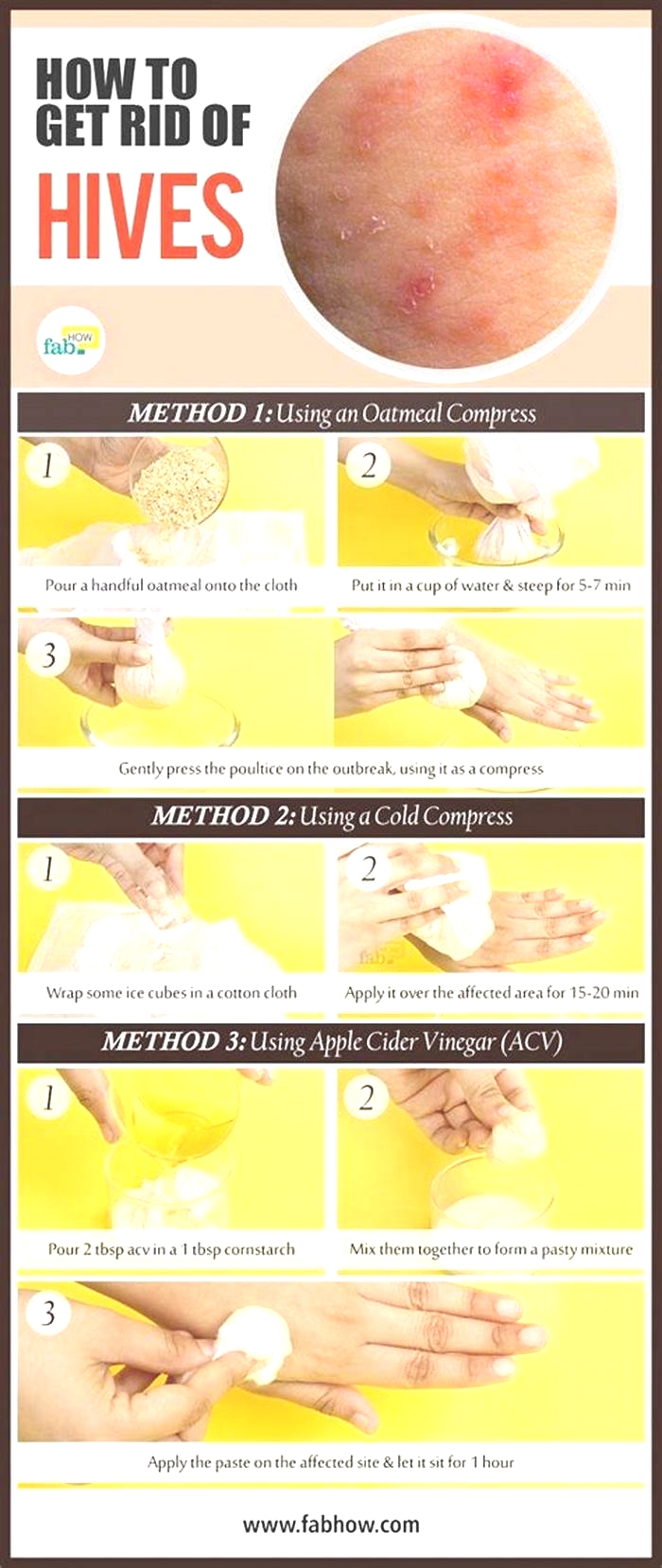
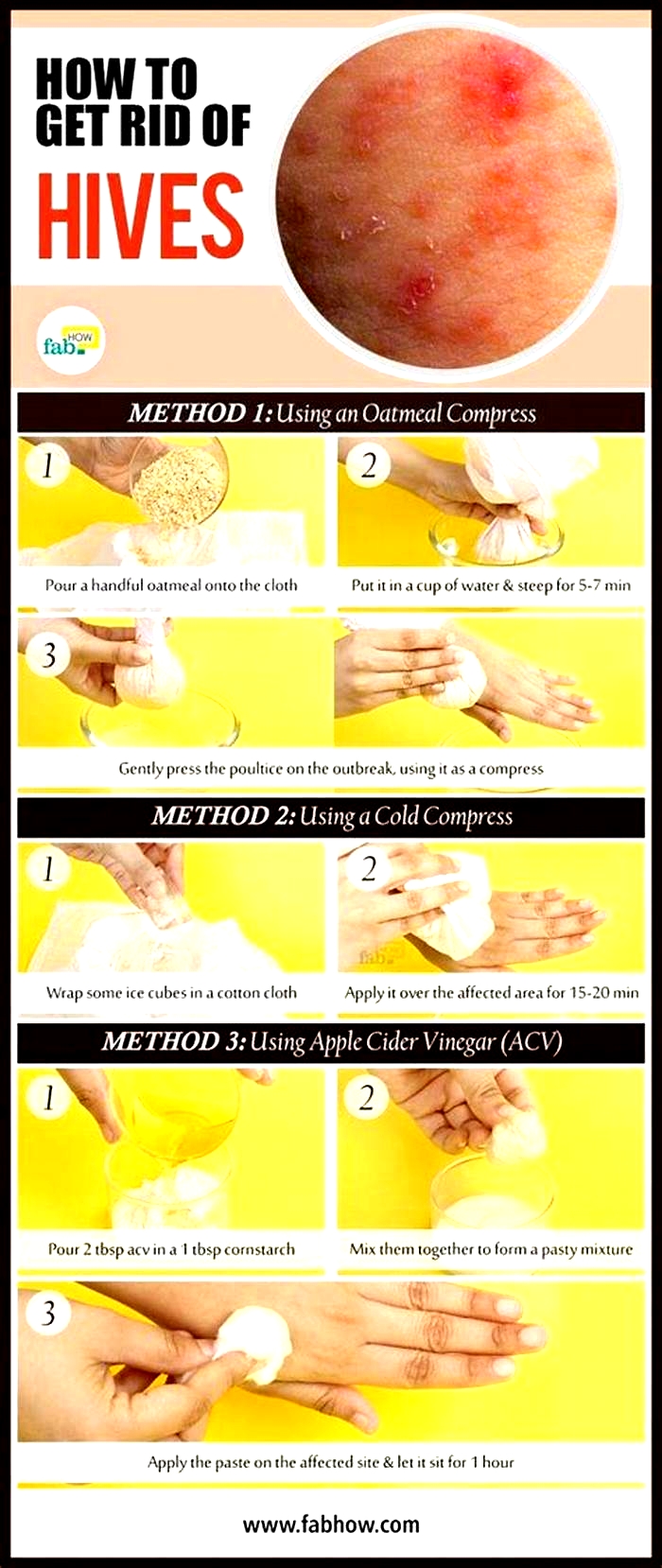
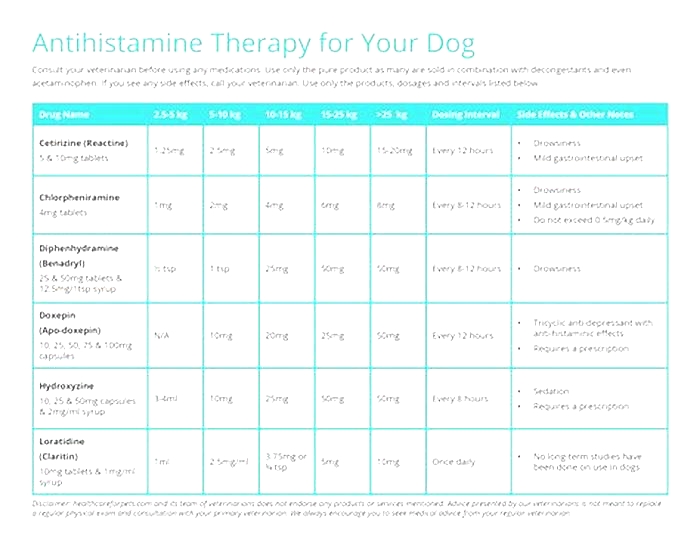
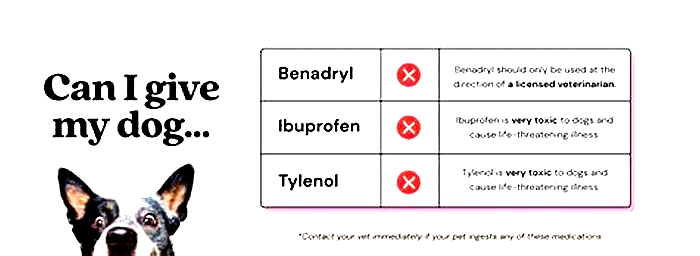
What is the fastest acting antihistamine for hives

Zyrtec vs. Claritin for Allergy Relief
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
Zyrtec and Claritin are similar over-the-counter allergy medicines. Your choice may come down to a subtle difference.
Among the most popular over-the-counter (OTC) allergy meds are Zyrtec and Claritin. These two allergy drugs produce very similar results. They both calm your immune systems reaction to allergens.
However, the potential side effects are different. They also take effect at different times and stay effective for different durations. These factors could determine which of these two drugs is better for you.
These drugs have different active ingredients. The active ingredient in Zyrtec is cetirizine. In Claritin, its loratadine. Both cetirizine and loratadine are nonsedating antihistamines.
Antihistamines have a reputation of making you sleepy because the first types crossed into your central nervous system more easily and had a direct effect on your alertness. However, newer antihistamines like Zyrtec and Claritin are less likely to cause this side effect.
Claritin is long acting. Most people experience at least 24 hours of relief after a single dose. Zyrtec, on the other hand, is fast acting. People who take it may feel relief in as little as one hour.
Antihistamines like Zyrtec and Claritin are designed to calm the histamine reaction your body has when its exposed to an allergen. When your body encounters something its allergic to, it sends out white blood cells and goes into fight mode. It also releases a substance called histamine. This substance causes many of the symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Antihistamines are designed to block the effects of the histamine that your body produces. In turn, they decrease the symptoms of the allergy.
Zyrtec and Claritin have very few side effects and are generally recognized as safe for most people. However, some side effects may still occur.
Zyrtec can cause sleepiness, but only in some people. Take it for the first time when you will be at home for a few hours in case it makes you sleepy. Claritin is less likely to cause sleepiness than Zyrtec when you take either at recommended doses.
Shared side effects
Mild side effects caused by both medications include:
More serious side effects of these medications are rare. If you have one of the following side effects after taking either medication, seek emergency medical attention:
In children
Children may have any of the side effects that adults do, but they can also have completely different reactions to antihistamines. Children may become stimulated, restless, or sleepless. However, if you give your children a dose of either drug thats too large, they can become groggy.
Claritin and Zyrtec both come in the same forms:
- solid tablets
- chewable tablets
- dissolving tablets
- gel capsules
- oral solution
- oral syrup
The dosage depends on your age and the severity of your symptoms.
Claritin is active in the body for at least 24 hours. The typical daily dose of Claritin for adults and children who are 6 years and older is 10 mg per day. For Zyrtec, its 5 mg or 10 mg. The typical daily dose of Claritin for children aged 25 years is 5 mg. Children this age using Zyrtec should be given 2.55 mg.
People with chronic medical conditions like kidney disease may need less frequent doses because the drug may take longer for them to process. Older adults and adults who have chronic illness should only take 5 mg of Zyrtec per day. For the best possible results, check with your doctor or pharmacist before deciding what dose to use.
In children
Remember that children may be different sizes at different ages, so when in doubt, start with a smaller dose. For the best results, talk to your childs doctor or a pharmacist before deciding what dose to give your child. And always check the package for dosing guidelines.
Zyrtec and Claritin are both priced about the same. Theyre available over the counter, so prescription drug insurance will likely not cover any portion of their expense. However, manufacturer coupons are often available for both medications. This will reduce your overall cost.
Generic versions of both antihistamines are readily available, as well. Theyre often less expensive than the brand-name versions, and new forms and flavors often appear. Be sure to read the generic medications label to confirm you are getting the right type of active ingredient.
Both Zyrtec and Claritin may make you drowsy or tired. For that reason, you shouldnt take these medications if you also take muscle relaxers, sleeping pills, or other drugs that cause drowsiness. Taking them at the same time that you take sedating drugs can make you extremely sleepy.
Do not take either of these medicines and then consume alcohol. Alcohol may multiply side effects and make you dangerously drowsy.
Both Zyrtec and Claritin are effective over-the-counter allergy relief drugs. If your choice has brought you to down to these two drugs, you may ask yourself, will drowsiness have an impact on my daily routine?
If the answers to this question doesnt bring you closer to an answer, ask your doctor or pharmacist for a recommendation. If you find that the recommended medicine works well, stick with it. If it doesnt, try the other. If none of the OTC options seem to help, see an allergist. You may need a different course of treatment for your allergies.
Shop for Zyrtec.
Shop for Claritin.
Allergy medications: Know your options
Allergy medications: Know your options
Several types of medications are used to treat allergy symptoms. Here's more information.
By Mayo Clinic StaffAllergy medications are available as pills, liquids, inhalers, nasal sprays, eyedrops, skin creams and shots (injections). Some are available over-the-counter; others are available by prescription only. Here's a summary of the types of allergy medications and why they're used.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines block histamine, a symptom-causing chemical released by your immune system during an allergic reaction.
Pills and liquids
Oral antihistamines are available over-the-counter and by prescription. They ease a runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, hives, swelling, and other signs or symptoms of allergies. Because some of these drugs can make you feel drowsy and tired, take them with caution when you need to drive or do other activities that require alertness.
Antihistamines that tend to cause drowsiness include:
- Diphenhydramine
- Chlorpheniramine
These antihistamines are much less likely to cause drowsiness:
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec, Zyrtec Allergy)
- Desloratadine (Clarinex)
- Fexofenadine (Allegra, Allegra Allergy)
- Levocetirizine (Xyzal, Xyzal Allergy)
- Loratadine (Alavert, Claritin)
Nasal sprays
Antihistamine nasal sprays help relieve sneezing, itchy or runny nose, sinus congestion, and postnasal drip. Side effects of antihistamine nasal sprays might include a bitter taste, drowsiness or feeling tired. Prescription antihistamine nasal sprays include:
- Azelastine (Astelin, Astepro)
- Olopatadine (Patanase)
Eyedrops
Antihistamine eyedrops, available over-the-counter or by prescription, can ease itchy, red, swollen eyes. These drops might have a combination of antihistamines and other medicines.
Side effects might include headache and dry eyes. If antihistamine drops sting or burn, try keeping them in the refrigerator or using refrigerated artificial-tear drops before you use them. Examples include:
- Ketotifen (Alaway, Zaditor)
- Olopatadine (Pataday, Patanol, Pazeo)
- Pheniramine and naphazoline (Visine, Opcon-A, others)
Decongestants
Decongestants are used for quick, temporary relief of nasal and sinus congestion. They can cause trouble sleeping, headache, increased blood pressure and irritability. They're not recommended for people with high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, glaucoma or hyperthyroidism.
Pills and liquids
Oral decongestants relieve nasal and sinus congestion caused by hay fever (allergic rhinitis). Many decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed), are available over-the-counter.
A number of oral allergy medications contain a decongestant and an antihistamine. Examples include:
- Cetirizine and pseudoephedrine (Zyrtec-D 12 Hour)
- Desloratadine and pseudoephedrine (Clarinex-D)
- Fexofenadine and pseudoephedrine (Allegra-D)
- Loratadine and pseudoephedrine (Claritin-D)
Nasal sprays and drops
Nasal decongestant sprays and drops relieve nasal and sinus congestion if used only for a short time. Repeated use of these drugs for more than three consecutive days may result in a cycle where congestion recurs or gets worse. Examples include:
- Oxymetazoline (Afrin)
- Tetrahydrozoline (Tyzine)
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids relieve symptoms by suppressing allergy-related inflammation.
Nasal sprays
Corticosteroid sprays prevent and relieve stuffiness, sneezing and runny nose. Side effects can include an unpleasant taste, nasal irritation and nosebleeds. Examples include:
- Budesonide (Rhinocort)
- Fluticasone furoate (Flonase Sensimist)
- Fluticasone propionate (Flonase Allergy Relief)
- Mometasone (Nasonex)
- Triamcinolone (Nasacort Allergy 24 Hour)
For people who are bothered by the feeling of liquid running down their throats or the unpleasant taste of these sprays, there are two aerosol formulas:
- Beclomethasone (Qnasl)
- Ciclesonide (Zetonna)
Inhalers
Inhaled corticosteroids are often used daily as part of treatment for asthma caused or complicated by reactions to airborne allergy triggers (allergens). Side effects are generally minor and can include mouth and throat irritation and oral yeast infections.
Some inhalers combine corticosteroids with long-acting bronchodilators. Prescription inhalers include:
- Beclomethasone (Qvar Redihaler)
- Budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler)
- Ciclesonide (Alvesco)
- Fluticasone (Flovent)
- Mometasone (Asmanex Twisthaler)
Eyedrops
Corticosteroid eyedrops are used to relieve persistent itchy, red or watery eyes when other interventions aren't effective. A physician specializing in eye disorders (ophthalmologist) usually monitors the use of these drops because of the risk of problems, such as cataracts, glaucoma and infection. Examples include:
- Fluorometholone (Flarex, FML)
- Loteprednol (Alrex, Lotemax)
- Prednisolone (Omnipred, Pred Forte, others)
Pills and liquids
Oral corticosteroids are used to treat severe symptoms caused by all types of allergic reactions. Long-term use can cause cataracts, osteoporosis, muscle weakness, stomach ulcers, increased blood sugar (glucose) and delayed growth in children. Oral corticosteroids can also worsen high blood pressure.
Prescription oral corticosteroids include:
- Prednisolone (Prelone)
- Prednisone (Prednisone Intensol, Rayos)
- Methylprednisolone (Medrol)
Skin creams
Corticosteroid creams relieve allergic skin reactions such as itching, redness or scaling. Some low-potency corticosteroid creams are available without a prescription, but talk to your doctor before using these drugs for more than a few weeks.
Side effects can include skin discoloration and irritation. Long-term use, especially of stronger prescription corticosteroids, can cause thinning of the skin and abnormal hormone levels. Examples include:
- Betamethasone (Dermabet, Diprolene, others)
- Desonide (Desonate, DesOwen)
- Hydrocortisone (Locoid, Micort-HC, others)
- Mometasone (Elocon)
- Triamcinolone
Mast cell stabilizers
Mast cell stabilizers block the release of chemicals in the immune system that contribute to allergic reactions. These drugs are generally safe but usually need to be used for several days to produce the full effect. They're usually used when antihistamines are not working or not well-tolerated.
Nasal spray
Over-the-counter nasal sprays include cromolyn (Nasalcrom).
Eyedrops
Prescription eyedrops include the following:
- Cromolyn (Crolom)
- Lodoxamide (Alomide)
- Nedocromil (Alocril)
Leukotriene inhibitors
A leukotriene inhibitor is a prescription medication that blocks symptom-causing chemicals called leukotrienes. This oral medication relieves allergy signs and symptoms including nasal congestion, runny nose and sneezing. Only one type of this drug, montelukast (Singulair), is approved for treating hay fever.
In some people, leukotriene inhibitors can cause psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression, strange dreams, trouble sleeping, and suicidal thinking or behavior.
Allergen immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is carefully timed and gradually increased exposure to allergens, particularly those that are difficult to avoid, such as pollens, dust mites and molds. The goal is to train the body's immune system not to react to these allergens.
Immunotherapy might be used when other treatments aren't effective or tolerated. It is also helpful in reducing asthma symptoms in some patients.
Shots
Immunotherapy may be given as a series of injections, usually one or two times a week. The dose may be increased weekly or every two weeks based on the patient's tolerance. Injections of the maximum tolerated dose may then be given every two to four weeks year round.
Side effects might include irritation at the injection site and allergy symptoms such as sneezing, congestion or hives. Rarely, allergy shots can cause anaphylaxis, a sudden life-threatening reaction that causes swelling in the throat, difficulty breathing, and other signs and symptoms.
Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT)
With this type of immunotherapy, you place an allergen-based tablet under your tongue (sublingual) and allow it to be absorbed. This treatment has been shown to reduce runny nose, congestion, eye irritation and other symptoms associated with hay fever. It also improves asthma symptoms.
One SLIT tablet contains dust mites (Odactra). Several SLIT tablets contain extracts from pollens of different types of grass, including the following:
- Short ragweed (Ragwitek)
- Sweet vernal, orchard, perennial rye, Timothy and Kentucky blue grass (Oralair)
- Timothy grass (Grastek)
Biological medications
Some medications target a specific reaction in the immune system and try to prevent it from happening. These medications are given as injections. They include dupilumab (Dupixent) to treat allergic skin reactions and omalizumab (Xolair) to treat asthma or hives when other medications don't help.
Side effects of biological medications may include redness, itchiness, or irritation of the eyes and irritation at the injection site.
Emergency epinephrine shots
Epinephrine shots are used to treat anaphylaxis, a sudden, life-threatening reaction. The drug is administered with a self-injecting syringe and needle device (auto-injector). You might need to carry two auto-injectors if there's a chance you could have a severe allergic reaction to a certain food, such as peanuts, or if you're allergic to bee or wasp venom.
A second injection is sometimes needed. As a result, it's important to call 911 or get immediate emergency medical care.
A health care professional will train you on how to use an epinephrine auto-injector. It's important to get the type that your doctor prescribes, as the method for injection may differ slightly for each brand. Also, be sure to replace your emergency epinephrine before the expiration date.
Examples of these medications include:
- Adrenaclick
- Auvi-Q
- EpiPen
- EpiPen Jr
Get your doctor's advice
Work with your doctor to choose the most effective allergy medications and avoid problems. Even over-the-counter allergy medications have side effects, and some allergy medications can cause problems when combined with other medications.
It's especially important to talk to your doctor about taking allergy medications in the following circumstances:
- You're pregnant or breast-feeding.
- You have a chronic health condition, such as diabetes, glaucoma, osteoporosis or high blood pressure.
- You're taking other medications, including herbal supplements.
- You're treating allergies in a child. Children need different doses of medication or different medications from adults.
- You're treating allergies in an older adult. Some allergy medications can cause confusion, urinary tract symptoms or other side effects in older adults.
- You're already taking an allergy medication that isn't working. Bring the medication with you in its original bottle or package when you see your doctor.
Keep track of your symptoms, when you use your medications and how much you use. This will help your doctor figure out what works best. You might need to try a few medications to determine which are most effective and have the least bothersome side effects for you.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
ErrorEmail field is required
ErrorInclude a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
March 05, 2022- Allergy meds could affect your driving. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/allergy-meds-could-affect-your-driving. Accessed Feb. 8, 2020.
- Overview of allergy and atopic disorders. Merck Manual Professional Version. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/immunology-allergic-disorders/allergic,-autoimmune,-and-other-hypersensitivity-disorders/overview-of-allergic-and-atopic-disorders?qt=allergy%20medication&alt=sh%20-%20v6515259. Accessed Feb. 8, 2020.
- deShazo RD, et al. Pharmacotherapy of allergic rhinitis. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Feb. 8, 2020.
- AAAAI allergy and asthma drug guide. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. https://www.aaaai.org/conditions-and-treatments/drug-guide. Accessed Feb. 8, 2020.
- Burks AW, et al. Allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. In: Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2020. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed Feb. 29, 2020.
- Hamrah P, et al. Allergic conjuctivitis: Management. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed March 3, 2017.
- Weston WL, et al. Treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema). https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Feb. 8, 2020.
- AskMayoExpert, Allergy immunotherapy. Mayo Clinic; 2019.
- Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT). American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. https://acaai.org/allergies/allergy-treatment/allergy-immunotherapy/sublingual-immunotherapy-slit. Accessed Feb. 29, 2020.