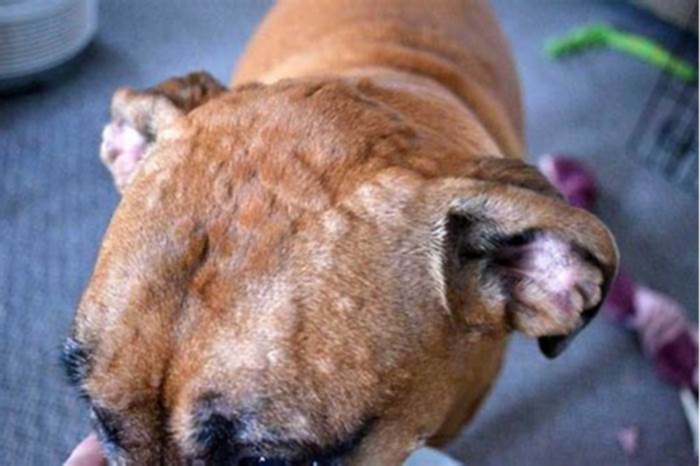
What vitamin gets rid of hives

How to treat hives
Home remedies and medications can help treat hives quickly and effectively. Examples include cold compresses, aloe vera, antihistamines, and more.
Hives are intensely itchy, discolored, raised areas of skin. They may occur anywhere on the body. Hives usually have a trigger, both allergic and non-allergic.
While the symptoms of hives can be very irritating, there are many ways to treat, soothe, and get rid of them.
In this article, we detail how to treat hives at home, medical options, and possible complications.
What does hives look like? Pictures and more
People often use home remedies to treat hives and do not seek further medical attention or intervention. In fact, many cases of hives disappear naturally within minutes or hours of appearing. Most often, symptoms of hives will disappear within 24 hours, but in some cases, it may take a few days.
Effective home remedies to treat hives include:
- Applying a cold compress: A person can apply a cool, damp cloth to the affected area. This can provide relief from itchiness and help reduce inflammation. A person can use a cold compress as often as necessary.
- Bathing in an anti-itch solution: Oatmeal and baking soda baths can soothe skin and reduce irritation. Adding witch hazel to a bath is another effective home remedy.
- Applying aloe vera: The healing properties of aloe vera may soothe and reduce hives. However, it is best to do a patch test before applying aloe vera to a wider area.
- Avoiding irritants: This includes perfumes, fragranced soaps or moisturizers, and staying out of the sun. A person should also aim to maintain a comfortable temperature and wear loose, cotton clothing.
Some people with chronic hives
In more severe cases of hives, medical treatment may be preferable. Some over-the-counter options include:
People with more severe and persistent hives may need to see a dermatologist. These doctors specialize in conditions of the skin, hair, and nails.
Hives are a skin condition that usually results in a raised, itchy rash. There are several different types of hives, although the effects are mostly the same.
Hives may be the same color as the surrounding skin or may have a reddish hue. This discoloration may be less evident on darker skin tones.
Learn more about hives on black skin here.
Acute urticaria and acute angioedema
Acute urticaria is a short-lived type of hives. In this condition, rashes last less than 6 weeks and usually occur due to an adverse or allergic reaction to certain foods or medications. Urticaria only affects the upper layer of the skin, called the dermis.
Infections and insect bites can also cause this type of rash.
Angioedema is the rapid swelling of the area beneath the skin, known as the mucosa. A person with hives will not always experience this type of swelling. Angioedema can occur with many different disorders.
Acute angioedema can occur with acute urticaria and is essentially anaphylaxis of the subcutaneous tissues. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction. It can lead to anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal.
Learn more about anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock here.
Chronic urticaria and chronic angioedema
Chronic urticaria and chronic angioedema last for more than 6 weeks.
In these conditions, a person will typically experience daily, or almost daily, symptoms without an allergic, infectious, or drug-related cause.
Chronic urticaria and chronic angioedema more commonly result from underlying medical causes, such as thyroid disease, cancer, or hepatitis.
Hives affect around 20% of people at some point during their lifetime. They are more common in children and female adults than in male adults.
A hives outbreak happens when high levels of histamine and other chemical messengers release into the skin, causing a rash and other symptoms to surface.
The high levels of histamine cause blood vessels in the affected area to open up and start to leak. The resulting fluid in the tissues causes swelling and itchiness.
Different triggers may cause a person to have an outbreak of hives. Some common causes include:
- an allergic reaction to food, an insect bite, or an animal
- a reaction to a plant irritant, such as nettles
- an infection, such as the flu or a cold
- certain medications
- preservatives and food additives
If hives develop, it is useful to identify the trigger. Factors that can worsen hives include:
Physical urticaria
The effects of heat exposure and overheating can cause a type of hives called physical urticaria.
Common triggers for physical urticaria include:
- extreme heat or cold
- overexposure to the sun
- excessive sweating
- clothes rubbing the skin
This rash rarely spreads beyond its original location.
Some people experience dermatographism, a type of physical urticaria. This condition occurs
Some people refer to dermatographism as skin writing. The condition is
What is the difference between hives and a rash? Pictures and more
The severity of a hives can vary between individuals. Most symptoms are manageable at home, but medical attention may be necessary in some cases.
A person should see a doctor if:
- symptoms last more than a few days
- symptoms worsen over time
- the rash is painful or leaves a bruise
- symptoms interfere with daily life
- they experience dizziness
A person will need immediate medication attention if they experience:
- any swelling of the tongue, mouth, or throatSimilarly
- difficulty breathing
- tightness in their chest
A doctor will examine the rash and ask questions to determine the cause. Doctors may also use blood and allergy tests to rule out specific causes.
Hives are usually treatable and do not cause complications on their own. However, in more severe cases, angioedema may occur.
Angioedema is a buildup of fluid in layers of the skin that causes swelling and can affect the eyes, lips, hands, feet, and genitals. Doctors can prescribe medication to manage and reduce swelling.
Recurrent hives can negatively impact the quality of a persons life, causing them to feel stressed or anxious and can even lead to depression. A person should always speak to a doctor if hives are affecting their quality of life.
Here are some questions people often ask about hives.
How do you treat hives naturally?
Ways of treating hives naturally include:
- avoiding scratching
- applying a cool compress
- bathing in lukewarm water with colloidal oatmeal
- wearing loose, cotton clothing
- avoiding soaps with fragrances or strong chemicals
- applying aloe vera
What is the fastest remedy for hives?
A cool compress may offer immediate relief from discomfort, but topical medicines may be more effective. Ask a pharmacist about over-the-counter options.
Hives are a skin condition that results in itchy, raised, patches of skin. There may also be discoloration.
Hive can result from allergic or non-allergic causes. Home remedies and medications can often reduce symptoms.
People with severe hives may have a risk of further complications. A person should seek medical advice if symptoms are severe, ongoing, or affect their quality of life.
10 ways to get relief from chronic hives
 Biosimilars: 14 FAQs
Biosimilars: 14 FAQsFind answers to questions patients ask about this newer treatment option, including, Whats involved in switching from a biologic to a biosimilar?
Featured
 Laser hair removal
Laser hair removalYou can expect permanent results in all but one area. Do you know which one?
 Scar treatment
Scar treatmentIf you want to diminish a noticeable scar, know these 10 things before having laser treatment.
 Botox
BotoxIt can smooth out deep wrinkles and lines, but the results arent permanent. Heres how long botox tends to last.
Featured
 Find a Dermatologist
Find a DermatologistYou can search by location, condition, and procedure to find the dermatologist thats right for you.
 What is a dermatologist?
What is a dermatologist?A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in treating the skin, hair, and nails. Dermatologists care for people of all ages.
Chronic hives
Diagnosis
To diagnose chronic hives, your health care provider will likely talk with you about your symptoms and look at your skin. One of the telling features of chronic hives is that the welts come and go at random. You might be asked to keep a diary to keep track of:
- Your activities
- Any medications, herbal remedies or supplements you take
- What you eat and drink
- Where hives appear and how long it takes a welt to fade and whether it leaves behind a bruise or other mark
- Whether your hives come with painful swelling
You may also need blood tests to determine the cause of your symptoms. An accurate diagnosis will guide your treatment options. If needed to clarify the diagnosis, your doctor might take a skin sample (biopsy) to examine under a microscope.
Treatment
Treatment for chronic hives often starts with nonprescription anti-itch drugs (antihistamines). If these don't help, your health care provider might suggest that you try one or more of these treatments:
Prescription anti-itch drugs. The usual treatment for chronic hives is prescription antihistamine pills that don't make you drowsy. These drugs ease itching, swelling and other allergy symptoms. Daily use of these drugs helps block the symptom-producing release of histamine. Examples include:
- Cetirizine
- Desloratadine (Clarinex)
- Fexofenadine
These medications have few side effects. If the nondrowsy antihistamines don't help you, your health care provider may increase the dose or add another type of antihistamine.
Check with your health care provider before taking any of these medications if you're pregnant or breastfeeding, have a long-term medical condition, or take other medications.
Other medications
If the first-choice drugs don't ease your symptoms, other drugs may help. For example:
- Famotidine (Pepcid AC)
- Montelukast (Singulair)
- Doxepin (Silenor, Zonalon)
- Cimetidine (Tagamet HB)
- Nizatidine (Axid AR)
- Ranitidine (Zantac)
- Omalizumab (Xolair)
For chronic hives that resist these treatments, your health care provider might prescribe a drug that can calm an overactive immune system. Examples are cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune), tacrolimus (Prograf, Protopic, others), hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) and mycophenolate (Cellcept, Myfortic).
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Chronic hives can go on for months and years. They can interfere with sleep, work and other activities. The following self-care tips may help you manage your condition:
- Avoid triggers. These can include foods, medications, pollen, pet dander, latex and insect stings. If you think a medication caused your welts, stop using it and contact your primary care provider. Some studies suggest that stress or fatigue can trigger hives.
- Use a nonprescription anti-itch drug. A nonprescription anti-itch (antihistamine) pill that doesn't cause drowsiness may help ease itching. Examples include loratadine (Alavert, Claritin, others) and cetirizine (Zyrtec Allergy).
- Apply cold. Soothe the skin by covering the itchy area with a cold washcloth or rubbing an ice cube over it for a few minutes.
- Take a comfortably cool shower or bath. Some people might relieve itching in the short term by taking a cool shower or bath. Try sprinkling the bath water with baking soda or oatmeal powder (Aveeno, others).
- Apply an anti-itch cream or lotion. Try a cream with menthol for a soothing effect.
- Wear loose, smooth-textured cotton clothing. Avoid wearing clothing that's rough, tight, scratchy or made from wool.
- Protect your skin from the sun. Liberally apply sunscreen about a half hour before going outdoors. When outdoors, seek shade to help relieve discomfort.
- Track your symptoms. Keep a diary of when and where hives occur, what you were doing, what you were eating, and so on. This may help you and your health care provider identify triggers.
Preparing for your appointment
You'll likely start by seeing your primary care provider. Or you may be referred to an allergy specialist or a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions (dermatologist).
What you can do
Here are some tips to help you get ready for your appointment.
- List your symptoms, when they occurred and how long they lasted.
- List any medications you're taking, including vitamins, herbs and supplements. Even better, take the original bottles and a list of the doses and directions.
- List questions to ask your doctor.
For chronic hives, questions you may want to ask include:
- What is likely causing my symptoms?
- How long will hives last?
- What kinds of tests do I need? Do these tests require any special preparation?
- What treatments are available, and which do you suggest?
- What are the alternatives to the primary approach that you're suggesting?
- Do these treatments have any side effects?
- Do I need prescription medication, or can I use nonprescription drugs to treat the condition?
- Does the medicine you're prescribing have a generic version?
What to expect from your doctor
Your health care provider is likely to ask you a few questions, such as:
- When did you first have symptoms?
- What did your skin reaction look like when it first appeared?
- Have your symptoms changed over time?
- Have you noticed anything that makes your symptoms worse or better?
- Do your skin lesions mainly itch, or do they burn or sting?
- Do your skin lesions go away completely without leaving a bruise or a mark?
- Do you have any known allergies?
- Have you ever had a similar skin reaction before?
- Have you tried a new food for the first time, changed laundry products or adopted a new pet?
- What prescriptions, nonprescription medications and supplements are you taking?
- Have you started taking any new medications or started a new course of a medication you've taken before?
- Has your overall health changed recently? Have you had any fevers or have you lost weight?
- Has anyone else in your family ever had this kind of skin reaction? Do other family members have any known allergies?
- What at-home treatments have you used?