When should I be worried about hives
What Causes Hives That Recur Daily?
Hives that come back daily for 6 weeks or more are called chronic hives, or chronic urticaria. The condition often has no known cause, but allergies, autoimmune conditions, physical stimuli, and infections can play a role.
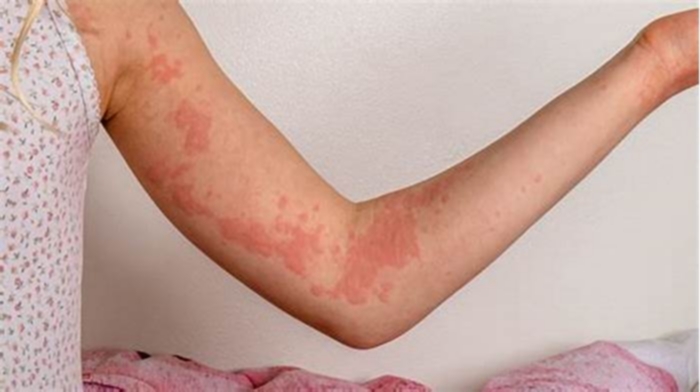
Hives are itchy, raised welts on the skin. They are often caused by an allergic reaction but might also have an unknown cause.
Hives that recur (go away and come back) frequently are known as chronic hives. Chronic hives of unknown cause can last for months or years. They can affect 1.4% of people, twice as often in women as in men.
Chronic hives can affect your quality of life, as severe itchiness can lead to discomfort and trouble sleeping. Yet treatment can help you manage them.
Lets look at the symptoms, possible causes, and treatment for hives that recur daily.
If you get new hives as others are clearing up for 6 weeks or more, you have chronic hives.
You can identify hives by their:
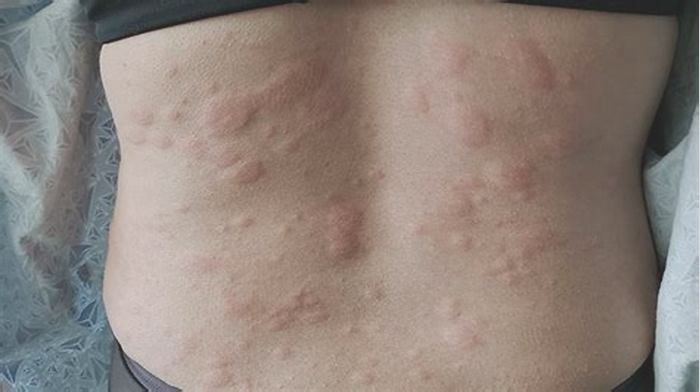
- raised patches or bumps on the skin
- itchiness on the patches or bumps
- stinging or burning sensation
- swollen skin appearance
Hives come in all different shapes and sizes, from just a small speck to several inches in diameter. A group of hives that appear in the same area is known as a plaque.
Medical emergencyCall emergency medical services or go to the nearest emergency room if you or someone youre with experience:
- sudden swelling of the lips, mouth, throat, or tongue
- fast breathing, choking, or wheezing
- trouble swallowing
- blue, gray, or pale color in lighter skin or on palms or soles of the feet in darker skin
- confusion, drowsiness, or dizziness
- inability to be woken up
Chronic hives look the same as other hives. Hives on light skin can appear pink or red. On dark skin, the color of the hives might be similar to the rest of your skin or slightly darker. Hives can also blanche on lighter skin, which is when a red hive becomes white if you press on it.
On all skin colors, hives are bumps or raised patches.
Chronic hives have many possible causes. Differences in symptoms, such as how quickly the hives appear, can help identify the cause.
Chronic idiopathic urticaria
Chronic idiopathic urticaria is when you get daily hives but doctors cant determine why. Symptoms include:
- hives that recur daily or nearly every day
- hives that last for 6 weeks or longer
- when each hive lasts 24 hours or fewer
- hives that do not bruise or scar your skin
Allergies
Hives can be triggered by exposure to a specific allergen.
Depending on the type of allergy, hives might come on quickly or over a few hours. Some common food allergens and the timing of related hives include:
- peanuts, shellfish, eggs, and nuts (hives often appear within 1 hour)
- bananas and chestnuts if you have a latex allergy (hives often appear within 1224 hours)
- food additives like colors and preservatives (hives often appear within 1224 hours)
Other types of allergies that might cause recurring hives include:
- insect bites or stings
- pet dander
- pollen
- certain plants
Autoimmune conditions
Several autoimmune conditions can cause chronic hives. Although researchers dont know exactly why this happens, chronic inflammation might
Among the autoimmune conditions that might cause hives are:
Infection or medication
If you have an infection or are taking medication, these might also lead to hives that recur daily. Examples include:
- Bacterial or viral infections:
- Medications:
When a doctor is trying to find the cause of your recurring hives, they might try to rule out infection or medication as a cause. Chronic hives last longer than 6 weeks, but an acute infection like the common cold might last less time than that.
A doctor might then look for another cause of your hives.
Physical stimuli
Your environment or certain activities can cause you to break out in hives. If these stimuli are a regular part of your life, it might lead to chronic hives.
Examples of stimuli that lead people to have hives almost immediately or within a few minutes include:
- cold
- heat
- ultraviolet light (outdoor sun exposure or tanning beds)
- vibration
- adrenaline (exercise or stress)
- water
- certain animals like jellyfish
Skin pressure from clothes or accessories can lead to hives right away or up to 424 hours later.
If you dont know the reason for your chronic hives, consider seeing a doctor. The hives might have a treatable cause like an allergy or physical stimulus. Treatment can relieve symptoms even if the cause is unknown.
Also consider seeing a doctor if hives:
- do not get better after 2 days
- seem to be spreading
- accompany high temperature
- accompany a feeling of unwellness
- accompany swelling under the skin
A doctor, usually a specialist such as an allergist, diagnoses chronic hives by:
- taking a medical history
- asking about your symptoms
- performing a physical exam
- conducting an allergy patch test
If your chronic hives are from a specific trigger, avoiding that trigger might make them go away.
Self-care options include:
- applying cool compresses
- using anti-itch creams or ointments
- bathing in colloidal oatmeal
- wearing loose-fitting clothes
- avoiding scratching
- using fragrance-free, gentle skin cleansers
Medications include:
- antihistamines (prescription or over-the-counter)
- corticosteroids
- omalizumab (injectable medication)
- phototherapy
Chronic hives can go away without treatment. About half of people with chronic hives no longer experience them within a year.
Here are some answers to common questions about chronic hives.
Why do I keep getting hives every day?
Chronic hives can have a variety of causes, including allergies, autoimmune conditions, infections, or physical stimuli. Many cases of chronic hives have no known cause.
What do autoimmune hives look like?
Autoimmune hives appear as raised, itchy patches of skin or bumps. They might appear pink or red on light skin and on dark skin as a bit darker than the rest of your skin. Hives can be of any size or shape.
When should I be worried about recurring hives?
You should consider seeing a doctor whenever you have hives that keep coming back. A doctor might be able to help you find a cause. Even if the cause is unknown, treatments such as antihistamines and self-care can help improve your symptoms.
Treatment for chronic hives with antihistamines, corticosteroids, light therapy, and home care can help improve symptoms.
What to Know If Youre Breaking Out in Hives for No Apparent Reason
If your skin is breaking out in hives, it may be a sign of an underlying health condition like lupus or infection. It could also be an allergic reaction. Speaking to an allergist can help with diagnosis and treatment.
Sometimes the source of the raised, red, and itchy bumps on your skin can be a mystery.
One reason hives can be so surprising is that they can be caused by many things you might not expect including stress and exercise. Most of these unexpected causes for hives arent serious, but some are a sign its a good idea to make a medical appointment.
Read on for more information about reasons you may have hives.
Hives are an itchy reaction on your skin. They happen when a chemical called histamine is released in your body.
They can appear anywhere on your body and can be tiny pinprick-sized bumps or large raised areas that cover an entire limb. Hives often appear red or pink on white or light skin. People with darker skin might have hives that are slightly lighter or slightly darker than the skin surrounding them.

No matter the color of your hives rash, all hives share these qualities:
- raised
- itchy
- tender
- round, oval, or uneven shaped
- clearly defined border
Hives are also called urticaria. Sometimes, the cause of hives is obvious. For instance, you might have an immediate reaction to something youre allergic to such as pollen or pet dander. However, the cause isnt always clear. Hives can be sudden and surprising and seem to not have a cause.
Hives are a very common skin reaction that can come from some unexpected sources. Some causes you might not have thought of include:
- Colds and other viral infections. Sometimes hives can be caused by your immune system fighting colds and other viral infections. These hives often appear near the end of your cold or virus as youre starting to feel better. Theyre most common in children but can happen to anyone.
- Bacterial infections. Bacterial infections such as strep throat or urinary tract infections can also sometimes trigger hives as your body reacts to the bacteria. These hives will fade as the antibiotics help your body fight the infection. They might peel before healing completely.
- Chronic conditions such as lupus. Hives that last for longer than 6 weeks might be a sign of an autoimmune condition such as lupus, type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, or rheumatoid arthritis. These hives wont go away on their own. Its a good idea to make a medical appointment to get this type of hive checked out and see if a chronic condition is the cause.
- Stress. Stress can raise your internal body temperature and release adrenalin and other chemicals that might trigger hives. Stress hives tend to be located on the face, neck, chest, and arms. Theyre common in people with eczema, allergies, or sensitive skin.
- Temperature changes. Suddenly encountering hot or cold, such as stepping into a steamy shower or entering a swimming pool, can cause histamine to release and hives to form. Hives that form in response to temperature are called cold urticaria. A red and itchy area of skin often forms around these hives.
- Tight clothing. Tight clothing can cause friction that leads to irritation and to hives. Clothes that sit close to your skin can also push any bacteria on your skin surface into your pores and hair follicles.
- Exercise. A chemical called acetylcholine is released in your body when you exercise can affect your skin cells and cause irritation and hives. Exercise hives are known as exercise-induced urticaria. Some people have additional symptoms along with hives such as shortness of breath, headache, flushing, and stomach cramps.
- Inflammation of blood vessels. An inflammation of your blood vessels known as vasculitis can cause painful hives. They can leave a bruise on your skin and last for several days. Vasculitis is a serious medical condition that requires treatment by a medical professional.
- Medications. Some medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, and opioids can cause an allergic reaction that leads to hives. Hives following medication might be the first sign of a medical emergency called anaphylaxis. Other symptoms of anaphylaxis include shortness of breath, wheezing, vomiting, and loss of consciousness.
Hives are often caused by identifiable allergies. Avoiding these allergens can help you avoid breaking out in hives. Common hive triggers include:
Hives can be a sign of a serious allergic reaction that needs emergency medical emergency attention. Its important to take action if you hives along with any of these symptoms:
- wheezing
- tightness in your chest or throat
- trouble breathing
- trouble talking
- swelling in your throat, face, or tongue
- nausea
- lightheadedness
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, call 911.
A doctor may prescribe you an epinephrine injector, such as an EpiPen, for future allergic reactions. Theyll teach you how to use it and answer any questions you might have. Youll keep your epinephrine injector on hand and use it if you develop hives in the future.
Youll still need to visit the emergency room after you use your epinephrine injector, but it can stop anaphylaxis from becoming deadly.
A doctor can diagnose hives and help you find the cause. They might recommend you keep a food diary to find out if there is any link between food and your hives.
You might be sent to an allergist, a doctor who specializes in treating allergies, for additional testing. This might include blood work and urine tests to look for chemicals in your body that might tell the allergists whats causing your hives.
You might also have a skin biopsy, especially if your allergist suspects vasculitis causing your hives. Hives that have lasted for longer than 6 weeks will likely necessitate testing for underlying chronic conditions.
Sometimes, a specific cause isnt found. In this case, your hives will be diagnosed as idiopathic urticaria. The word idiopathic means unknown. In this case, your doctor will still be able to help you with a treatment plan, but you wont be able to tell what to avoid to prevent hives in the future.
Treatment for hives will depend on the severity of your hives and on the cause. For instance, youll need to avoid the cause of your hives if it has been found.
Your doctor will work with you to find the right treatment for you. Common options include:
- Antihistamines. Both over-the-counter and prescription antihistamines block histamine and can treat hives. You might find that certain antihistamines are more effective for you than others. Sometimes a combination of antihistamines is recommended.
- Anti-itch lotions. Lotions to calm down itching and redness can provide relief from hives and prevent scratching.
- Antibiotics. Hives that are linked to bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics
- Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids can be taken on a short-term basis to help with severe cases of hives.
Read more about hives treatment options.
Hives can sometimes be surprising and have no obvious cause. There are actually a wide variety of things that can cause hives, including stress, colds, exercise, and temperature changes. Chronic hives can point to an underlying condition such as lupus.
An allergist can help you determine the cause of your hives and start treatment.