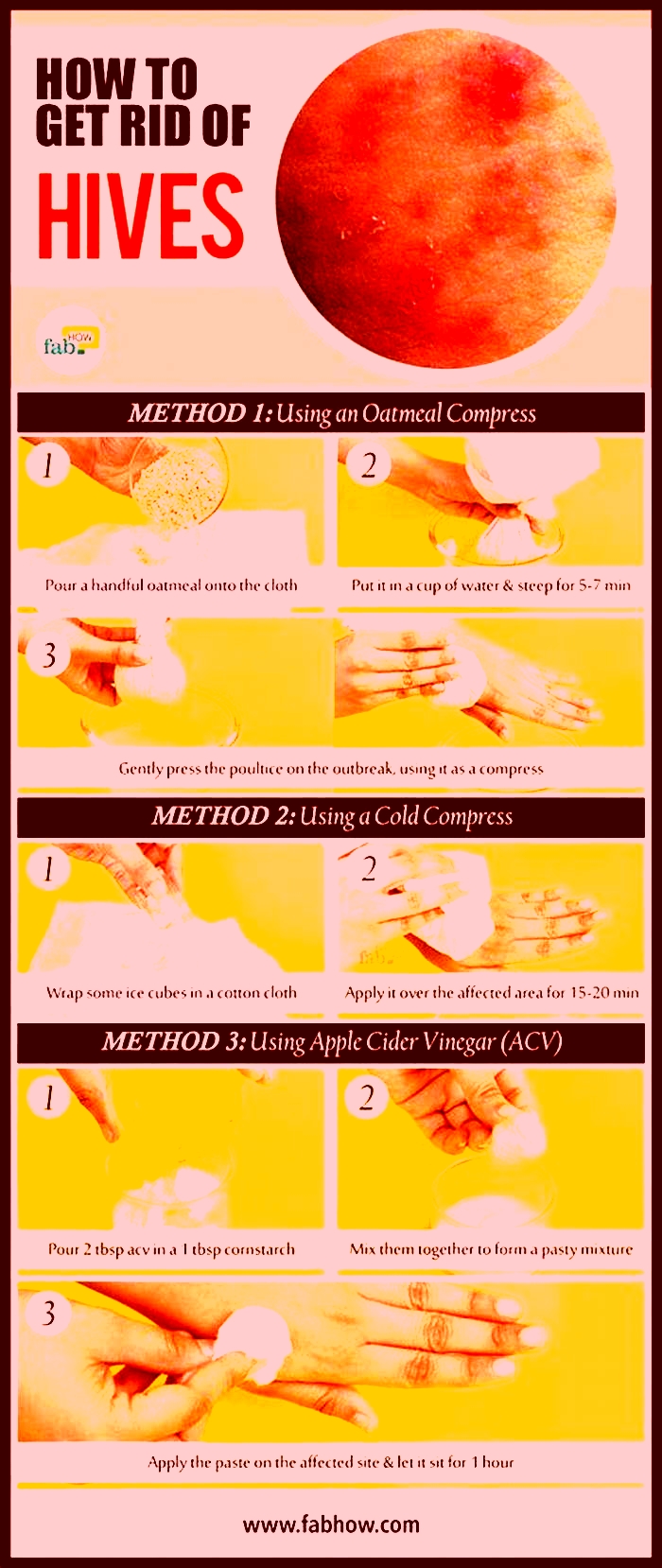
Will hives go away on their own
What Causes Hives That Recur Daily?
Hives that come back daily for 6 weeks or more are called chronic hives, or chronic urticaria. The condition often has no known cause, but allergies, autoimmune conditions, physical stimuli, and infections can play a role.
Hives are itchy, raised welts on the skin. They are often caused by an allergic reaction but might also have an unknown cause.
Hives that recur (go away and come back) frequently are known as chronic hives. Chronic hives of unknown cause can last for months or years. They can affect 1.4% of people, twice as often in women as in men.
Chronic hives can affect your quality of life, as severe itchiness can lead to discomfort and trouble sleeping. Yet treatment can help you manage them.
Lets look at the symptoms, possible causes, and treatment for hives that recur daily.
If you get new hives as others are clearing up for 6 weeks or more, you have chronic hives.
You can identify hives by their:
- raised patches or bumps on the skin
- itchiness on the patches or bumps
- stinging or burning sensation
- swollen skin appearance
Hives come in all different shapes and sizes, from just a small speck to several inches in diameter. A group of hives that appear in the same area is known as a plaque.
Medical emergencyCall emergency medical services or go to the nearest emergency room if you or someone youre with experience:
- sudden swelling of the lips, mouth, throat, or tongue
- fast breathing, choking, or wheezing
- trouble swallowing
- blue, gray, or pale color in lighter skin or on palms or soles of the feet in darker skin
- confusion, drowsiness, or dizziness
- inability to be woken up
Chronic hives look the same as other hives. Hives on light skin can appear pink or red. On dark skin, the color of the hives might be similar to the rest of your skin or slightly darker. Hives can also blanche on lighter skin, which is when a red hive becomes white if you press on it.
On all skin colors, hives are bumps or raised patches.
Chronic hives have many possible causes. Differences in symptoms, such as how quickly the hives appear, can help identify the cause.
Chronic idiopathic urticaria
Chronic idiopathic urticaria is when you get daily hives but doctors cant determine why. Symptoms include:
- hives that recur daily or nearly every day
- hives that last for 6 weeks or longer
- when each hive lasts 24 hours or fewer
- hives that do not bruise or scar your skin
Allergies
Hives can be triggered by exposure to a specific allergen.
Depending on the type of allergy, hives might come on quickly or over a few hours. Some common food allergens and the timing of related hives include:
- peanuts, shellfish, eggs, and nuts (hives often appear within 1 hour)
- bananas and chestnuts if you have a latex allergy (hives often appear within 1224 hours)
- food additives like colors and preservatives (hives often appear within 1224 hours)
Other types of allergies that might cause recurring hives include:
- insect bites or stings
- pet dander
- pollen
- certain plants
Autoimmune conditions
Several autoimmune conditions can cause chronic hives. Although researchers dont know exactly why this happens, chronic inflammation might
Among the autoimmune conditions that might cause hives are:
Infection or medication
If you have an infection or are taking medication, these might also lead to hives that recur daily. Examples include:
- Bacterial or viral infections:
- Medications:
When a doctor is trying to find the cause of your recurring hives, they might try to rule out infection or medication as a cause. Chronic hives last longer than 6 weeks, but an acute infection like the common cold might last less time than that.
A doctor might then look for another cause of your hives.
Physical stimuli
Your environment or certain activities can cause you to break out in hives. If these stimuli are a regular part of your life, it might lead to chronic hives.
Examples of stimuli that lead people to have hives almost immediately or within a few minutes include:
- cold
- heat
- ultraviolet light (outdoor sun exposure or tanning beds)
- vibration
- adrenaline (exercise or stress)
- water
- certain animals like jellyfish
Skin pressure from clothes or accessories can lead to hives right away or up to 424 hours later.
If you dont know the reason for your chronic hives, consider seeing a doctor. The hives might have a treatable cause like an allergy or physical stimulus. Treatment can relieve symptoms even if the cause is unknown.
Also consider seeing a doctor if hives:
- do not get better after 2 days
- seem to be spreading
- accompany high temperature
- accompany a feeling of unwellness
- accompany swelling under the skin
A doctor, usually a specialist such as an allergist, diagnoses chronic hives by:
- taking a medical history
- asking about your symptoms
- performing a physical exam
- conducting an allergy patch test
If your chronic hives are from a specific trigger, avoiding that trigger might make them go away.
Self-care options include:
- applying cool compresses
- using anti-itch creams or ointments
- bathing in colloidal oatmeal
- wearing loose-fitting clothes
- avoiding scratching
- using fragrance-free, gentle skin cleansers
Medications include:
- antihistamines (prescription or over-the-counter)
- corticosteroids
- omalizumab (injectable medication)
- phototherapy
Chronic hives can go away without treatment. About half of people with chronic hives no longer experience them within a year.
Here are some answers to common questions about chronic hives.
Why do I keep getting hives every day?
Chronic hives can have a variety of causes, including allergies, autoimmune conditions, infections, or physical stimuli. Many cases of chronic hives have no known cause.
What do autoimmune hives look like?
Autoimmune hives appear as raised, itchy patches of skin or bumps. They might appear pink or red on light skin and on dark skin as a bit darker than the rest of your skin. Hives can be of any size or shape.
When should I be worried about recurring hives?
You should consider seeing a doctor whenever you have hives that keep coming back. A doctor might be able to help you find a cause. Even if the cause is unknown, treatments such as antihistamines and self-care can help improve your symptoms.
Treatment for chronic hives with antihistamines, corticosteroids, light therapy, and home care can help improve symptoms.
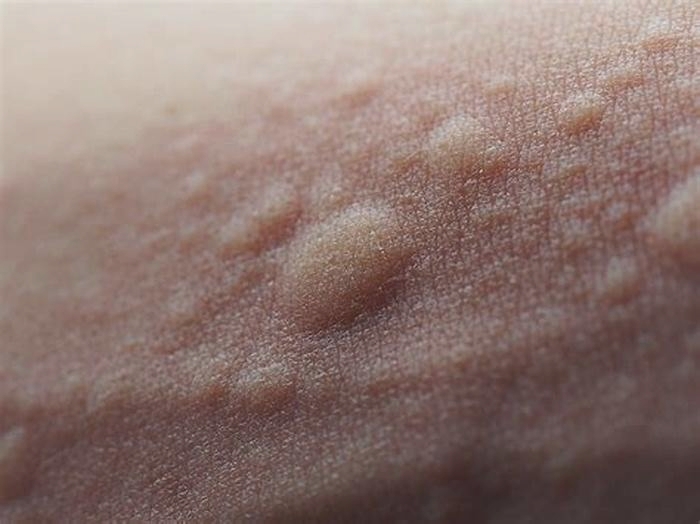
Hives: Pictures, Causes, and How to Treat Them
Hives typically occur as an allergic response to something in your environment or something you ate. But they may sometimes happen because of an underlying health issue.
Hives, also known as urticaria, are itchy, raised welts that are found on the skin. Theyre usually red, pink, or flesh colored on lighter skin and may be flesh colored or slightly lighter or darker than your skin tone on brown or black skin.
Sometimes they sting or hurt. In most cases, hives are caused by an allergic reaction to a medication or food or are a reaction to an irritant in the environment.
In many cases, hives are an acute (temporary) problem that may be alleviated with allergy medications. Most rashes go away on their own. However, chronic (ongoing) cases, as well as hives accompanied by a severe allergic reaction, are larger medical concerns.



Hives are usually caused by an
In some people, histamines can cause swelling, itching, and many of the symptoms that are experienced with hives. In terms of allergens, hives can be
Hives might also be caused by circumstances besides allergies. Its not uncommon for people to experience hives as the result of stress, tight clothes, exercise, illnesses, or infections.
Its also possible to develop hives as the result of excessive exposure to hot or cold temperatures or from irritation due to excessive sweating. Because there are several potential triggers, many times the actual cause of hives cant be determined.
People who are known to have allergies are more likely to get hives. You may also be at risk of developing hives if youre taking medication or if youre unknowingly exposed to things you may be allergic to, such as food or pollen. If youre already ill with an infection or a health condition, you may be more vulnerable to developing hives.
The most noticeable symptom of hives is the welts that appear on the skin. Welts may be red but can also be the same color as your skin. They can be small and round, ring-shaped, or large and of random shape. Hives are itchy, and they tend to appear in batches on the affected part of the body. They can grow larger, change shape, and spread.
Hives may disappear or reappear over the course of the outbreak. Individual hives welts can last anywhere from
Hives can occur in a variety of places on the body. Call 911 or get medical attention immediately if you develop a hives outbreak around your throat or on your tongue or have trouble breathing along with hives.
Hives can occur in response to an allergic reaction or may not have an identifiable cause.
Allergic reactions
The most common causes of hives are allergic reactions. These can be caused by any allergen you might be sensitive to, including:
- foods (such as nuts, milk, and eggs)
- pet dander
- pollen
- dust mites
- insect bites or stings
- medications (primarily antibiotics, cancer drugs, or ibuprofen)
Mild cases of hives caused by allergies are typically treated with long- or short-term allergy medications and avoidance of the trigger.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, life threatening allergic reaction. In this condition, hives are often
Chronic hives
Chronic hives are ongoing cases that dont necessarily have an identifiable cause. Also called chronic urticaria, this condition is marked by recurring hives that can interfere with your daily life. Chronic cases
You may suspect chronic hives if you have welts that dont go away within 6 weeks. While not life threatening, this form of hives can be uncomfortable and difficult to treat. Chronic hives may also be a symptom of an
- an autoimmune disorder
- celiac disease
- lupus
- type 1 diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis
- thyroid disease
Dermatographism
This form of acute hives is considered mild. Excessive scratching or continuous pressure on the skin causes it. Dermatographism usually clears up on its own in a short period of time without treatment.
Temperature-induced hives
Sometimes changes in temperature can induce hives in people who are sensitive to such changes. Cold-induced hives may occur from cold water or air exposure, while body heat from physical activity may cause exercise-induced hives. Exposure to sunlight or tanning beds may also bring about solar hives in some people.
Infection-induced hives
Both viral and bacterial infections can cause hives. Common bacterial infections causing hives include urinary tract infections and strep throat. Viruses that cause infectious mononucleosis (mono), hepatitis, and colds often cause hives.
The first step in getting treatment is to figure out if you actually have hives. In most cases, a doctor will be able to determine if you have hives from a physical exam. Your skin will show signs of the welts that are linked with hives.
A doctor may also perform blood tests or skin tests to find out what may have caused your hives especially if your hives were the result of an allergic reaction.
You may not need prescription treatment if youre experiencing a mild case of hives not related to allergies or other health conditions. In these circumstances, a doctor might suggest that you find temporary relief by:
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency that needs to be treated immediately by a physician. If you think you may be experiencing anaphylaxis, contact 911 or your local emergency services.
Simple changes to your lifestyle may be able to help you prevent hives from reoccurring in the future. If you have allergies and you know which substances are likely to cause an allergic reaction, a doctor will suggest that you avoid any possible exposure to these factors. Allergy shots are another option that may help you reduce the risk of experiencing hives again.
Avoid being in high humidity areas or wearing tight clothing if you have recently had a hives outbreak.
Below are some of the most commonly asked questions about hives.
Are hives contagious?
No, hives are not contagious and cant spread from one person to another.
Do hives mean Im allergic to something?
In many cases, hives are the result of an allergic reaction to something you have been exposed to, such as certain medications or pollen. It could also be caused by an infection, stress, or wearing clothes that are too tight. If you have hives that persist for more than a few days, contact a doctor to see if an allergy test is needed to determine the cause of your symptoms.
How long do hives last?
A hives outbreak can last anywhere from
Are there any home remedies for hives?
Yes, there are several home remedies that may help alleviate the symptoms of hives. Taking an antihistamine is one option, as well as taking a cool or lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal or baking soda. Avoid hot water, as this may aggravate the hives. Also, try to avoid any potential irritants or allergens that may have caused the hives in the first place.
Although hives can be itchy and uncomfortable, usually theyre not severe and will disappear after a period of time. However, be aware that as some hives go away, new ones may pop up.
Mild cases of hives are considered harmless. Hives can be dangerous if you are having a serious allergic reaction and your throat is swelling. Prompt treatment for a severe case of hives is important for a good outlook.