What is the strongest medication for hives

How to Treat Hives
If you have only one outbreak of hives and you dont have breathing difficulties, you probably dont need medical attention. Yet if you continue to get multiple bouts of hives that continue after a couple of weeks, you may want to call a doctor, Elmariah suggests. Most often, the hives will resolve during this time or youll figure out whats causing them.
But hives that continue for weeks warrant a trip to a specialist, such as a dermatologist or an allergist. If they continue for six weeks or longer theyre considered chronic hives, which tend to be caused by the same triggers as short-term or acute cases of hives. Because dermatologists and allergists are skilled at working with hives, theyre your best bet for getting appropriate treatment, Dr. Rossi explains.
How Doctors Diagnose Hives
Expect to undergo a thorough physical exam. The dermatologist or allergist will also likely ask you to review your hives experience in detail, including when the hives started, if you suspect anything in particular triggered your hives, what medications youve tried, and what type of response youve gotten. Come prepared with this information.
Doctors will also verify that the bump (or bumps) is hives, often circling the spot on your skin to see if it disappears the next day (if so, its a hive, Elmariah says).
Once theyve confirmed that it is hives, theyll work to determine the trigger. Rossi says: Figuring out the cause can be the most frustrating part of it, especially if the tests arent helpful.
You may require additional testing. If an allergy is suspected, you may need to undergo allergy testing. If you are diagnosed with a severe allergy, the doctor may prescribe an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen) in case youre accidentally exposed to your allergen. (1)
And because chronic hives can signal autoimmune disorders, you may need to have a blood draw in which doctors will look for a common antibody found in many autoimmune disorders. In rare cases when a bout of hives doesnt disappear within 24 hours, your doctor may do a skin biopsy to see if theres inflammation of the blood vessels, Rossi adds.
Treatments Doctors Use for Hives
Doctors usually prescribe antihistamines as the first course of treatment for hives. Acute cases can generally be treated with over-the-counter antihistamines like loratadine and pseudoephedrine,cetirizine, fexofenadine, or diphenhydramine.
If your hives are persisting (or youve already tried OTC antihistamines without success), your doctor may move to another class of antihistamines called histamine type 2 receptor antagonists, or H2 blockers, including cimetidine (Tagamet) and famotidine (Pepcid)(both available over the counter); up the dose of antihistamines (some as high as four times); or combine several antihistamines, Friedman says.
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe an oral steroid, such asprednisone (Deltasone), if your hives still arent responding. Oral steroids are stronger but can cause more significant side effects than antihistamines. (3)
If youre still not seeing results, your doctor may recommend even stronger medications, like an injectable prescription medication called omalizumab(Xolair). There is also evidence that off-label use of stronger medications that suppress the immune system under careful monitoring by a specialist may be helpful in patients with difficult-to-manage hives.
Its important to note that you shouldnt try taking high doses of vitamins or any other off-label medication on your own without instruction from your doctor. No one treatment works for everyone, Friedman says. And for some, such therapies may not be safe.
Hives (Urticaria)
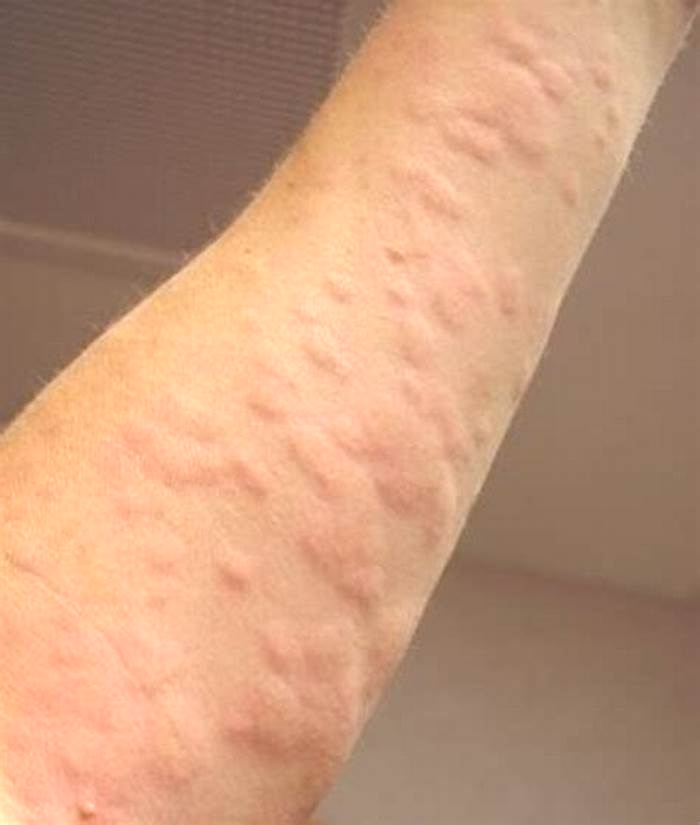
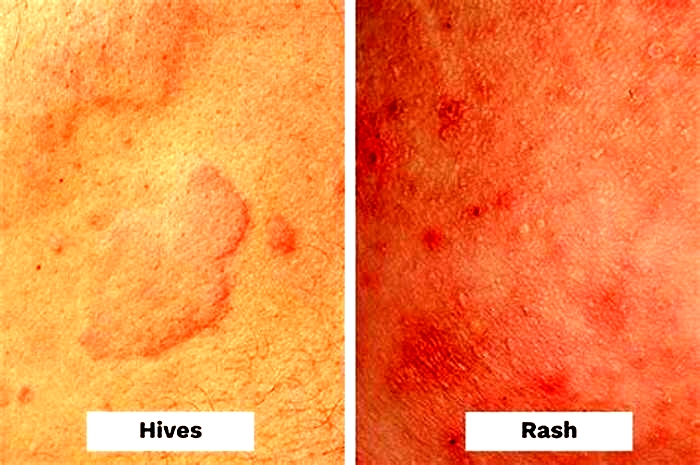
Hives (the common term for urticaria), are pink or red itchy rashes, that may appear as blotches or raised red lumps (wheals), on the skin. They range from the size of a pinhead to that of a dinner plate. When hives first start to appear, they can be mistaken for mosquito bites. Swellings usually disappear within minutes to hours in one spot, but may come and go for days or weeks at a time, sometimes longer. In most cases hives are not due to allergy and they can be effectively treated with a non-drowsy antihistamine. When hives occur most days for more than six weeks this is defined as chronic (ongoing) urticaria, which may require additional medication.
![]() ASCIA PCC Hives Urticaria 2021131.12 KB
ASCIA PCC Hives Urticaria 2021131.12 KB
Hives occur in the skin and are common
Up to 20% of people will develop hives at some time during their life. In most cases, hives are not due to allergy. Underneath the lining of the skin and other body organs (including the stomach, lungs, nose and eyes) are mast cells. Mast cells contain chemicals including histamine. When these are released into the skin they irritate nerve endings to cause local itch and irritation and make local blood vessels expand and leak fluid, triggering redness and swelling.
Can hives occur anywhere else?
Hives can also cause deeper swellings in the skin and mucosa, this is called angioedema. These swellings are often bigger, last longer, may itch less, sometimes hurt or burn and respond less well to antihistamines. Large swellings over joints, for example, can cause pain that feels like arthritis, even if the joint is not involved. Angioedema most frequently affects the face and lips. Although hives and facial swelling can be uncomfortable and cosmetically embarrassing, theyare not usually dangerous. Information on angioedema is available on the ASCIA website.
Hives are rarely due to a serious underlying disease
Whilst a clear cause of hives in not obvious in many cases, causes may include:
- Infection from a virus is the most common cause of hives in children, especially if they last for more than 24 hours.
- Contact allergy to plants or animals may cause localized hives.
- Allergic reactions to food, medicines or insect stings can appear as hives. They usually occur within one to two hours of exposure and disappear in most cases within six to eight hours.
An allergic cause for hives should be suspected if episodes are rare, short-lived and occur under specific circumstances, for example:
- Only when exercising.
- Always within two hours of a meal.
- When symptoms involving other organs occur around the same time, such as stomach pain, vomiting, difficulty breathing or dizziness.
- If hives occur with swelling of the tongue or throat, difficulty breathing or low blood pressure, anaphylaxis should be suspected. Urgent administration of adrenaline and medical assessment is required. Information about anaphylaxis is available on the ASCIA website.
Ongoing hives lasting days at a time are almost never allergic in origin, with the exception of some cases of allergy to medicines. Stress is a very rarely the cause of hives but may make the symptoms worse.
In some people hives are caused by physical triggers, including cold (such as cold air, water or ice), heat, sunlight (solar), vibration, rubbing or scratching of the skin (dermatographism), and delayed pressure (such as after carrying heavy bags. In other people, exercise (sweating), stress, alcohol, spicy food or coffee may cause symptoms.
Chronic urticaria is defined when hives occur most days for more than six weeks
Symptoms of chronic urticaria usually resolve, although this can take months or several years. Most people with chronic urticaria manage with appropriate doses of non-drowsy antihistamines. People with severe symptoms interfering with quality of life may be referred to a clinical immunology/allergy specialist or dermatologist for assessment and consideration of additional medications.
Most people with hives do not need tests
Tests are sometimes done when hives go on for long periods, or when unusual symptoms are occurring around the same time. This is to exclude other diseases, which may appear as hives first, and other conditions later. If hives are associated with high fever, bruising, bleeding into the skin, purple lumps that last for several days, or sore joints, a doctors appointment should be arranged promptly.
Allergy testing is performed when the history suggests an allergic cause.
Treatment of hives
Whilst most hives resolve within a couple of weeks without any specific treatment, the following treatments may be useful:
- Avoid aggravating factors such as avoiding excessive heat, spicy foods or alcohol.
- Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)should be avoided as they often make symptoms worse.
- Medications like non-drowsy antihistamines are often used to reduce the severity of the itch. Severe throat swelling requires early use of adrenaline and attention by your doctor or treatment in hospital.
- Severe chronic urticaria sometimes requires a trial of medicines which reduce inflammation, often called immune modulators or immunosuppressive medications. Recurrent courses of cortisone/steroid tablets need to be avoided due to a significant risk of side effects.
- Special diets appear to have a limited role to play in the management of hives. Unfortunately, it is difficult to predict who will, or will not respond to diet on the basis of history or allergy testing. A temporary elimination diet under close medical supervision, followed by challenges may be useful in a small number of cases.
For patient support organisations goto www.allergy.org.au/patients/patient-support-organisations
ASCIA 2021
ASCIA is the peak professional body of clinical immunology/allergy specialists in Australia and New Zealand.
ASCIA resources are based on published literature and expert review, however, they are not intended to replace medical advice. The content of ASCIA resources is not influenced by any commercial organisations.
For more information go towww.allergy.org.au/patients/skin-allergy
To support allergy and immunology research go to www.allergyimmunology.org.au/donate
Updated March 2021
Hives: Diagnosis and treatment
 Biosimilars: 14 FAQs
Biosimilars: 14 FAQsFind answers to questions patients ask about this newer treatment option, including, Whats involved in switching from a biologic to a biosimilar?
Featured
 Laser hair removal
Laser hair removalYou can expect permanent results in all but one area. Do you know which one?
 Scar treatment
Scar treatmentIf you want to diminish a noticeable scar, know these 10 things before having laser treatment.
 Botox
BotoxIt can smooth out deep wrinkles and lines, but the results arent permanent. Heres how long botox tends to last.
Featured
 Find a Dermatologist
Find a DermatologistYou can search by location, condition, and procedure to find the dermatologist thats right for you.
 What is a dermatologist?
What is a dermatologist?A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists care for people of all ages.