What if a vaccinated dog scratches you

Health Risks of a Dog Scratch
Dogs are among the most popular animal companions. In fact, its estimated that dogs live in about
Still, as with having any other pet, its important to be aware of the variety of diseases and health risks that may be transmitted from your canine companion. Some of these health risks may be derived from dog scratches that arise from playing, feeding, and coming into contact with an unknown animal.
Not all dog scratches are serious, but its important to be on the lookout for possible signs of infection, and call a doctor to rule out more serious health consequences.
Read on to learn about possible health risks from dog scratches and how to treat and prevent them.
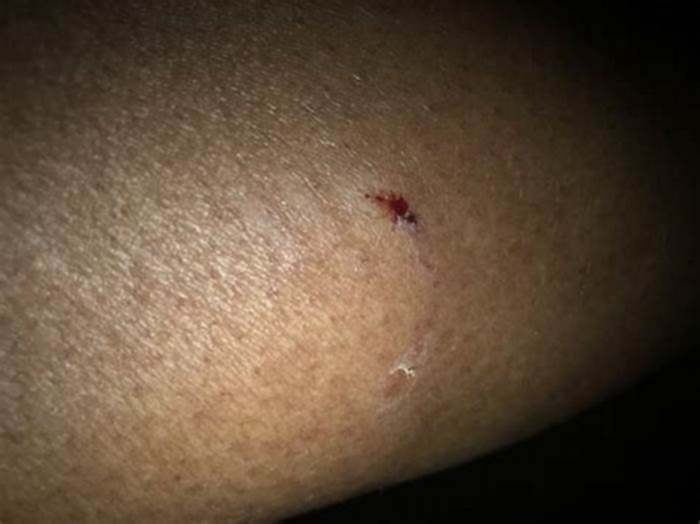
Daily interactions with your dog including playtime can sometimes result in scratches. These might occur from your dogs nails when they step on you or jump up on you, as well as accidentally scratching you with their teeth while playing fetch or during feedings.
When you get scratched by a dog, you may notice red marks on your skin. These may temporarily become painful and swollen and, in more severe cases, lead to more serious health risks. Possibilities may include:
- excessive bleeding
- infections, such as Capnocytophaga bacteria
- tetanus, which is caused by Clostridium tetani bacteria
- rabies, a serious viral infection
- sepsis, a life-threatening emergency caused by the spread of an infection to vital organs
Any dog scratch including those that seem mild and harmless ought to be treated immediately to prevent infection and other health complications. Consider the following steps:
- First, wash (but dont scrub) the dog scratch wound with warm water and soap. Rinse for at least 5 minutes. Pat dry with a clean towel.
- If the dog scratch is bleeding, apply pressure to the area with a clean gauze pad.
- Apply an over-the-counter (OTC) antibiotic cream or ointment.
- Cover the wound with a sterile bandage.
Some dogs carry a bacteria in their mouths called Capnocytophaga. While these bacteria
Capnocytophaga infections can progress quickly, even becoming life-threatening. Possible symptoms
- swelling
- redness and blisters
- pus from the bite
- fever
- headache
- muscle or joint aches
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Call or visit a doctor if youre experiencing any signs of infection post-dog scratch. Its also a good idea to seek medical attention any time youve been scratched by a dog especially if the dog isnt your own.
Rabies is a type of viral infection that can occur when bitten by an animal thats infected. This is a serious infection that can be fatal in both animals and humans, due to the viruss attack on the nervous system.
While animal-to-animal transmission is possible, its not as common for humans to be infected by household pets in the United States. Part of this reduced risk is attributed to rabies vaccines in domesticated animals.
Still, rabies ought to be considered in the case of a serious wound from a dog, particularly if its a stray dog or one who hasnt been vaccinated against rabies. The virus may be transmitted through an infected dogs saliva from biting or accidental scratching.
How a dog with rabies may behave
A dog who is infected with rabies may have
- behavioral changes
- reduced appetite
- voice changes/changes to their barks
- panting
- anxiety and restlessness
- attempted attacks on people and other animals
- paralysis
What to do if you suspect youve been bitted by a dog with rabies
If youve been bitten or scratched by a dog with an unknown rabies vaccination status, call a doctor. They may recommend treatment with rabies vaccines as well as antibodies.
Humans (with the exception of veterinarians and other professionals who handle animals) dont typically get the rabies vaccine unless theyve been exposed to the virus from an infected animal.
Symptoms of a rabies infection
Symptoms of rabies are slow to develop,
Possible signs of rabies in humans may include:
- fatigue
- fever
- headache
- weakness
- anxiety
- hallucinations, and other neurological changes
While its not always possible to avoid all cases of dog scratches, you may help minimize your risk of getting sick by:
- washing your hands after playing with and feeding your dog
- carefully washing scratches that do occur
- bandaging dog scratches and any subsequent open wounds
- keeping your dog up-to-date on their vaccines
- avoiding contact with other dogs that may be feral or unvaccinated
- walking your dog on a leash to prevent exposure to wild animals
- asking your doctor if youre up to date on your vaccines
Also, if you have your own dog, you may help reduce the risk of scratches from toenails and bites by training your dog not to jump up on you, and to use their mouths softly during playtime and feedings.
Getting scratched by your dog can happen, especially during feeding and playtime. While you can train your dog to be more gentle, occasional scratches are still inevitable. Your risk may also be greater when coming into contact with a wild dog, or a domesticated one whos not your own.
Washing a dog scratch wound is critical in preventing infections. Depending on the severity of the wound, you may consider calling your doctor regarding next steps.
Seek medical care if youre injured by a dog who isnt yours, if youve been bitten, are bleeding excessively, or are experiencing flu-like symptoms.
What type of exposure occurred?
Rabies is transmitted only when the virus is introduced into a bite wound, open cuts in skin, or onto mucous membranes such as the mouth or eyes.
Other factors to consider when evaluating a potential rabies exposure include the natural occurence in the area, the biting animals history and current health status (e.g., abnormal behavior, signs of illness), and the potential for the animal to be exposed to rabies (e.g., presence of an unexplained wound or history of exposure to a rabid animal).
A currently vaccinated dog, cat, or ferret is unlikely to become infected with rabies.
When an exposure has occurred, the likelihood of rabies infection varies with the nature and extent of that exposure. Under most circumstances, two categories of exposure bite and nonbite should be considered.
Bite
Any penetration of the skin by teeth constitutes a bite exposure. All bites, regardless of body site, represent a potential risk of rabies transmission, but that risk varies with the species of biting animal, the anatomic site of the bite, and the severity of the wound.
Bites by some animals, such as bats, can inflict minor injury and thus be difficult to detect.
Was the bite from a provoked or an unprovoked attack? Bites inflicted on a person attempting to feed or handle an apparently healthy animal should generally be regarded as provoked. If it was an unprovoked attack, thats more likely to indicate that the animal is rabid.
Nonbite
The contamination of open wounds, abrasions, mucous membranes, or theoretically, scratches (potentially contaminated with infectious material from a rabid animal) constitutes a nonbite exposure.
Nonbite exposures from terrestrial animals rarely cause rabies. However, occasional reports of rabies transmission by nonbite exposures suggest that such exposures should be evaluated for possible postexposure prophylaxis administration.
Other contact by itself, such as petting a rabid animal and contact with blood, urine, or feces of a rabid animal, does not constitute an exposure and is not an indication for postexposure vaccination.