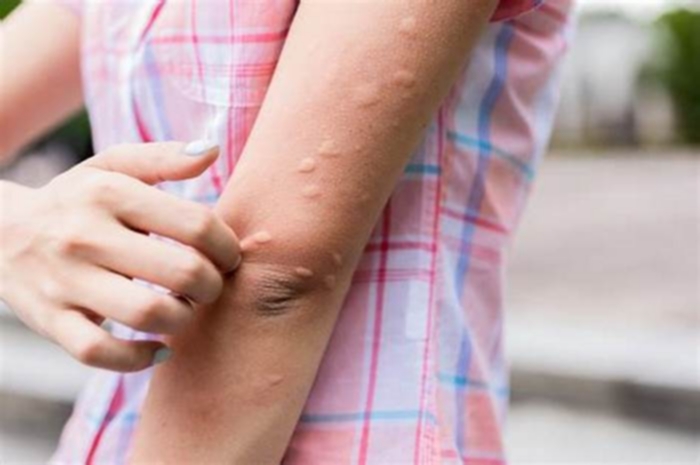
What if hives get worse after Benadryl
How long can hives last?
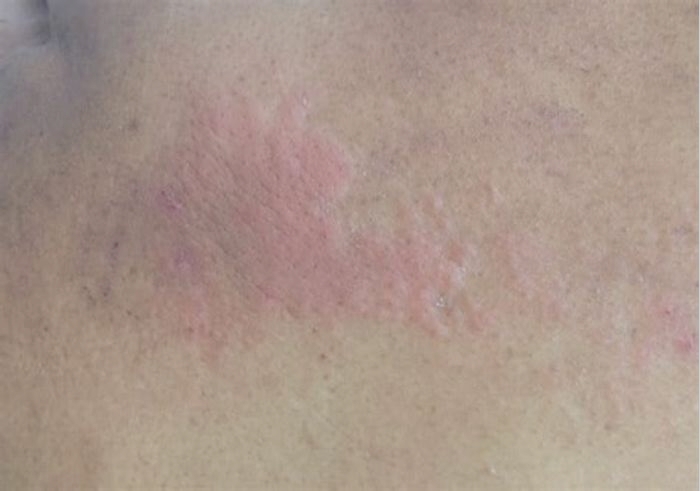
Hives can appear and disappear quickly, with each hive only lasting around 23 hours. However, depending on the cause, they may reappear and continue affecting someone for days, weeks, or longer.
People can have acute hives, which occurs due to a specific trigger and resolves within
This article looks at how long hives last, factors that influence their duration, and treatment.
Each hive lasts only
Acute hives appear quickly and do not last long. Doctors classify hives as acute if the overall duration is less than 6 weeks.
However, around 25% of people go on to develop chronic hives. This is when hives regularly reappear over 6 weeks or more.
For many individuals, chronic hives eventually clear on their own, but this can take months. According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD), around half of people with chronic hives spontaneously recover within 1 year.
Acute hives often occur in response to an allergen or irritant. When the immune system perceives a substance as a threat, it releases histamine and other chemicals. This causes tiny blood vessels under someones skin to leak fluid, which accumulates and causes the bump.
Some
- food allergens, such as milk, eggs, tree nuts, peanuts, or shellfish
- contact allergens, such as latex or animal dander
- insect bites or stings
- medications
Any drug can cause hives, but some of the medications most commonly associated with this symptom include:
Acute hives can also occur in response to viral infections, parasitic infections, or during times of stress.
According to a 2018 review, doctors are unsure of the cause of acute hives in
Chronic hives may have the same cause as acute hives, but with symptoms lasting longer than 6 weeks. However, chronic hives are often not due to an allergen and instead have a physical cause.
There are two subcategories of chronic hives: inducible urticaria and chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Chronic idiopathic hives
Chronic idiopathic urticaria has no clear cause and is the most common form of chronic hives. Researchers are working to understand why this type of hives occurs, but a leading theory links it with autoimmunity.
Autoimmunity occurs when a persons immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, and several autoimmune conditions are associated with chronic hives. The most common is thyroid disease, which is present in
This suggests that the hives may result from someones immune system not functioning as it should. Other conditions that can occur alongside chronic hives include type 1 diabetes, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Infections can also be associated with the onset of chronic hives. This includes bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections. Again, this may result from autoimmunity an infection may trigger a change in how the persons immune system works.
Inducible hives
Inducible or physical urticaria is less common than chronic idiopathic urticaria. With this subtype, it is possible to purposely induce the hives by a person exposing their skin to certain triggers, which could include:
- Scratching or pressure: The
most common type of inducible hives is known as dermatographia. This condition involves developing hives as a response to scratching or drawing on the skin. - Cold: Cold hives occur on someones skin or mouth after exposure to cold temperatures. Triggers include consuming iced drinks, touching cold water, or going outside in cold weather.
- Heat: Cholinergic hives occurs when an individuals body becomes hot or sweaty. Hot baths, exercise, and spicy food can be triggers.
- UV light: Solar hives occur in response to UV light from the sun and certain light bulbs, such as those in tanning beds.
- Water: Some people develop hives if their skin comes into contact with water. This is known as aquagenic urticaria and is very rare.
Doctors diagnose hives by performing a physical examination. There is no test to determine whether the persons hives are acute or chronic, so they will use the length of time they recur to do this.
The doctor may also ask an individual:
- when the rash began
- the shape, size, and distribution of the rash
- where on the body they first noticed the rash
- if they have had any insect bites
- if they live or work with common hive triggers, such as chemicals, animals, or latex gloves
- if they have bone or joint pain, fever, or abdominal pain
- if anyone in their family experiences hives
- if they take any medications or supplements
The doctor may use a skin prick test and serum-specific IgE test to check if the acute hives result from a specific substance, such as food, dust mites, or chemicals. Alternatively, they may refer someone to an allergy clinic for these tests.
However, in cases of chronic hives, allergy testing is rarely useful. A doctor may check for other underlying health conditions by performing additional tests, such as:
The most suitable treatment depends on whether the person has acute hives or chronic hives.
Acute hives
Doctors typically recommend second-generation antihistamines as the first-line treatment for acute hives, such as:
- loratadine (Claritin)
- desloratadine (Clarinex)
- fexofenadine (Allegra)
- cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- levocetirizine (Xyzal)
They may prescribe a standard dose or increase by up to 4 times if the individual does not respond.
If these medications do not improve symptoms, the doctor may recommend an additional antihistamine, such as cimetidine (Tagamet), famotidine (Pepcid), or ranitidine (Zantac). They may recommend a 310-day course of corticosteroids to help control the symptoms in severe cases.
The doctor may prescribe an epinephrine auto-injector if they think the individual is at risk of anaphylaxis, which is a severe allergic reaction that restricts breathing. This provides emergency medicine to treat anaphylaxis quickly.
The doctor will then reassess the individual in 26 weeks.
Chronic hives
Doctors may recommend a four-step treatment plan for chronic hives. This approach involves using an antihistamine daily, which may be up to 4 times the regular dosage depending on how the individual responds.If necessary, they may prescribe a second antihistamine or another medication, such as montelukast (Singulair). With persistent hives, they may suggest a high potency antihistamine, such as hydroxyzine or doxepin.
The final step is for a doctor to refer the individual to a specialist for immunomodulatory therapy. This may involve taking medications such as omalizumab (Xolair) or cyclosporine (Sandimmune).
Once symptoms are under control, a doctor may gradually reduce the dosage of these medications. If the hives have an identifiable cause, such as cold or heat exposure, adopting changes to avoid the triggers wherever possible is also important.
The AAD suggests the following methods for people to reduce irritation and itchiness in hives:
- applying topical anti-itch medications, such as calamine lotion
- wearing loose-fitting clothing
- moisturizing with fragrance-free lotion to prevent dry skin
- using cold compresses several times per day
However, it is important for individuals to try to determine whether the hives have a specific trigger, in addition to relieving symptoms. If someone has cold hives, for example, a cold compress may make them worse.
Therefore, it is a good idea for people to keep a symptom diary, recording when the hives occur and any factors that might have contributed. Symptom diaries are also useful to refer to at medical appointments. A person can take note of:
- the date and time the hives appear
- what they were doing just before they developed
- what they have had to eat or drink
If any common factors emerge when the hives occur, a person can try to temporarily avoid these to see if it helps. It is important for people to do this with the guidance of a doctor, allergist, or dietitian if someone has food-related hives.
Learn more about remedies and treatments for hives here.
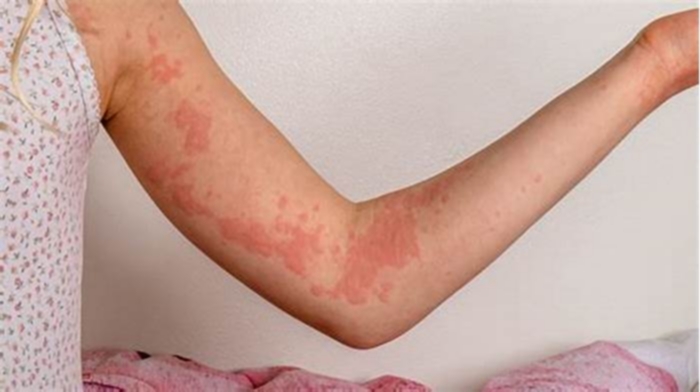
Hives do not last long, taking only 23 hours to fade. However, more can appear, which makes the symptoms last longer. Acute hives can develop and resolve on their own within 6 weeks, while chronic hives can last much longer.
Doctors treat acute and chronic hives differently, so it is advisable for people to speak with a medical professional about this symptom, especially if the hives last longer than 6 weeks.
If hives or swelling occur in the mouth and airways, making it difficult to breathe, dial 911 or the number of the nearest emergency department immediately.
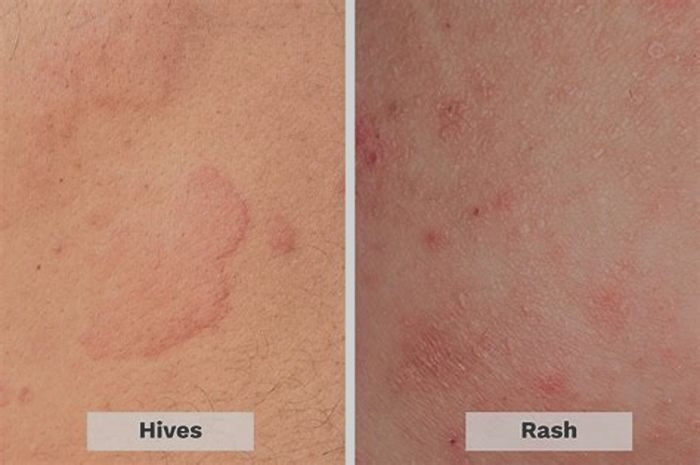
Hives (Urticaria)
What are hives?
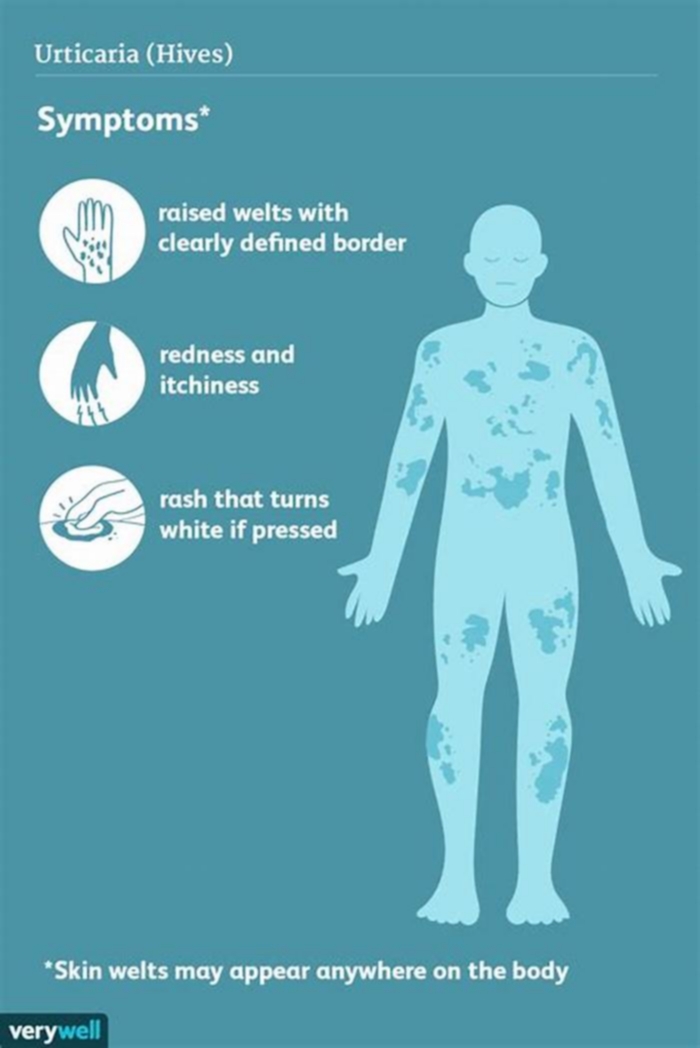
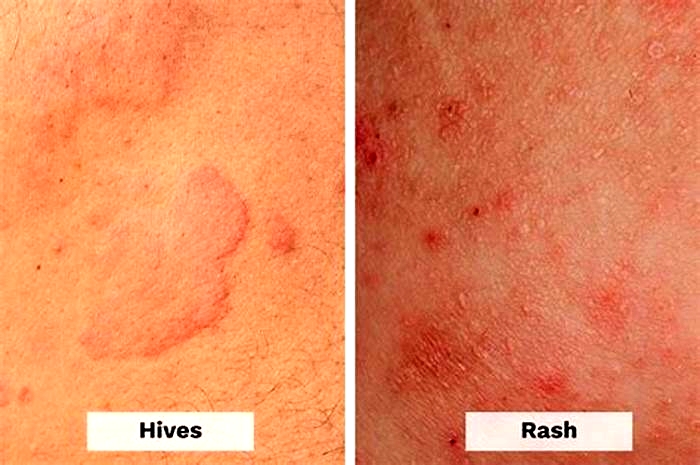
Hives, or urticaria, are flat red welts that can appear anywhere on the skin and usually itch. Hives often occur as an allergic reaction to something eaten or something that has contacted the skin. Foods, medicines, and plants are common causes, but sun exposure, stress, infections, and autoimmune diseases have also been known to cause hives.
Symptoms include an itchy, stinging pink rash of slightly swollen skin. The rash may wax and wane in severity. Acute hives typically resolve within six weeks, but chronic hives (urticaria) can persist for months or years.
Hives often resolve on their own, especially in children. Otherwise, treatment for acute hives involves oral antihistamine medications to help relieve the itching and stinging. Chronic hives that do not improve with antihistamines may be treated additionally with corticosteroids, antibiotics, and other stronger medicines. A study found that 35% of people with chronic hives, are symptom free within one year, with another 29% having some reduction of symptoms.
You can safely treat this condition on your own as long as you does not develop trouble breathing. Any antihistamine (like Zyrtec, Clarinex, etc) works.
Does Benadryl Help With Hives?
Jul 05, 2018
shley asked
Does Benadryl help with hives? I have red and itchy bumps on my arm and I think they are due to allergies.
Answer
 Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) is a first generation antihistamine used in the treatment of allergies, urticaria (hives), insomnia and motion sickness. Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) can be used to help manage hives. Hives are swollen, red patches of skin that can occur as a reaction to allergens or for unknown reasons.
Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) is a first generation antihistamine used in the treatment of allergies, urticaria (hives), insomnia and motion sickness. Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) can be used to help manage hives. Hives are swollen, red patches of skin that can occur as a reaction to allergens or for unknown reasons.
Benadryl For Hives
Most times, hives can be itchy. Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) can help reduce the swelling of hives and alleviate the itching. While Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) will help with the symptoms of hives, the best treatment is to determine the cause of the hives and remove that allergen.
Some common causes according toAmerican College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunologyare:
- Foods like peanuts, nuts, eggs and shellfish
- Drugs like antibiotics (penicillins and sulfa drugs), aspirin and NSAIDs (Ibuprofen and Naproxen)
- Insect bites and stings
- Pets
- Outside allergens such as pollen, trees and grasses
- Bacterial and viral infections
- Latex exposure
If hives continue to occur and a cause cannot be determined, an allergist should be consulted. In the meantime, Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) is a good choice of treatment to get some relief from the hives. More information on Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) can be found below.
Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) Information
Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) is a first generation antihistamine. First generation antihistamine are sedating antihistamines that can cause a significant amount of drowsiness. As such, caution should be taken when driving or operating machinery until the full effects of the medication are known. Some additional side effects of Diphenhydramine include:
- Drowsiness or sedation
- Dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Coordination problems
- Thickening of mucus in the nose or throat
SinceBenadryl (Diphenhydramine) can cause drowsiness or sedation, care should be used when used in elderly patients due to an increased risk of falls. Care should also be taken when patients are on other medications that can cause drowsiness. If there are any questions about taking medications together, patients should talk to their pharmacist or other health care providers.
Conclusion
When patients get hives, the first thing on most patients mind is getting relief from the symptoms. Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) is a good choice to help with the swelling and itchiness that can occur with hives. For hives that continue with unknown causes, a trip to the allergist is needed to determine the cause of the hives and further treatment.
Benadryl Side Effects: Examples and Treatment Options
Benadryl (diphenhydramine) is used for allergies and allergic reactions, as well as common cold symptoms. It may cause mild or serious side effects, such as sleepiness and seizures, among others.
Benadryl is available as a prescription and an over-the-counter (OTC) medication. It helps reduce symptoms of hay fever (nasal allergies), other allergies, and colds. Examples include a runny nose and sneezing.
This drug is also used to treat certain allergic reactions, such as swelling and hives. For these purposes, the OTC version of Benadryl can be taken by adults and children ages 6 years and older.
The active ingredient in Benadryl is diphenhydramine. (An active ingredient is what makes a drug work.) The drug comes in many different forms. Some you take by mouth, such as tablets or liquid solutions. Others you apply to your skin, such as creams or gels.
Keep reading to learn about the common, mild, and serious side effects that Benadryl can cause. For a general overview of the drug, including details about its uses, see this article.
Some people may have mild or serious side effects during their Benadryl treatment. Examples of a few of Benadryls more commonly reported side effects include:
* To learn more about this side effect, see the Side effects explained section below.
Examples of mild side effects that have been reported with Benadryl include:
In most cases, these side effects should be temporary. And some may be easily managed. But if you have any symptoms that are ongoing or that bother you, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
Benadryl may cause mild side effects other than the ones listed above. For more information, talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
* To learn more about this side effect, see the Side effects explained section below.
Serious side effects that have been reported with Benadryl include:
If you develop serious side effects while taking Benadryl, call your doctor right away. If the side effects seem life threatening or if you think youre having a medical emergency, immediately call 911 or your local emergency number.
Note: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) tracks side effects of medications. If youd like to notify the FDA about a side effect youve had with Benadryl, visit MedWatch.
* To learn more about this side effect, see the Side effects explained section below. An allergic reaction is possible after using Benadryl. But its not clear whether this side effect occurred in studies.
The side effects of Benadryl in children are generally similar to the drugs side effects in adults. But its also possible for this medication to cause hyperactivity and excitability in children.
Benadryl typically should not be used in children younger than age 6 years because they can have more serious side effects from the drug. This includes seizures and a fast heartbeat.
The OTC forms of Benadryl are approved only for children ages 6 years and older, as well as adults. If your child is younger than age 6 years, talk with their doctor about whether Benadryl is safe for them.
Get answers to some frequently asked questions about Benadryls side effects.
Are there any long-term side effects of Benadryl?
Yes, there are. Some long-term side effects that Benadryl may cause include:
Benadryl is recommended only as a short-term treatment for people with symptoms of allergies or other conditions that the drug treats. If you take Benadryl long term, you may develop long-term side effects of the medication.
Which side effects you experience can determine how long your side effects last. For example, if you feel sleepy, this side effect may last a few hours or until the medication is no longer in your body. But other side effects can be longer lasting.
Talk with your doctor about your Benadryl use and which other medications may be better for your condition.
* With dependence, your body needs the drug to feel like you usually do. With withdrawal, you experience uncomfortable symptoms after stopping a drug that youve become dependent on.
Do seniors have a higher risk of side effects from Benadryl?
Yes, older adults (ages 65 years and older) likely have a higher risk of side effects from Benadryl than younger adults. This is because their bodies may get rid of the drug more slowly.
Older adults may have more side effects from Benadryl, including sleepiness, dizziness, or heart problems. Sleepiness and dizziness can increase the risk of falling, which can be very serious.
If youre an older adult interested in taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor. They may recommend that you take a lower dose of Benadryl to reduce your risk of side effects. Or they may suggest that you take a different medication to treat your allergy or cold symptoms.
Can Benadryl be used in babies or toddlers? If so, what are the possible side effects?
OTC forms of Benadryl should not be used in babies or toddlers. This is because children younger than age 6 years old have an increased risk of side effects from Benadryl.
Children can have the same side effects of Benadryl as adults, such as dizziness or drowsiness. But Benadryl can also cause more serious side effects in children, such as a fast heartbeat or seizures. The drug may also cause children to become more excitable or hyperactive.
You should never use Benadryl to help your child fall asleep. This can be very dangerous.
Due to these risks, you should not give Benadryl to your baby or toddler without the direction of their doctor. If your child has symptoms of an allergy or cold, talk with their doctor about the best way to treat those symptoms.
Does Benadryl cause side effects in dogs?
Possibly. If your veterinarian recommends giving Benadryl to your dog, be sure to discuss possible side effects to watch for and the correct dosage. The dosage may be based on how much your dog weighs, to reduce the risk of side effects.
Benadryl is not approved to be used in dogs, but a veterinarian may recommend it in some cases. Its important to talk with a veterinarian before giving any medication to your pet. They can recommend whether Benadryl is safe for your dog and which dosage to give.
Does my risk of side effects from Benadryl vary, depending on the dose (such as 25 mg or 50 mg)?
Yes, your risk of side effects can vary, depending on the dose of Benadryl you take.
A higher dose of Benadryl can increase the risk of side effects. So youre more at risk of side effects from taking 50 milligrams (mg) of Benadryl than from taking 25 mg.
If you have concerns about side effects from your dose of Benadryl, talk with your doctor.
Does Benadryl cause diarrhea?
No, you shouldnt have diarrhea from taking Benadryl. In fact, Benadryl can cause constipation.
Some other medications used to treat allergy symptoms, such as Allegra Allergy (fexofenadine), may cause diarrhea.
If you have diarrhea while taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor about what may be causing it.
Learn more about some of the side effects Benadryl may cause.
Fast heartbeat
A fast heartbeat is a common side effect of Benadryl. In rare cases, it can become serious.
Symptoms of a fast heartbeat may include:
What might help
If you have symptoms of a fast heartbeat while taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor. They may recommend that you take a lower dose of the medication to treat your symptoms. Or they may recommend a different medication for you.
Blurry vision
Benadryl works by drying out your body, which may result in blurry vision. This is a more common side effect of Benadryl.
What might help
If you have blurry vision from taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor or pharmacist. They can recommend ways to decrease this side effect. They may also suggest a different medication to treat your symptoms.
Until your vision has cleared, you should not drive a car or operate other machinery.
Memory loss or dementia
Taking Benadryl may cause memory loss or dementia. Although rare, this side effect may be more common in older adults or people whove taken the drug long term. Symptoms can include:
What might help
If youre experiencing memory loss or dementia while taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor. Theyll likely suggest that you stop taking Benadryl. Theyll also look for the cause of your memory loss or dementia so that they can recommend the right treatment for you.
Dizziness
Dizziness is a common side effect of Benadryl. This side effect can be serious.
Until you know how Benadryl will affect you, you should not drive a car or operate other machinery after taking the drug. If it causes you to feel dizzy, avoid doing either activity until the effects of the medication have worn off.
In addition, dizziness may lead to an increased risk of falling for older adults. Falls can be very dangerous for people who are older.
What might help
If you have dizziness from taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor. Theyll recommend that you do not drive a car or operate other machinery while youre dizzy.
In addition, they may suggest a different medication for your symptoms, one that doesnt make you dizzy.
Allergic reaction
Like most drugs, Benadryl can cause an allergic reaction in some people. But its not clear whether this side effect occurred in studies.
Symptoms can be mild or serious and can include:
- skin rash
- itchiness
- flushing (temporary warmth, redness, or deepening of skin color)
- swelling under your skin, typically in your eyelids, lips, hands, or feet
- swelling of your mouth, tongue, or throat, which can make it hard to breathe
What might help
If you have mild symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as a mild rash, call your doctor right away. They can suggest treatments to manage your symptoms.
If your doctor confirms that you had a mild allergic reaction to Benadryl, theyll decide if you should continue using it.
If you have symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, such as swelling or trouble breathing, call 911 or your local emergency number right away. These symptoms could be life threatening and require immediate medical care.
If your doctor confirms that you had a serious allergic reaction to Benadryl, they may have you switch to a different treatment.
Keeping track of side effectsDuring your Benadryl treatment, consider keeping notes about any side effects youre having. Then, you can share this information with your doctor. This is especially helpful to do when you first start taking new drugs or using a combination of treatments.
Your side effect notes can include things such as:
- what dose of drug you were taking when you had the side effect
- how soon after starting that dose you experienced it
- the specific symptoms of the side effect
- how it affected your daily activities
- any other medications you were also taking
- any other information you feel is important
Keeping notes and sharing them with your doctor will help them learn more about how Benadryl affects you. And your doctor can use this information to adjust your treatment plan if needed.
Benadryl may not be right for you if you have certain medical conditions or other factors that affect your health. Talk with your doctor about your health history before you take Benadryl. The list below includes factors to consider.
Dementia: Benadryl may cause dementia, as well as worsen symptoms of dementia in a person with this condition. If you have dementia, talk with your doctor before you take Benadryl. Your doctor may recommend that you take a different medication instead.
Allergic reaction: If youve had an allergic reaction to Benadryl or any of its ingredients, you should not take it. Ask your doctor what other medications are better options for you.
Heart problems or high blood pressure: Benadryl can increase your heart rate and may cause more serious heart-related side effects, such as heart rhythm problems. If you already have heart disease, taking Benadryl can make your condition worse. Talk with your doctor about whether its safe for you to take Benadryl.
Liver problems: Benadryl is removed from your body through your liver. If your liver isnt working properly, it may take your body longer to remove the medication. This can increase your risk of side effects. If you have any liver conditions, tell your doctor before taking Benadryl.
Kidney, bladder, or prostate problems: Benadryl may decrease the amount of urine that you make. If you have kidney or bladder problems, you may already produce a decreased amount of urine. If you have prostate problems, you may have urinary retention (not being able to fully empty your bladder). These conditions may worsen due to Benadryl. If you have kidney, bladder, or prostate problems, talk with your doctor before you take this drug.
Respiratory conditions, including asthma: Benadryl works by drying out your nose and mouth, which decreases symptoms of an allergy or a cold. This can make mucus in your nose or mouth thicker. If you have trouble breathing, thickened mucus can make it even harder for you to breathe. Before you start taking Benadryl, talk with your doctor if you have any respiratory conditions.
Certain eye conditions: Benadryl may increase pressure in your eyes. If you already have a condition that increases eye pressure, taking Benadryl may worsen your condition. An example of this type of condition is glaucoma. Talk with your doctor to see if its safe for you to take Benadryl with your eye condition.
Alcohol use and Benadryl
You should not drink alcohol while youre taking Benadryl. Alcohol can increase your risk of drowsiness or dizziness. It may also cause more serious side effects, such as trouble breathing or slowed breathing.
If you drink alcohol, talk with your doctor about other medications you can take to treat your cold or allergy symptoms.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding while taking Benadryl
Its usually safe to take Benadryl during pregnancy. Benadryl doesnt seem to increase the risk of fetal harm.
And taking small doses of Benadryl for a short time may be safe while breastfeeding. However, Benadryl does pass into breast milk, and it can also decrease milk supply.
If youre breastfeeding and you take high doses of Benadryl, it may increase your childs risk of side effects. This is also the case if you take the drug long term.
High doses or long-term use of Benadryl may also reduce your supply of breast milk.
If youre pregnant or planning to become pregnant, talk with your doctor about the safety of Benadryl treatment during pregnancy. Also talk with your doctor about this if youre breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed.
Most side effects of Benadryl are mild, and some people may not have any side effects at all from it. In some rare cases, the drug can cause serious side effects.
Before you take Benadryl, be sure to talk with your doctor about whether the drug is safe for you. Some questions that you may wish to ask about Benadryls side effects include:
- How can I lower my risk of side effects from Benadryl?
- How long can I take Benadryl for my condition without increasing my risk of side effects?
- If I have serious side effects from taking Benadryl, what other medications can I use instead?
To learn more about Benadryl, refer to these articles:
To get information on different conditions and tips for improving your health, subscribe to any of Healthlines newsletters. You may also want to check out the online communities at Bezzy. Its a place where people with certain conditions can find support and connect with others.
Disclaimer: Healthline has made every effort to make certain that all information is factually correct, comprehensive, and up to date. However, this article should not be used as a substitute for the knowledge and expertise of a licensed healthcare professional. You should always consult your doctor or another healthcare professional before taking any medication. The drug information contained herein is subject to change and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. The absence of warnings or other information for a given drug does not indicate that the drug or drug combination is safe, effective, or appropriate for all patients or all specific uses.