic hives
 Biosimilars: 14 FAQs
Biosimilars: 14 FAQsFind answers to questions patients ask about this newer treatment option, including, Whats involved in switching from a biologic to a biosimilar?
Featured
 Laser hair removal
Laser hair removalYou can expect permanent results in all but one area. Do you know which one?
 Scar treatment
Scar treatmentIf you want to diminish a noticeable scar, know these 10 things before having laser treatment.
 Botox
BotoxIt can smooth out deep wrinkles and lines, but the results arent permanent. Heres how long botox tends to last.
Featured
 Find a Dermatologist
Find a DermatologistYou can search by location, condition, and procedure to find the dermatologist thats right for you.
 What is a dermatologist?
What is a dermatologist?A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists care for people of all ages.
Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (CIU) and Diet: Foods to Eat and Avoid
Chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) is the term for hives that last at least 6 weeks and have no known underlying cause. Learn how reducing histamines in your diet may help improve symptoms.
Many people think that hives are always an allergic reaction to something specific. This isnt the case with chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU).
CIU is the medical term for hives that last
Symptoms can come and go for months or even years. A variety of factors can make the condition worse, including:
- exercise
- stress
- heat
- cold
- pressure
- infections
Hives can also appear spontaneously, prompted by what seems like nothing at all.
Even though CIU isnt an allergic reaction, adjusting your diet may provide symptom relief.
At the moment, theres not much concrete evidence about the effects of particular diets on CIU symptoms. Still, some limited trials show that dietary changes may help relieve symptoms, at least on an individual level.
Here are some possible diets and foods that may help you manage your CIU symptoms.
High levels of histamine may play a significant role in CIU since many people with the condition respond well to antihistamine medications.
For people who dont respond well to antihistamine medications, trying a low histamine diet may be worthwhile.
In a small 2018 study, 22 people with chronic urticaria restricted histamine-rich foods for 4 weeks. There was a statistically significant decrease in participants urticaria severity scores.
Blood samples from people in the study also showed that the level of histamines in their blood had decreased after 4 weeks on the low histamine diet.
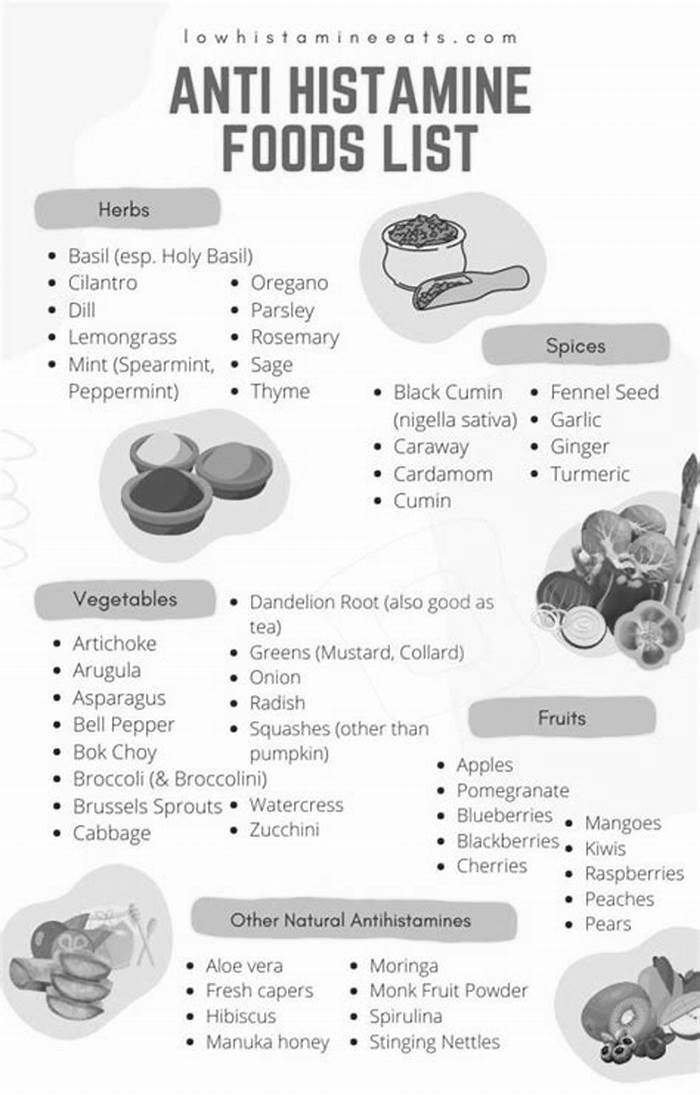
The following foods are low in histamines and may help you manage your CIU symptoms:
- most vegetables
- fresh meat
- certain varieties of fresh fish, including salmon, cod, and trout
- dairy products other than cheese and yogurt
- bread
- pasta
- rice
You may want to consider avoiding or limiting the following foods that are high in histamines:
- spinach, tomatoes, and eggplant
- fruits, such as strawberries and cherries
- preserved meats
- canned, frozen, and smoked fish, including tuna, anchovies, and sardines
- cheese
- yogurt
- fermented foods
- fast food
- seasonings, such as chili powder, cinnamon, cloves, and vinegar
- alcoholic beverages
This list isnt exhaustive. The amount of histamine from dietary sources can vary.
Some foods, beverages, substances, and medications are also theorized to either help in the release of histamine or inhibit the enzymes needed to break it down. A few examples of these include:
- citrus fruits
- papaya
- pineapple
- nuts
- egg whites
- alcoholic beverages
- tea
- food additives, such as certain preservatives
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin
- antibiotics, such as isoniazid and doxycycline (Monodox, Oracea, Vibramycin)
Theres little evidence to support this theory, though, according to a 2021 study.
Even if a person tests negative for food allergies, its possible they may have a hypersensitivity to or intolerance of certain foods. Eating these pseudoallergens can result in reactions that resemble a true allergic reaction, including hives.
With this in mind, some doctors may recommend that people with CIU try a pseudoallergen elimination diet. This involves avoiding certain potential pseudoallergens for several weeks and slowly reintroducing them.
Some examples of pseudoallergens include:
- histamine
- food additives
- natural substances in fruits, spices, and vegetables
In a 2010 study of a type of CIU called chronic spontaneous urticaria, approximately
However, there havent been any randomized controlled trials to draw conclusive evidence about the diets effectiveness on a greater scale.
In fact, in 2014, the Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters recommended against a pseudoallergen-free diet for chronic urticaria. The expert panel comprises representatives from the:
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI)
- American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI)
- Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology
If you think your diet plays a role in your CIU symptoms, talk with a doctor about your options.
A doctor can help you figure out which foods and beverages to safely remove from your diet. A persons tolerance for histamine is unique, so its very important to create an individualized diet plan.
You might also find it useful to track your symptoms in a journal after each meal. Take notes that include:
- the specific foods you ate
- what time you ate them
- whether your symptoms got worse or better after eating (and how long it took for you to notice)
Share your findings with the doctor so you can work out a plan together.
Everyone reacts to foods differently. One type of diet may work for someone else, but it may not work for you. Before trying a new diet, talk with a doctor. They can help you understand what to do based on your personal circumstances.
Theres still not much evidence that adopting certain diets can consistently and significantly affect your CIU symptoms. However, the low risk and low cost of doing so can make dietary changes worth a try.
Hives (Urticaria)
What are hives?
Hives, or urticaria, are flat red welts that can appear anywhere on the skin and usually itch. Hives often occur as an allergic reaction to something eaten or something that has contacted the skin. Foods, medicines, and plants are common causes, but sun exposure, stress, infections, and autoimmune diseases have also been known to cause hives.
Symptoms include an itchy, stinging pink rash of slightly swollen skin. The rash may wax and wane in severity. Acute hives typically resolve within six weeks, but chronic hives (urticaria) can persist for months or years.
Hives often resolve on their own, especially in children. Otherwise, treatment for acute hives involves oral antihistamine medications to help relieve the itching and stinging. Chronic hives that do not improve with antihistamines may be treated additionally with corticosteroids, antibiotics, and other stronger medicines. A study found that 35% of people with chronic hives, are symptom free within one year, with another 29% having some reduction of symptoms.
You can safely treat this condition on your own as long as you does not develop trouble breathing. Any antihistamine (like Zyrtec, Clarinex, etc) works.
Foods to eat and avoid with chronic idiopathic urticaria
Certain foods may trigger or worsen hives in some people due to the reaction they cause within the body. Avoiding foods high in histamines and pseudoallergens may help.
Chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) is the term for hives that last 6 weeks or more and have no known cause.
This article examines the link between diet and CIU, potential elimination diets that may help, and when to contact a doctor.
Diet may play a role in certain cases of CIU. According to a
Oral or topical antihistamines are the first-line treatment for CIU. Altering diet may be helpful alongside medical treatments.
A
Histamine is a compound present in the body.
The immune system releases histamine in response to a threat, such as an infection, or when there is no threat, as in the case of an allergic reaction. Hives can form due to this release.
Certain foods contain higher levels of histamine than others. A low histamine diet includes foods with lower histamine levels and eliminates those with higher levels.
Some research suggests lowering the intake of histamine through the diet may help reduce histamine levels in the body and help manage hives.
A small-scale 2018 study looked at the effects of a low histamine diet on 22 people with chronic hives. The participants were not allowed to eat foods containing high histamine levels for 4 weeks.
The researchers recorded the severity of hives and histamine levels in the blood before and after the diet. They found that the low histamine diet resulted in reduced severity of hives and a significant reduction in histamine levels in the blood.
A low histamine diet may include the following foods:
- eggs
- rice
- millet
- beef
- salad ingredients, such as cucumber, radish, and lettuce
- unfermented soy products, such as soy milk and tofu
- sorghum
- milk
- certain fish, such as sole, cod, and pollack
Anecdotal reports also suggest that fruits, vegetables, grains, meat, and other foods not high in histamine may also be acceptable.
On a low histamine diet, people avoid foods with
- some seafood, such as canned fish and fish with darker meat
- fermented foods, including fermented soy, aged cheeses, and dry sausage
- tomatoes
- eggplant
- spinach
- avocado
Some research suggests that certain foods
- citrus fruits
- papaya
- tomato
- strawberries
- pineapple
- nuts
- chocolate
However, there is currently a lack of human studies to support the idea that foods can trigger the release of histamine.
According to a
A pseudoallergen elimination diet excludes foods that can act as psuedoallergens, such as certain spices, fruits, vegetables, and artificial additives.
Experts are not clear on the exact effects of pseudoallergens within the body, but some believe they may play a role in triggering hives in some people.
The article states that pseudoallergen elimination diets have proved effective in reducing hives and causing complete or partial remission. They may be a potential treatment alongside medication.
If people want to try using an elimination diet for hives, it is important that they speak with a healthcare professional.
Elimination diets
Diet may play a role in helping manage chronic idiopathic urticaria. Elimination diets that cut out pseudoallergens and foods high in histamine may help relieve symptoms.
People may try these diets for a few weeks and then begin to reintroduce foods to see if symptoms return.
It is best to work alongside a healthcare professional when using elimination diets to help avoid nutritional deficiencies.